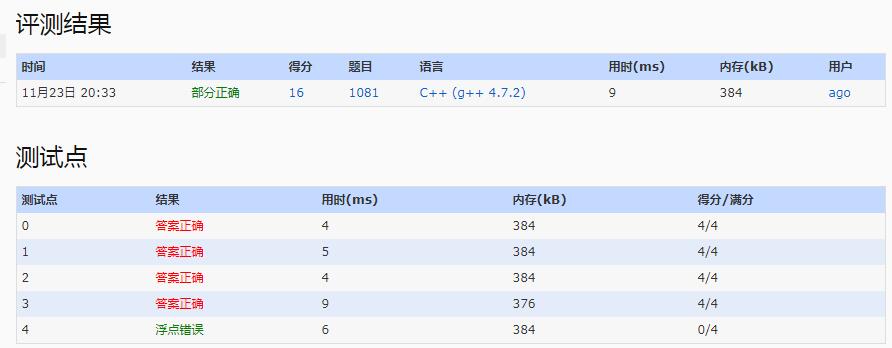
1081. Rational Sum (20)
Given N rational numbers in the form "numerator/denominator", you are supposed to calculate their sum.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a positive integer N (<=100), followed in the next line N rational numbers "a1/b1 a2/b2 ..." where all the numerators and denominators are in the range of "long int". If there is a negative number, then the sign must appear in front of the numerator.
Output Specification:
For each test case, output the sum in the simplest form "integer numerator/denominator" where "integer" is the integer part of the sum, "numerator" < "denominator", and the numerator and the denominator have no common factor. You must output only the fractional part if the integer part is 0.
Sample Input 1:
5 2/5 4/15 1/30 -2/60 8/3
Sample Output 1:
3 1/3
Sample Input 2:
2 4/3 2/3
Sample Output 2:
2
Sample Input 3:
3 1/3 -1/6 1/8
Sample Output 3:
7/24
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
long long a;
long long b;
};
long long find(long long x,long long y){
long long tmp;
if(x<y){
tmp=x;
x=y;
y=tmp;
}
while(x%y!=0){
tmp=x%y;
x=y;
y=tmp;
}
return y;
}
int main(){
vector<Node>vt;
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
vt.resize(n);
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%lld/%lld",&vt[i].a,&vt[i].b);
}
long long a=0;
long long b=1;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
a=a*vt[i].b+b*vt[i].a;
b=b*vt[i].b;
long long tmp = find((a<0?-a:a),b);
if(tmp==0)break;
a=a/tmp;
b=b/tmp;
}
long long m=a/b;
long long k=a%b;
if(m!=0&&k!=0){
printf("%lld %lld/%lld\n",m,a-m*b,b);
}else if(m==0&&k!=0){
printf("%lld/%lld\n",a,b);
}else if(m!=0&&k==0){
printf("%lld\n",m);
}else if(m==0&&k==0){
printf("0\n");
}
return 0;
}