接雨水系列问题
接雨水系列问题
作者:Grey
原文地址:
LeetCode 42. 接雨水
主要思路:考虑每个位置,顶部可以留下多少水,累加起来,就是总的接水量。
其中,最右侧和最左侧的顶部无法接到水,因为水会从两侧流走。
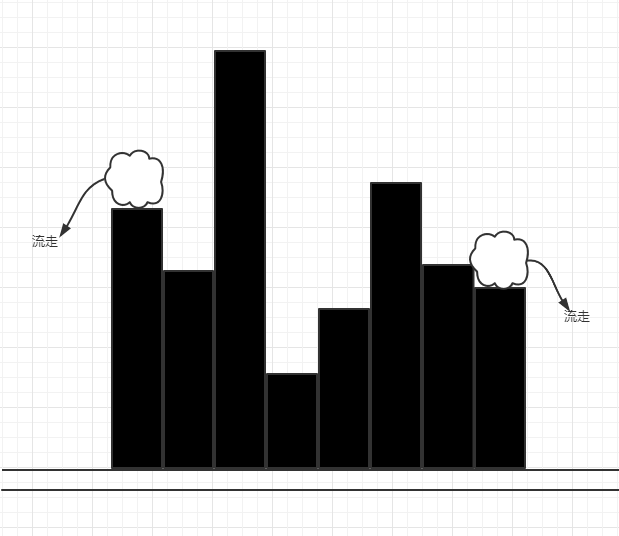
基于上述逻辑,至少可以判断,如果数组的长度小于等于2,直接返回0份水。
当数组的长度大于2,我们需要考虑,从1号位置到数组长度-2,每个位置顶部能接多少水。
设置四个变量
int l = 1;
int r = arr.length - 2;
// 左侧目前高度的瓶颈是多少
int lMax = arr[0];
// 右侧目前高度的瓶颈是多少
int rMax = arr[arr.length - 1];
lMax和rMax作为左侧和右侧的在当前状态下的瓶颈,我们实际遍历的位置从l到r,看下arr[l]和arr[r]位置基于左右侧的瓶颈能收集到的水量是多少。
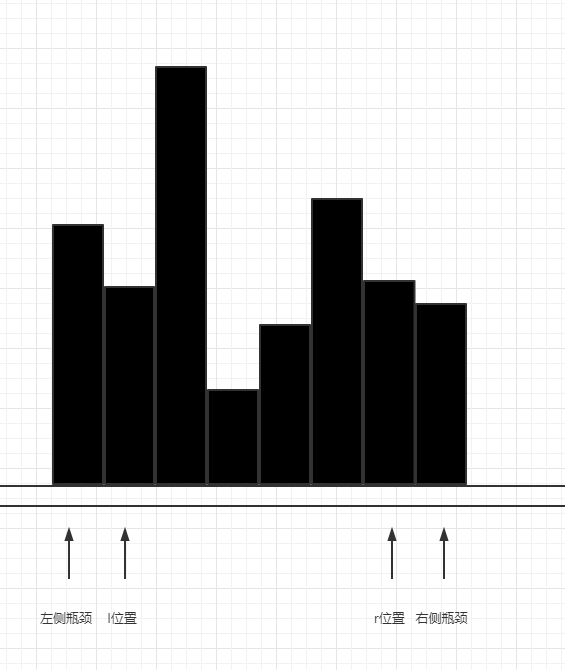
首先,虽然有两个瓶颈值,但是,我们在结算的时候,只能以较小的瓶颈值来结算,因为如果以较大瓶颈值来结算,小的瓶颈会拉低当前的结算值(木桶效应)。
所以,有两种情况:
情况一:lMax > rMax
情况二:lMax <= rMax
在情况一下,例如

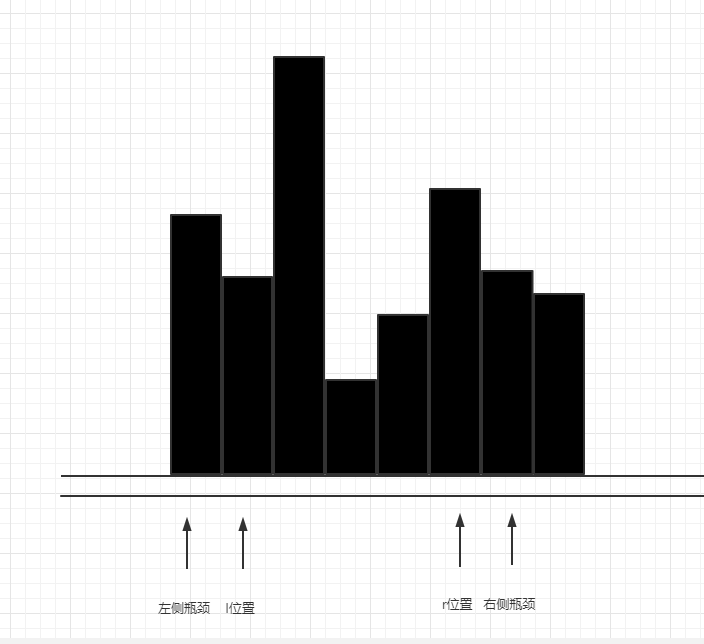
在这种情况下,我们可以确定arr[r]位置上的水能接多少,因为arr[r]和右侧瓶颈是确定的关系,左侧瓶颈虽然比arr[r]大,是水会因为右侧瓶颈让arr[r]收集的水流走,所以此时
arr[r]上可以收集的水量就是arr[r]和rMax之间的差值,如果是负数,则为0,相当于没有收到水,此时,r位置遍历完毕,右侧瓶颈更新为Math.max(arr[r],rMax),按上图示例,现在的右侧瓶颈变成了arr[r]上的值。如下图
在这种状态下,相对小的瓶颈是rMax,又可以结算当前arr[r]位置的水量,还是0。然后继续更新右侧瓶颈,如下图
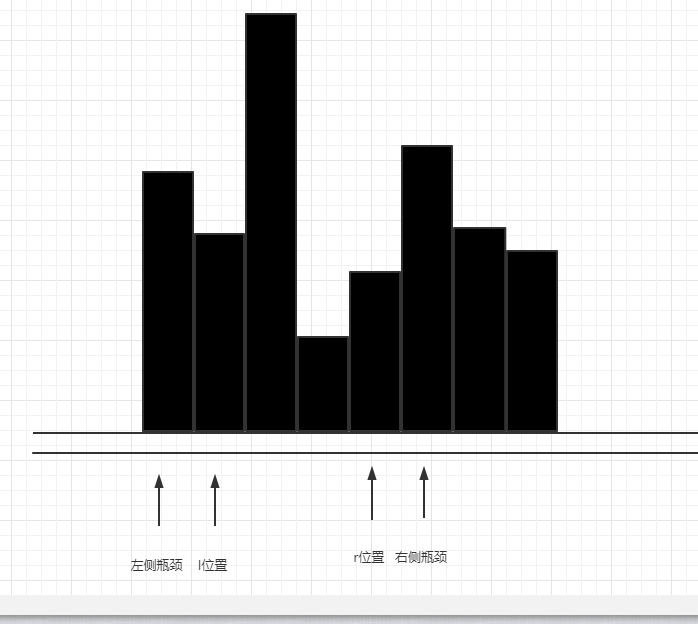
此时,左侧瓶颈是较小的那个,现在就要更新arr[l]头顶上的水量,即:arr[l]和lMax之间差值和0比较较大的那个,然后移动l指针,更新左侧瓶颈(由于arr[l]值没有lMax大,所以左侧瓶颈保留在原先lMax位置),如下图。

接下来lMax < rMax,继续结算arr[l],移动l和更新lMax
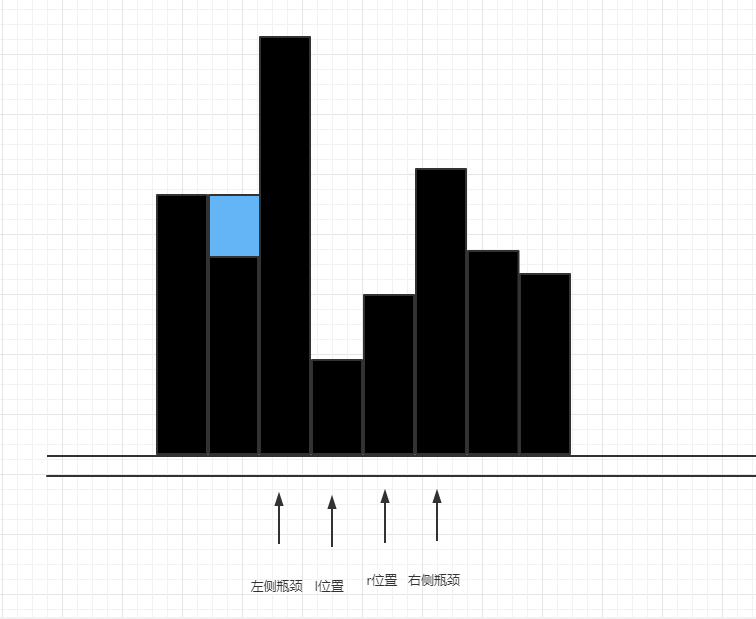
接下来的过程同理,示意图如下
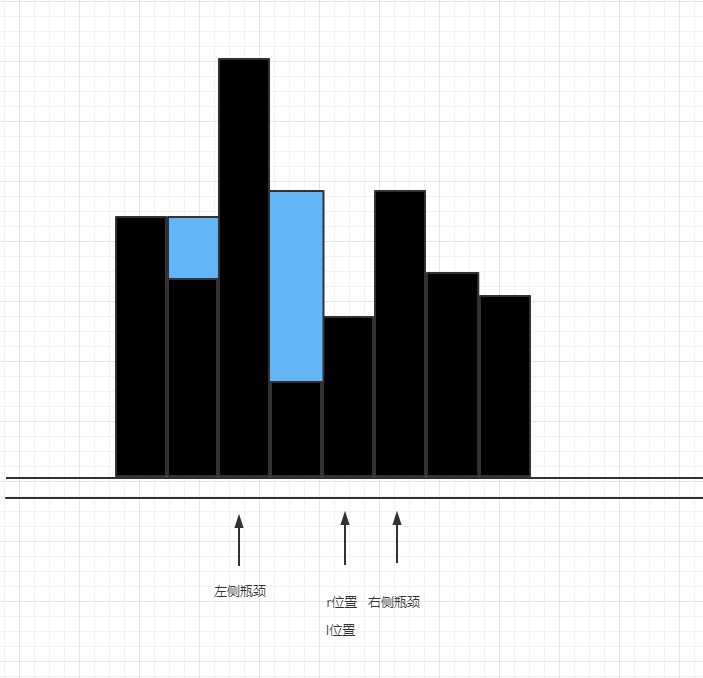
直到l>r
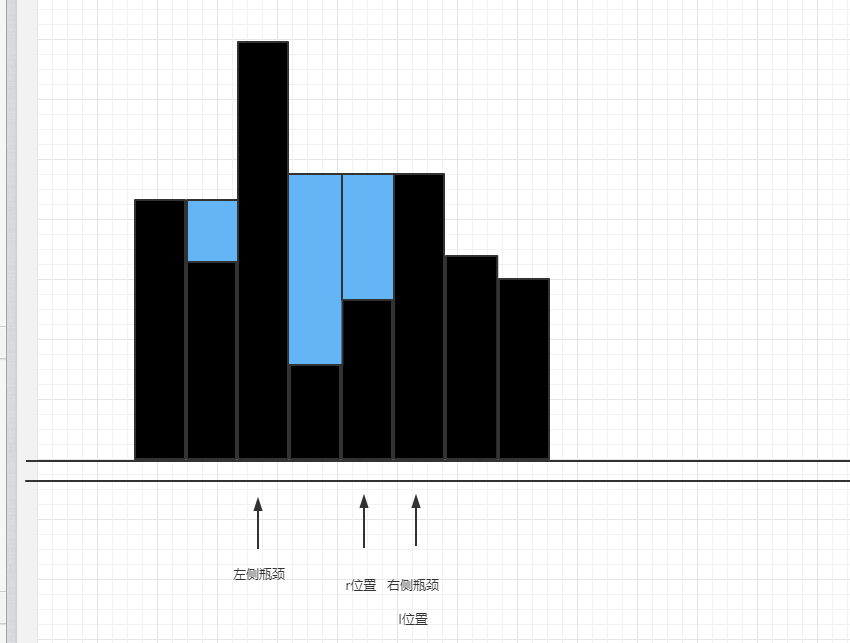
