曹工说Spring Boot源码(9)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context命名空间上)
写在前面的话#
相关背景及资源:
曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享
曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,咱们对着接口,逐个方法讲解
曹工说Spring Boot源码(3)-- 手动注册Bean Definition不比游戏好玩吗,我们来试一下
曹工说Spring Boot源码(4)-- 我是怎么自定义ApplicationContext,从json文件读取bean definition的?
曹工说Spring Boot源码(5)-- 怎么从properties文件读取bean
曹工说Spring Boot源码(6)-- Spring怎么从xml文件里解析bean的
曹工说Spring Boot源码(7)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(上)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(8)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(util命名空间)
工程结构图:
概要#
先给大家看看spring支持的xml配置,我列了个表格如下:
| namespace | element |
|---|---|
| util | constant、property-path、list、set、map、properties |
| context | property-placeholder、property-override、annotation-config、component-scan、load-time-weaver、spring-configured、mbean-export、mbean-server |
| beans | import、bean、alias |
| task | annotation-driven、scheduler、scheduled-tasks、executor |
| cache | advice、annotation-driven |
| aop | config、scoped-proxy、aspectj-autoproxy |
我题目的意思是,spring在解析每个不同的xml元素时,其实是有共性的。所有这些元素的解析器,都实现了BeanDefinitionParser。这个接口只有一个方法,作用就是解析元素时,根据元素的配置,来收集beanDefinition,正所谓:条条大道通罗马,各种xml配置元素,各种注解配置,就是那些大道,罗马是什么?
就是beanDefinition。
从第一篇到现在,已经第9篇了,我们还在讲bean definition,其实就是因为,只有深刻地理解了它,后面才能更方便地理解spring boot,理解configuration注解,理解enable,理解自动装配。
好了,切入本篇,本篇要讲解的xml元素是context命名空间里的。
context:property-placeholder#
用法#
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:application.properties"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.contextnamespace.TestPropertiesVO">
<property name="name" value="${name}"/>
</bean>
</beans>
@Data
public class TestPropertiesVO {
private String name;
}
#application.properties
name: Phil
测试代码:
package org.springframework.contextnamespace;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.util.MyFastJson;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
public class TestPropertyPlaceholder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
new String[]{"classpath:context-namespace-test-property-holder.xml"},false);
context.refresh();
Map<String, Object> map = context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory().getAllSingletonObjectMap();
log.info("singletons:{}", JSONObject.toJSONString(map));
List<BeanDefinition> list =
context.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinitionList();
MyFastJson.printJsonStringForBeanDefinitionList(list);
// 获取该bean,打印
Object bean = context.getBean(TestPropertiesVO.class);
System.out.println("bean:" + bean);
}
}
输出如下:
bean:TestPropertiesVO(name=Phil)
如果我们修改xml:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
//注释之,看看会怎样
<!--<context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:application.properties"/>-->
<bean class="org.springframework.contextnamespace.TestPropertiesVO">
<property name="name" value="${name}"/>
</bean>
</beans>
输出如下:
bean:TestPropertiesVO(name=${name})
可以看到,这样子呢,就没法解析到properties中的值了。
等价用法#
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--<context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:application.properties"/>-->
// 这个配置方式,和上面那个,效果其实是一样的;上面那个,是对下边这种的封装
<bean id="propertyPlaceholderConfigurer"
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath:application.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.contextnamespace.TestPropertiesVO">
<property name="name" value="${name}"/>
</bean>
</beans>
元素解析#
我们切入到org.springframework.context.config.ContextNamespaceHandler,查找下该元素的解析器。
