疑问:Spring 中构造器、init-method、@PostConstruct、afterPropertiesSet 孰先孰后,自动注入发生时间
一、前言#
spring的一大优点就是扩展性很强,比如,在spring bean 的生命周期中,给我们预留了很多参与bean 的生命周期的方法。
大致梳理一下,有以下几种:
- 通过实现 InitializingBean/DisposableBean 接口来定制初始化之后/销毁之前的操作方法;
- 通过 <bean> 元素的 init-method/destroy-method属性指定初始化之后 /销毁之前调用的操作方法;
- 在指定方法上加上@PostConstruct 或@PreDestroy注解来制定该方法是在初始化之后还是销毁之前调用;
- 自定义 org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor ,来让 spring 回调我们的方法来参与 bean的生命周期。
但有个问题是,如果同时使用上面四种方式,会是什么结果? 谁先,谁后呢?
二、验证#
1、新建工程#
我这边建立了测试工程,源码在文末:
xml中定义如下:
<bean class="com.ckl.springbeanlifecycle.DemoController" init-method="init" destroy-method="cleanUp"></bean>
重点是我们的DemoController,该类作为一个 bean,在xml中已经定义了,我们为该类,实现了各种接口,以及各种生命周期的相关注解:
1 package com.ckl.springbeanlifecycle;
2
3 import com.ckl.springbeanlifecycle.service.IDemoService;
4 import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
5 import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
6 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
7
8 import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
9 import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
10
11 /**
12 * desc:
13 *
14 * @author : caokunliang
15 * creat_date: 2019/7/20 0020
16 * creat_time: 18:45
17 **/
19 public class DemoController implements InitializingBean,DisposableBean {
20
21 @Autowired
22 private IDemoService iDemoService;
23
24 public DemoController() {
25 System.out.println();
26 System.out.println("constructor ");
27 System.out.println( "属性:" + iDemoService);
28 System.out.println();
29 }
30
31 @Override
32 public void destroy() throws Exception {
33 System.out.println();
34 System.out.println("implements DisposableBean interface");
35 System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + (iDemoService != null));
36 System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + iDemoService);
37 System.out.println();
38 }
39
40 @Override
41 public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
42 System.out.println();
43 System.out.println("afterPropertiesSet interface");
44 System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + (iDemoService != null));
45 System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + iDemoService);
46 System.out.println();
47 }
48
49 @PostConstruct
50 public void postConstruct(){
51 System.out.println();
52 System.out.println("@PostConstrut....");
53 System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + (iDemoService != null));
54 System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + iDemoService);
55 System.out.println();
56 }
57
58 @PreDestroy
59 public void preDestroy(){
60 System.out.println();
61 System.out.println("@PreDestroy.....");
62 System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + iDemoService);
63 System.out.println();
64 }
65
66 public void init(){
67 System.out.println();
68 System.out.println("init-method by xml 配置文件");
69 System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + (iDemoService != null));
70 System.out.println();
71 }
72 public void cleanUp(){
73 System.out.println();
74 System.out.println("destroy-method by xml 配置文件");
75 System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + iDemoService);
76 System.out.println();
77 }
78 }
因为我们还需要验证 org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor,所以我们自定义了一个 org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor:
1 package com.ckl.springbeanlifecycle;
2
3 import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
4 import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
5 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
6
7 import java.lang.reflect.Field;
8
9 /**
10 * desc:
11 *
12 * @author : caokunliang
13 * creat_date: 2019/7/20 0020
14 * creat_time: 18:52
15 **/
16 @Component
17 public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
18 @Override
19 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
20 if (bean instanceof DemoController){
21 System.out.println();
22 System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor:" + "postProcessBeforeInitialization");
23 Field field = null;
24 try {
25 field = bean.getClass().getDeclaredField("iDemoService");
26 field.setAccessible(true);
27 } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
28 e.printStackTrace();
29 }
30 try {
31 Object o = field.get(bean);
32 System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + (o != null));
33 System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + o);
34 System.out.println();
35 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
36 e.printStackTrace();
37 }
38 }
39 return bean;
40 }
41
42 @Override
43 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
44 if (bean instanceof DemoController){
45 System.out.println();
46 System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor:" + "postProcessAfterInitialization");
47 Field field = null;
48 try {
49 field = bean.getClass().getDeclaredField("iDemoService");
50 field.setAccessible(true);
51 } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
52 e.printStackTrace();
53 }
54 try {