所有水收集完毕。
完整代码见
public static int trap(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length <= 2) {
return 0;
}
int result = 0;
int l = 1;
int r = arr.length - 2;
int lMax = arr[0];
int rMax = arr[arr.length - 1];
while (l <= r) {
if (lMax < rMax) {
// 结算左侧
result += Math.max(0, lMax - arr[l]);
lMax = Math.max(lMax, arr[l++]);
} else {
// 结算右侧
result += Math.max(0, rMax - arr[r]);
rMax = Math.max(rMax, arr[r--]);
}
}
return result;
}
时间复杂度O(N),空间复杂度O(1)。
LeetCode 407. 接雨水 II
主要思路
和一维的思路一样,二维接雨水问题也是先定位瓶颈,一维接雨水的瓶颈是从左右两端来定位,二维的瓶颈就是从矩阵的四周来定位。要找到四周的最小瓶颈,我们需要用一个小根堆(按值组织),将四周的值加入小根堆,弹出的值即为最小瓶颈。首先,我们需要包装一下原始矩阵,设计一个Node数据结构,用于存放原始矩阵中的某个值以及其位置信息。
public static class Node {
public int v; // 值
public int i; // 行位置
public int j; // 列位置
public Node(int v, int i, int j) {
this.i = i;
this.j = j;
this.v = v;
}
}
小根堆里面存的就是Node,按照Node的v来组织,
PriorityQueue<Node> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.v));
每当弹出一个Node的时候,将这个位置的上下左右(先确保不越界)进行结算,结算完成后,将已经结算的位置加入小根堆(已经加入过的位置就不用重复加入了),由于需要知道哪些位置加入过小根堆,所以设置一个二维的boolean数组,用于标志某个位置是否进入过。
boolean[][] isEntered = new boolean[m][n];
if (isEntered[i][j]) {
// 某个位置进入过小根堆
} else {
// 否则没有进入过
}
首先,我们将矩阵四周的点加入小根堆,并且把isEntered设置好
// 以下两个for循环,是把四周都加入小根堆