public class ContextNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("property-placeholder", new PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("property-override", new PropertyOverrideBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-config", new AnnotationConfigBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("component-scan", new ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("load-time-weaver", new LoadTimeWeaverBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("spring-configured", new SpringConfiguredBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("mbean-export", new MBeanExportBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("mbean-server", new MBeanServerBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
我们可以看到,本元素的解析器是:PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser。
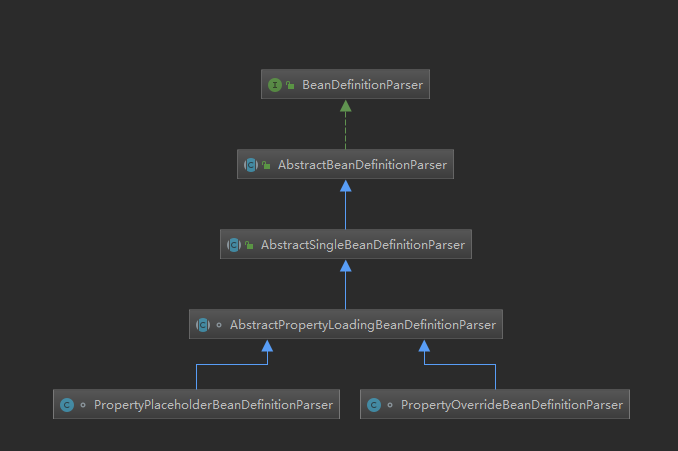
先看看类继承结构:
大家注意第三层,类名里,有Single字样,说明了它是单身狗?不是。说明这个xml元素解析器,最终只得到一个bean definition。
第四层的AbstractPropertyLoadingBeanDefinitionParser,就是提供一个抽象类,提取一些context:property-placeholder和context:property-override对应的解析器中公共的方法。
可以简单一看:
abstract class AbstractPropertyLoadingBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser {
@Override
protected boolean shouldGenerateId() {
return true;
}
// 获取一些属性
@Override
protected void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
String location = element.getAttribute("location");
if (StringUtils.hasLength(location)) {
String[] locations = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(location);
builder.addPropertyValue("locations", locations);
}
String propertiesRef = element.getAttribute("properties-ref");
if (StringUtils.hasLength(propertiesRef)) {
builder.addPropertyReference("properties", propertiesRef);
}
String fileEncoding = element.getAttribute("file-encoding");
if (StringUtils.hasLength(fileEncoding)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("fileEncoding", fileEncoding);
}
String order = element.getAttribute("order");
if (StringUtils.hasLength(order)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("order", Integer.valueOf(order));
}
builder.addPropertyValue("ignoreResourceNotFound",
Boolean.valueOf(element.getAttribute("ignore-resource-not-found")));
builder.addPropertyValue("localOverride",
Boolean.valueOf(element.getAttribute("local-override")));
builder.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
}
}
看了父,不看正主也说不过去,这里呢,正主是真的简单:
class PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractPropertyLoadingBeanDefinitionParser {
private static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_ATTRIB = "system-properties-mode";
private static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_DEFAULT = "ENVIRONMENT";
// 这里获取bean的class,注意,这里的class,是不是和前面:等价用法那一节里,配置的bean的class一样
// 所以啊,context:property-placeholder和等价用法里的底层实现,还是一样的
@Override
protected Class<?> getBeanClass(Element element) {
...
return PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.class;
}
@Override
protected void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
super.doParse(element, builder);
builder.addPropertyValue("ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders",
Boolean.valueOf(element.getAttribute("ignore-unresolvable")));
String systemPropertiesModeName = element.getAttribute(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_ATTRIB);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(systemPropertiesModeName) &&
!systemPropertiesModeName.equals(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_DEFAULT)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("systemPropertiesModeName", "SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_"+systemPropertiesModeName);
}
}
}
大家可以看注释,这里返回的class,和等价用法里的
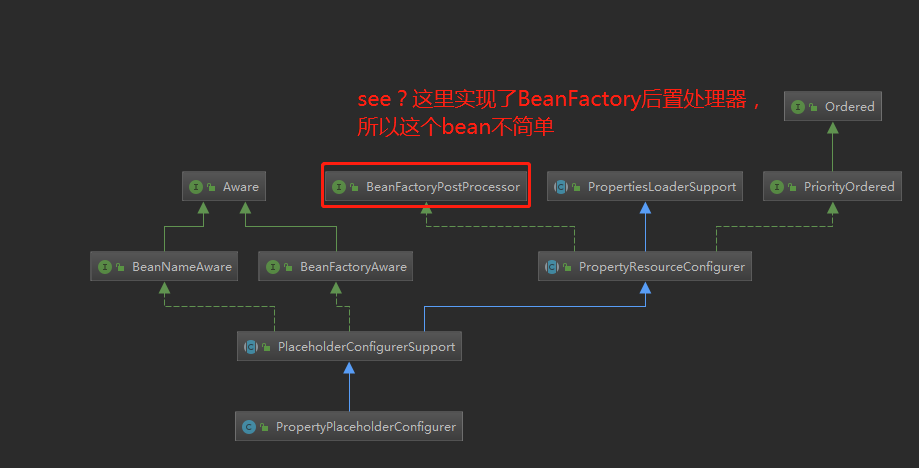
这个class,PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,其实还是比较特别的,我们看看其类图:
这里,我们发现这个bean class,竟然是一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor。这个接口有什么作用呢,大概就是,等所有的beanDefinition都装载了之后,会调用实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean,对beanDefinition进行处理。
如果对这块感兴趣,可以看博主之前的一篇文章,网上也很多解析,可自行搜索:
曹工杂谈:为什么很少需要改Spring源码,因为扩展点太多了,说说Spring的后置处理器