55 Object o = field.get(bean);
56 System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + (o != null));
57 System.out.println( "属性iDemoService已注入:" + o);
58 System.out.println();
59 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
60 e.printStackTrace();
61 }
62 }
63 return bean;
64 }
65 }
2、运行#
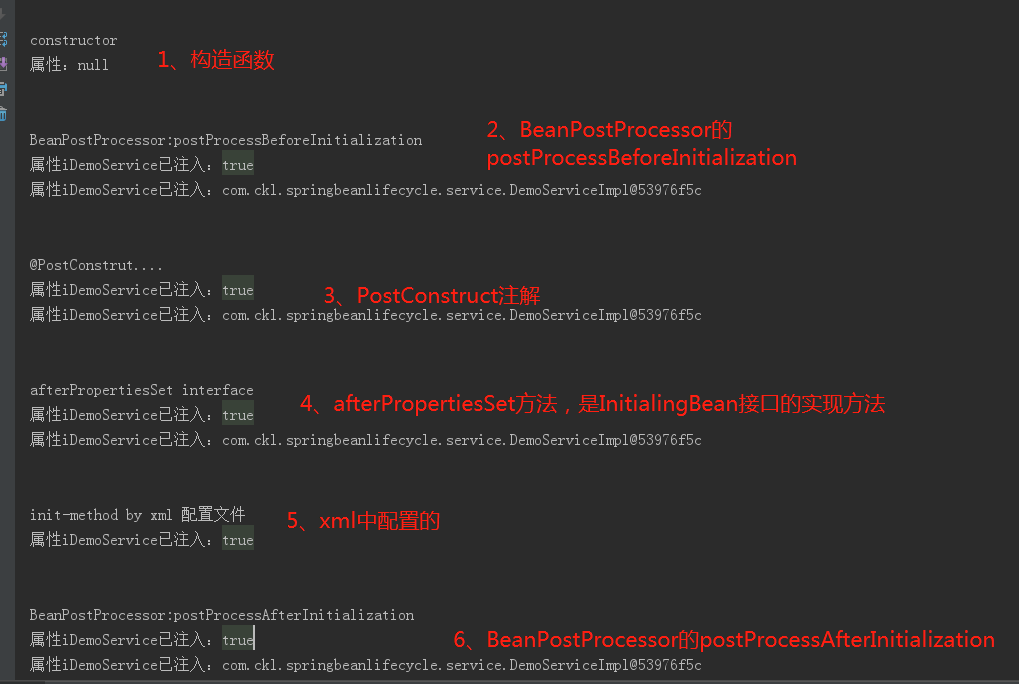
初始化时的顺序如下:
关闭容器时,执行顺序为:
3、扩展#
可能部分朋友,还有这样的需求,即,在程序启动完成后,做点事情,比如,预热缓存之类的,那么,你可以这样:
2
3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
4 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
5 import org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent;
6 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
7
8 /**
9 * desc:
10 *
11 * @author : caokunliang
12 * creat_date: 2018/11/20 0020
13 * creat_time: 14:50
14 **/
15 @Service
16 public class InitRunner implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
17
18 @Override
19 public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent contextRefreshedEvent) {
20 //root application context
21 if (contextRefreshedEvent.getApplicationContext().getParent() == null) {
22 /**
23 * 这里既是 root 容器初始化完毕后,会进入该分支,
24 */
25 todo。。。
26
27 }else {
28 /**
29 * 如果是spring mvc的话, dispatchServlet对应的 applicationContext 会进入这个分支
30 */
31
32 ApplicationContext applicationContext = contextRefreshedEvent.getApplicationContext();
33 todo。。。
34 }
35
36
37
38 }
39 }
上面是针对启动时做的事情,关闭时,如果想做点事情,可以这样:
1 package com.ceiec.webservice.init;
2
3 import org.slf4j.Logger;
4 import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
5 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
6 import org.springframework.context.event.ContextClosedEvent;
7 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
8
9 /**
10 * desc:
11 *
12 * @author : caokunliang
13 * creat_date: 2018/11/20 0020
14 * creat_time: 14:50
15 **/
16 @Service
17 public class CloseRunner implements ApplicationListener<ContextClosedEvent> {
18 private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CloseRunner.class);
19
20 @Override
21 public void onApplicationEvent(ContextClosedEvent contextClosedEvent) {
22 logger.info("clean resources when close applicationContext");
23 if(contextClosedEvent.getApplicationContext().getParent() == null){
24
25 }
26
27 }
28 }
4、spring boot 的扩展#
针对spring boot,也可以注册我们的 listener来参与生命周期。
实现 org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener 即可,并将自定义的 listener 配置到 meta-inf 下的 spring.factories 文件。
举例如下:
1 package com.ceiec.router.config;
2
3 import com.ceiec.router.config.servletconfig.MyServletContext;
4 import lombok.Data;
5 import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
6 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
7 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener;
8 import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext;
9 import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
10 import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
11 import org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource;
12 import org.springframework.core.env.MutablePropertySources;
13 import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource;
14
15 import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
16 import java.util.Map;
17
18 /**
19 * desc:
20 *
21 * @author : caokunliang
22 * creat_date: 2019/5/24 0024
23 * creat_time: 20:07
24 **/
25 @Data
26 @Slf4j
27 public class MyListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener {
28
29
30 public MyListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
31 super();
32 }
33
34
35 @Override
36 public void starting() {
37
38 }
39
40 @Override
41 public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
42 MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
43 for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : propertySources) {
44 Object value = propertySource.getProperty("spring.liveBeansView.mbeanDomain");
45
46 if (value != null) {
47 MapPropertySource source = (MapPropertySource) propertySource;
48 Map<String, Object> map = source.getSource();
49 map.remove("spring.liveBeansView.mbeanDomain");
50
51 log.info("spring.liveBeansView.mbeanDomain: after: {}",propertySource.getProperty("spring.liveBeansView.mbeanDomain"));
52 }
53 }
54 }
55
56 @Override
57 public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
58 log.info("contextPrepared");
59 ServletContext servletContext = new MyServletContext();
60 ServletWebServerApplicationContext applicationContext = (ServletWebServerApplicationContext) context;
61 applicationContext.setServletContext(servletContext);
62 }
63
64 @Override
65 public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
66 //Not used.
67 }
68
69 @Override
70 public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
71
72 }
73
74 @Override
75 public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
76
77 }
78
79 @Override
80 public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
81
82 }
83
84
85 }
源码在交友网站: https://github.com/cctvckl/spring-bean-lifecycle








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端