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
heap.offer(new Node(heightMap[i][0], i, 0));
heap.offer(new Node(heightMap[i][n - 1], i, n - 1));
isEntered[i][0] = true;
isEntered[i][n - 1] = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
heap.offer(new Node(heightMap[0][i], 0, i));
heap.offer(new Node(heightMap[m - 1][i], m - 1, i));
isEntered[0][i] = true;
isEntered[m - 1][i] = true;
}
然后我们设置一个max,用于标识此时最小瓶颈是哪个。接下来的流程就是:
每次从小根堆弹出一个元素,看下能否更新瓶颈值,且看其四面八方的位置上是否越界,如果没有越界,直接结算四面八方位置的值,累加到water这个变量中,同时把四面八方的Node加入小根堆,循环往复,直到小根堆为空。water的值即为收集到的水量。
完整代码见
public static int trapRainWater(int[][] heightMap) {
if (null == heightMap || heightMap.length <= 2 || heightMap[0].length <= 2) {
return 0;
}
int m = heightMap.length;
int n = heightMap[0].length;
int max = 0;
PriorityQueue<Node> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.v));
boolean[][] isEntered = new boolean[m][n];
// 以下两个for循环,是把四周都加入小根堆
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
heap.offer(new Node(heightMap[i][0], i, 0));
heap.offer(new Node(heightMap[i][n - 1], i, n - 1));
isEntered[i][0] = true;
isEntered[i][n - 1] = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
heap.offer(new Node(heightMap[0][i], 0, i));
heap.offer(new Node(heightMap[m - 1][i], m - 1, i));
