复制带随机指针的链表
复制带随机指针的链表
作者:Grey
原文地址:
题目描述
一种特殊的单链表节点类描述如下
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
random 指针是单链表节点结构中新增的指针,random 可能指向链表中的任意一个节点,也可能指向 null,
给定一个由 Node 节点类型组成的无环单链表的头节点 head,请实现一个函数完成这个链表的复制,返回复制的新链表的头节点。
注:要求时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度O(1)
OJ见:LeetCode 138. Copy List with Random Pointer
主要思路
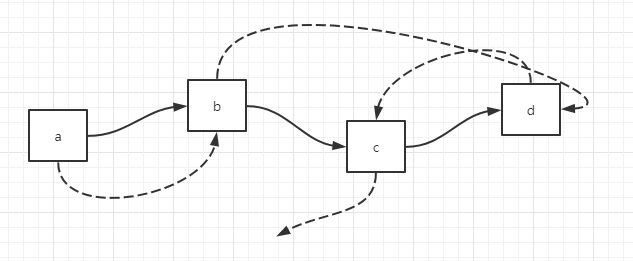
假设原始链表如下,其中虚线表示 random 指针
由于空间复杂度需要O(1),所以使用辅助数组的方式不可取,只能在链表上进行原地调整。
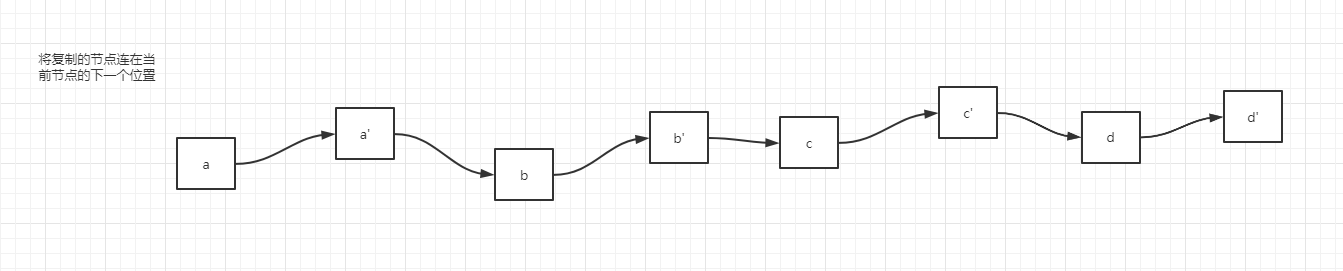
第一步,将当前节点的复制节点连在当前节点的下一个位置上,如上链表,a'为a的复制节点,其他节点同理,首先会得到如下链表
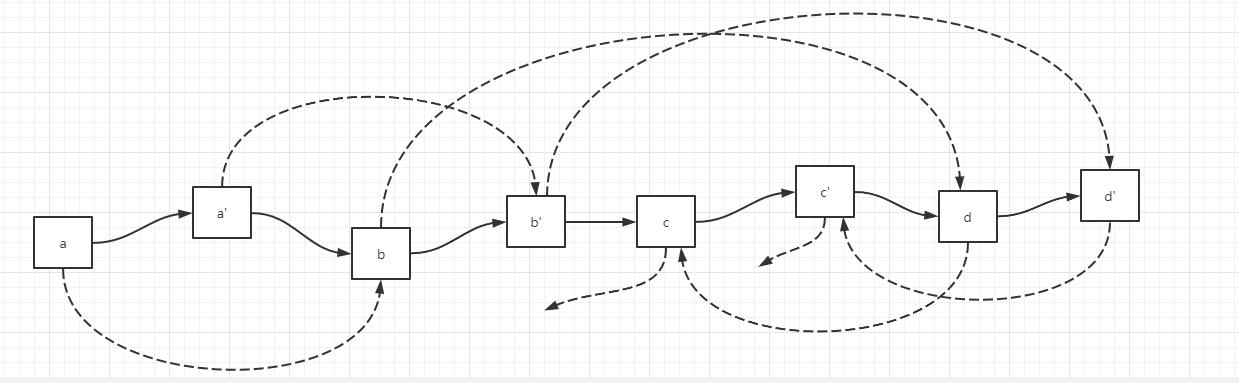
第二步,复制节点的 random 指针指向当前节点的 random 指针的下一个位置,以a节点为例,a节点的next就是a的复制节点a',a节点的random节点的next就是a'的random指针
即a.next.random = a.random.next,由于random指针可能为空,所以a.next.random = a.random == null?null:a.random.next,其余节点类似,示例图如下
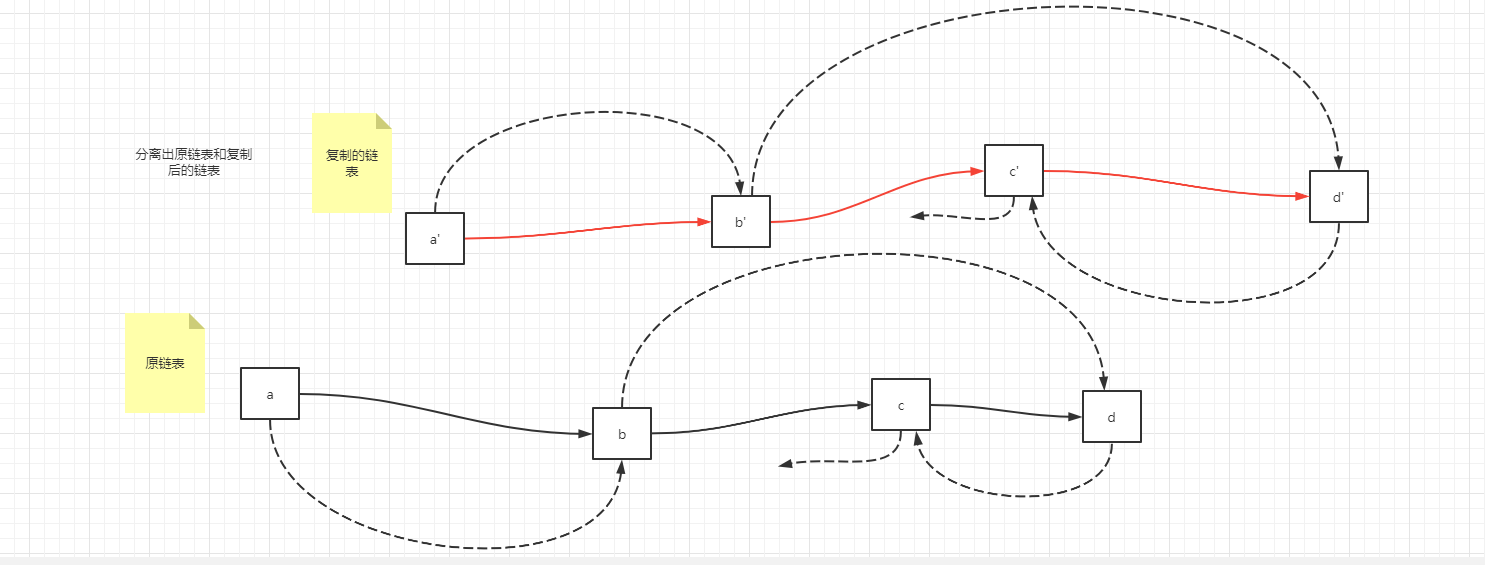
第三步,以上已经完成了链表元素的复制,接下来是分离原链表和复制链表。
以a和a'节点为例,分离的过程就是
a.next = a.next.next;
a'.next = a'.next.next;
特别要注意最后一个节点,因为最后一个节点的next为空,所以,针对最后一个节点d和d'来说
d.next = null;
d'.next = null;
最后返回复制链表的头部即可,本例中,返回a'节点即可。
完整代码见
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
Node cur = head;
// 复制节点接在当前节点的后面
while (cur != null) {
Node next = cur.next;
Node copy = new Node(cur.val);
cur.next = copy;
copy.next = next;
cur = next;
}
// 设置复制节点的random指针
cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
cur.next.random = cur.random == null ? null : cur.random.next;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
cur = head;
// 切割原链表和复制链表
Node newHead = cur.next;
cur = head;
Node copyCur = newHead;
while (cur != null) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
copyCur.next = copyCur.next == null ? null:copyCur.next.next;
cur = cur.next;
copyCur = copyCur.next;
}
return newHead;
}
}
本题的所有图例见: processon:复制带随机指针的链表
更多#
作者:GreyZeng
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/greyzeng/p/16750999.html
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。
你可以在这里自定义其他内容
本文来自博客园,作者:Grey Zeng,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/greyzeng/p/16750999.html



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
2019-10-03 Git 推送到多个远程仓库