context:property-override#
用法#
这个元素,一般比较少用,但今天查了一下,我觉得这个还比较有意思,而且很奇妙地和当前spring boot外部化配置的思想吻合。
它的用途说起来比较晦涩,我们看例子就知道了:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean id="person" class="org.springframework.contextnamespace.Person" >
<property name="name" value="Ram"/>
<property name="age" value="20"/>
<property name="location" value="Varanasi"/>
</bean>
</beans>
package org.springframework.contextnamespace;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private String location;
}
测试代码:
package org.springframework.contextnamespace;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.util.MyFastJson;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* desc:
*
* @author : caokunliang
* creat_date: 2019/12/25 0025
* creat_time: 15:50
**/
@Slf4j
public class TestPropertyOverride {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
new String[]{"classpath:context-namespace-test-property-override.xml"},false);
context.refresh();
// 获取bean
Object bean = context.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println("bean:" + bean);
}
}
输出如下:
bean:Person(name=Ram, age=20, location=Varanasi)
这个应该大家都懂。
接下来,我们在xml里定义一个元素:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
// 配置了这个玩意
<context:property-override location="classpath:beanOverride.properties"/>
<bean id="person" class="org.springframework.contextnamespace.Person" >
<property name="name" value="Ram"/>
<property name="age" value="20"/>
<property name="location" value="Varanasi"/>
</bean>
</beans>
#beanOverride.properties
person.age=40
person.location=Delhi
测试程序不变,这次的输出如下:
bean:Person(name=Ram, age=40, location=Delhi)
也就是说,外部配置文件:beanOverride.properties中的属性,覆盖了xml中的bean的属性。
而现在,spring boot的environment解析变量时,也是外部的配置文件、命令行参数、环境变量等,优先级高于jar包内的配置,是不是和我们这个元素的作用比较像呢?
等价用法#
如果不使用:context:property-override,也可以像下面这样使用:
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyOverrideConfigurer">
<property name="location" value="classpath:beanOverride.properties" />
</bean>
元素解析#
从ContextNamespaceHandler,我们可以找到该元素对应的parser:PropertyOverrideBeanDefinitionParser
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("property-placeholder", new PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("property-override", new PropertyOverrideBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-config", new AnnotationConfigBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("component-scan", new ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("load-time-weaver", new LoadTimeWeaverBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("spring-configured", new SpringConfiguredBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("mbean-export", new MBeanExportBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("mbean-server", new MBeanServerBeanDefinitionParser());
}
类实现也很简单,和前面的context:property-placeholder一样,都继承了同一个基类:AbstractPropertyLoadingBeanDefinitionParser。
简单看看其实现吧:
class PropertyOverrideBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractPropertyLoadingBeanDefinitionParser {
@Override
protected Class getBeanClass(Element element) {
return PropertyOverrideConfigurer.class;
}
@Override
protected void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
super.doParse(element, builder);
builder.addPropertyValue("ignoreInvalidKeys",
Boolean.valueOf(element.getAttribute("ignore-unresolvable")));
}
}
这里,看看我们获得的bean class:
和前面讨论的一样,也是一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
总结#
又需要回答题目的问题了,从xml文件里,解析得到了什么呢,答案依然是beanDefinition。
不过呢,这次的beanClass,略有不同,因为他们是特殊的class,是可以参与beanDefinition生命周期的class,
因为他们实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
大家可以再看看前面util命名空间,那些bean class呢,主要就是FactoryBean。
本篇源码位置:
由于context命名空间都是些大人物,所以本篇主要是先给大家热身,下一讲,我们讲讲这里面的:
annotation-config、component-scan
我简单看了两眼,还挺有意思,欢迎大家和我一起学习。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端