isEntered[0][i] = true;
isEntered[m - 1][i] = true;
}
int water = 0;
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
// 最薄弱的位置
Node weakest = heap.poll();
max = Math.max(weakest.v, max);
int i = weakest.i;
int j = weakest.j;
if (i + 1 < m && !isEntered[i + 1][j]) {
water += Math.max(0, max - heightMap[i + 1][j]);
isEntered[i + 1][j] = true;
heap.offer(new Node(heightMap[i + 1][j], i + 1, j));
}
if (i - 1 >= 0 && !isEntered[i - 1][j]) {
water += Math.max(0, max - heightMap[i - 1][j]);
isEntered[i - 1][j] = true;
heap.offer(new Node(heightMap[i - 1][j], i - 1, j));
}
if (j + 1 < n && !isEntered[i][j + 1]) {
water += Math.max(0, max - heightMap[i][j + 1]);
isEntered[i][j + 1] = true;
heap.offer(new Node(heightMap[i][j + 1], i, j + 1));
}
if (j - 1 >= 0 && !isEntered[i][j - 1]) {
water += Math.max(0, max - heightMap[i][j - 1]);
isEntered[i][j - 1] = true;
heap.offer(new Node(heightMap[i][j - 1], i, j - 1));
}
}
return water;
}
public static class Node {
public int v;
public int i;
public int j;
public Node(int v, int i, int j) {
this.i = i;
this.j = j;
this.v = v;
}
}
空间复杂度O(M*N),时间复杂度是O(M*N*log(M+N))。
更多
本文来自博客园,作者:Grey Zeng,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/greyzeng/p/16418808.html


