值类型和引用类型
值传递与引用传递
关于值类型与引用类型,值传递与引用传递的总结笔记。
一、值类型与引用类型
1.堆栈中的存放:
-
值类型默认存放在栈中,但当值类型是在引用类型中声明的时候,则存放在其所在的引用类型的堆中。
-
引用类型存放在堆中。其在堆中的内存地址存放在栈中。
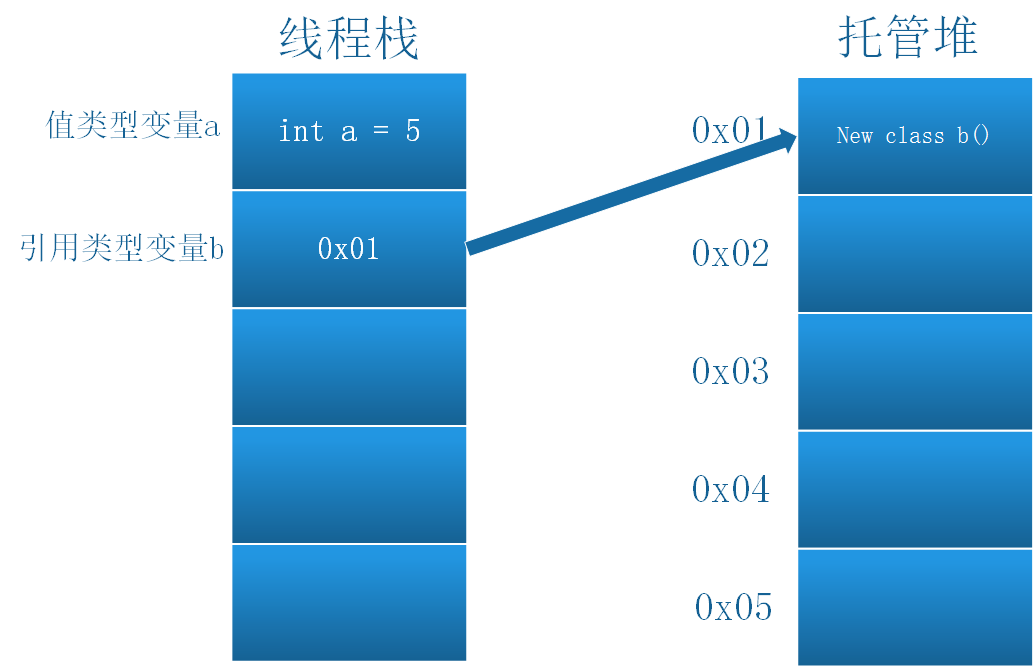
2.参数传递方式
-
值类型参数可以值传递,也可通过ref、out关键字修饰,进行引用传递。
-
引用类型参数只能以引用传递方式传递。
二、值传递与引用传递
1.值传递
值传递是将变量的一个副本传递到方法中,方法中如何操作该变量副本,都不会改变原变量的值。
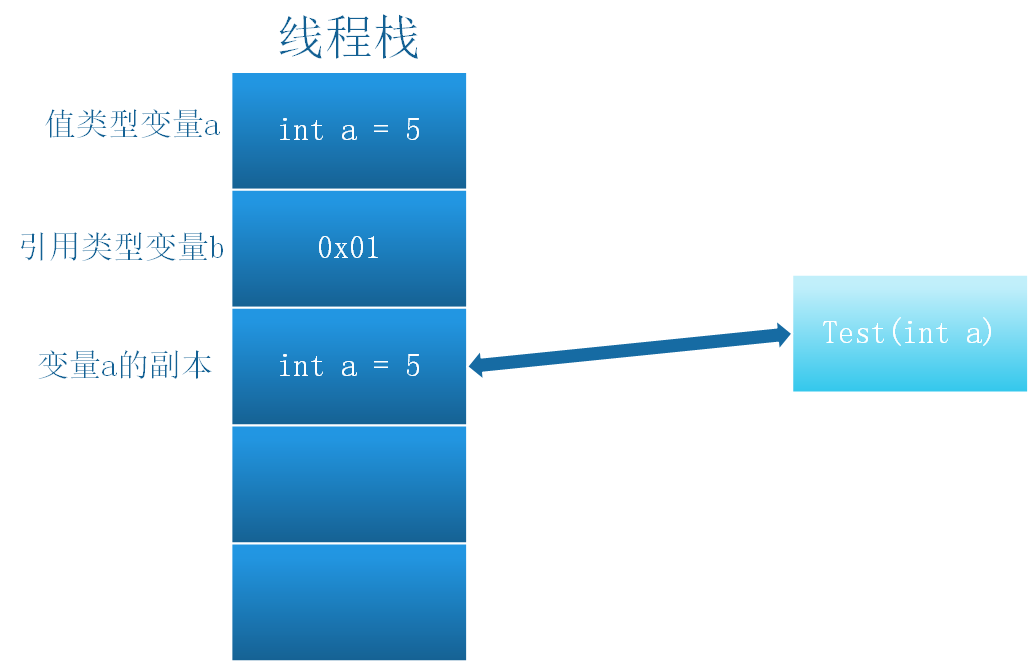
在下面的例子中。将变量 a 以值传递方式传给方法 Test(),在Test执行a++操作时,实际是对a的副本进行操作,Main方法中打印a的值,结果仍为 a=1 。
1 class Program
2 {
3 public static void Main(string[] args)
4 {
5 int a = 1;
6 Test(a);
7 Console.WriteLine(a);
8
9 Console.Write("Press any key to continue . . . ");
10 Console.ReadKey(true);
11 }
12
13 //值传递
14 static void Test(int a)
15 {
16 a++;
17 }
18 }
结果:1
2.引用传递
