CXF处理JavaBean以及复合类型
前面讲的是处理简单类型,今天这里来讲下CXF处理JavaBean以及复合类型,比如集合;
这里实例是客户端传一个JavaBean,服务器端返回集合类型;
在原来的项目实例基础上,我们先创建一个实体类User:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
package com.java1234.entity;/** * 用户实体类 * @author Administrator * */public class User { private Integer id; // 编号 private String userName; // 用户名 private String password; // 密码 public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getUserName() { return userName; } public void setUserName(String userName) { this.userName = userName; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } } |
再创建一个Role实体类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
package com.java1234.entity;/** * 角色实体 * @author Administrator * */public class Role { private Integer id; // 编号 private String roleName; // 角色名称 public Role() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Role(Integer id, String roleName) { super(); this.id = id; this.roleName = roleName; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getRoleName() { return roleName; } public void setRoleName(String roleName) { this.roleName = roleName; } } |
然后HelloWorld再加一个接口方法getRoleByUser,通过用户查找角色:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
package com.java1234.webservice;import java.util.List;import javax.jws.WebService;import com.java1234.entity.Role;import com.java1234.entity.User;@WebServicepublic interface HelloWorld { public String say(String str); public List<Role> getRoleByUser(User user);} |
然后HelloWorld接口实现类 HelloWorldImpl写下新增的方法的具体实现,我们这里写死,模拟下即可:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
package com.java1234.webservice.impl;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import javax.jws.WebService;import com.java1234.entity.Role;import com.java1234.entity.User;import com.java1234.webservice.HelloWorld;@WebServicepublic class HelloWorldImpl implements HelloWorld{ public String say(String str) { return "Hello "+str; } public List<Role> getRoleByUser(User user) { List<Role> roleList=new ArrayList<Role>(); // 模拟 直接写死 if(user!=null){ if(user.getUserName().equals("java1234") && user.getPassword().equals("123456")){ roleList.add(new Role(1,"技术总监")); roleList.add(new Role(2,"架构师")); }else if(user.getUserName().equals("jack") && user.getPassword().equals("123456")){ roleList.add(new Role(3,"程序员")); } return roleList; }else{ return null; } } } |
服务端其他地方不用动;
下面我们来处理下客户端,和前面讲的一样。我们用wsdl2java工具重新生成代码,这里就不再讲;
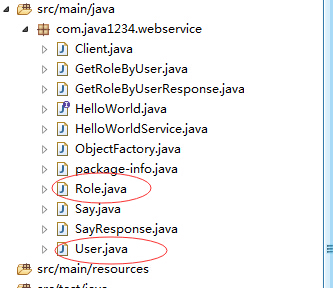
这里我看到,实体类,以及接口实现,代码都生成了。
我们改下Client类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
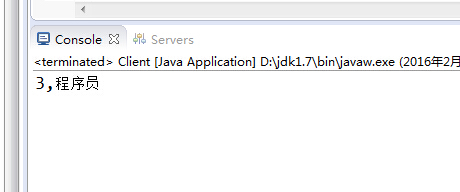
package com.java1234.webservice;import java.util.List;public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { HelloWorldService service=new HelloWorldService(); HelloWorld helloWorld=service.getHelloWorldPort(); //System.out.println(helloWorld.say("java1234")); User user=new User(); user.setUserName("jack"); user.setPassword("123456"); List<Role> roleList=helloWorld.getRoleByUser(user); for(Role role:roleList){ System.out.println(role.getId()+","+role.getRoleName()); } }} |
运行截图:
学习时的痛苦是暂时的 未学到的痛苦是终生的



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号