引用传递是将变量的内存地址传递给方法,方法操作变量时会找到保存在该地址的变量,对其进行操作。会对原变量造成影响。
这里用“原变量”一词只是为了与值传递进行对比说明,实际上所有方法都是操作同一对象,不应有“原变量”一说。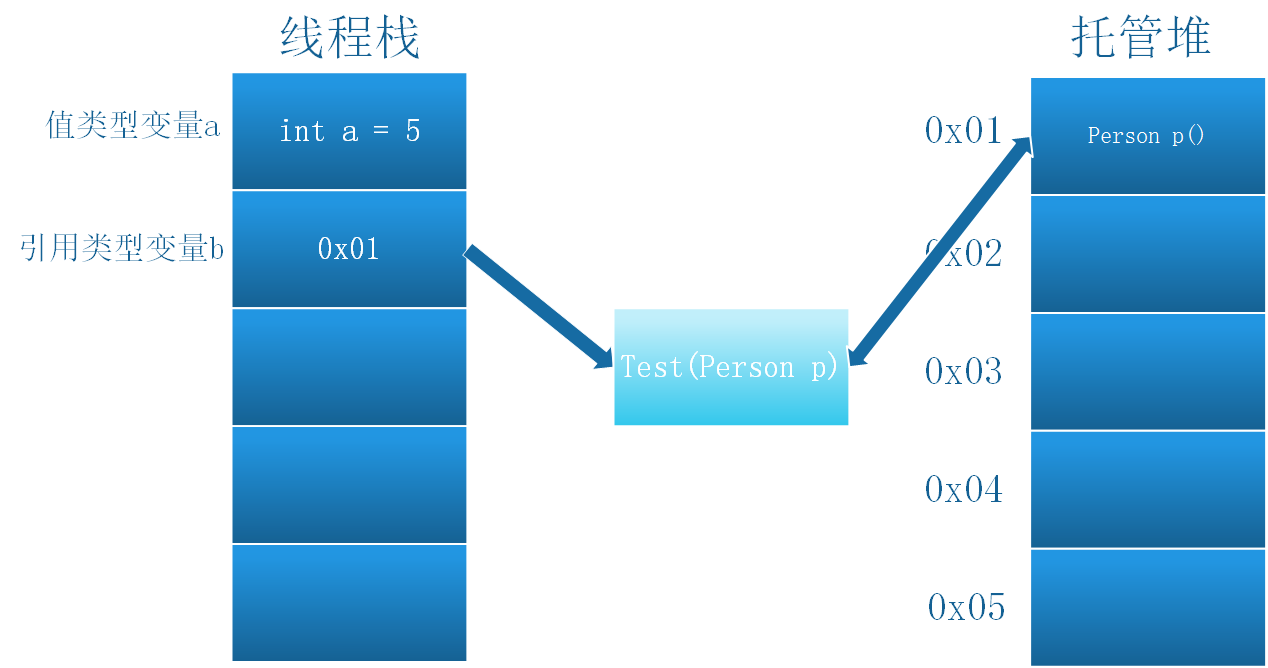
例子中,将Person对象p和变量 a (通过ref关键字修饰)以引用传递方式传给方法 Test()。在Test对变量进行操作时,是通过传递过来的地址010x,在堆中找到p,并对其进行操作。所以Main函数中再打印结果,已经发生变化。
1 class Program
2 {
3 public static void Main(string[] args)
4 {
5 int a = 1;
6 Person p=new Person{Age=20};
7 //通过ref关键字,对值类型变量a进行引用传递
8 Test(ref a,p);
9 Console.WriteLine(a);
10 Console.WriteLine(p.Age);
11
12 Console.Write("Press any key to continue . . . ");
13 Console.ReadKey(true);
14 }
15
16 //引用传递
17 static void Test(ref int a,Person p)
18 {
19 a++;
20 p.Age++;
21 }
22
23 }
24
25 class Person
26 {
27 public int Age{get;set;}
28 }
结果:2
21


