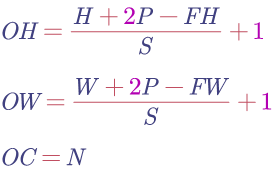动手实现深度学习(12): 卷积层的实现与优化(img2col)
9.1 卷积层的运算
传送门: https://www.cnblogs.com/greentomlee/p/12314064.html
github: Leezhen2014: https://github.com/Leezhen2014/python_deep_learning
卷积的forward
卷积的计算过程网上的资料已经做够好了,没必要自己再写一遍。只把资料搬运到这里:
https://www.zhihu.com/question/43609045
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44106928/article/details/103079668
这里总结一下有padding\stride的卷积操作:
假设,输入大小为(H,W,C),fileter大小为(FH,FW,C)*N ; padding=P, stride=S,卷积后的形状为(OH,OW,OC)
1 def forward(self, x): 2 ''' 3 使用im2col 将输入的x 转换成2D矩阵 4 然后 y= w*x+b 以矩阵的形式完成 5 最后返回y 6 :param x: x为4D tensor, 输入数据 7 :return: out=w*x+b 8 ''' 9 FN, C, FH, FW = self.W.shape 10 N, C, H, W = x.shape 11 out_h = 1 + int((H + 2 * self.pad - FH) / self.stride) 12 out_w = 1 + int((W + 2 * self.pad - FW) / self.stride) 13 14 col = im2col(x, FH, FW, self.stride, self.pad) 15 col_W = self.W.reshape(FN, -1).T 16 print("col.shape=%s"%str(col.shape)) 17 print("col_W.shape=%s"%str(col_W.shape)) 18 19 out = np.dot(col, col_W) 20 print("out.shape=%s"%str(out.shape)) 21 out=out+ self.b 22 out = out.reshape(N, out_h, out_w, -1).transpose(0, 3, 1, 2) 23 24 self.x = x 25 self.col = col 26 self.col_W = col_W 27 28 return out 29
卷积的backward
概念介绍: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33802329
卷积的backward是对卷积的求导。
代码实现如下:
1 def backward(self, dout): 2 ''' 3 反馈过程中也需要将2D 矩阵转换为4D tensor 4 :param dout: 梯度差 5 :return: 6 ''' 7 FN, C, FH, FW = self.W.shape 8 dout = dout.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(-1, FN) # NCHW 9 10 self.db = np.sum(dout, axis=0)# NHWC , 求和 11 self.dW = np.dot(self.col.T, dout) # 点乘w 12 self.dW = self.dW.transpose(1, 0).reshape(FN, C, FH, FW) 13 14 dcol = np.dot(dout, self.col_W.T) 15 dx = col2im(dcol, self.x.shape, FH, FW, self.stride, self.pad) 16 17 return dx
9.2 引入im2col 概念
再讲卷积的实现之前,首先抛出一个问题:如果按照上述的卷积方式计算,是否会影响性能?
答案是肯定会受影响的。
因此,我们需要向优化一下conv的计算方式.
按照“以空间换时间”的思想,我们可以做一些优化,使得在conv和pool的时候运算速度加快。
首先,我们知道Numpy对大型矩阵的运算是有做优化的,这个特点我们应该好好利用;
其次,我们知道Numpy在做多个嵌套的for循环的时候,O(n)会很大;应该避免做多个for循环;
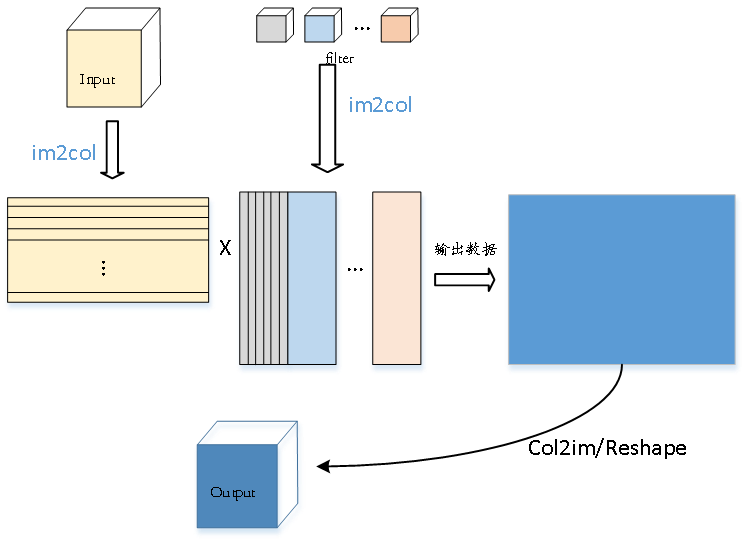
因此,要是将4D的卷积运算转换成2D的矩阵乘法就会好很多;filter也可以变成2D的数组;
Im2col便是将4D数据转换成2D矩阵的函数。
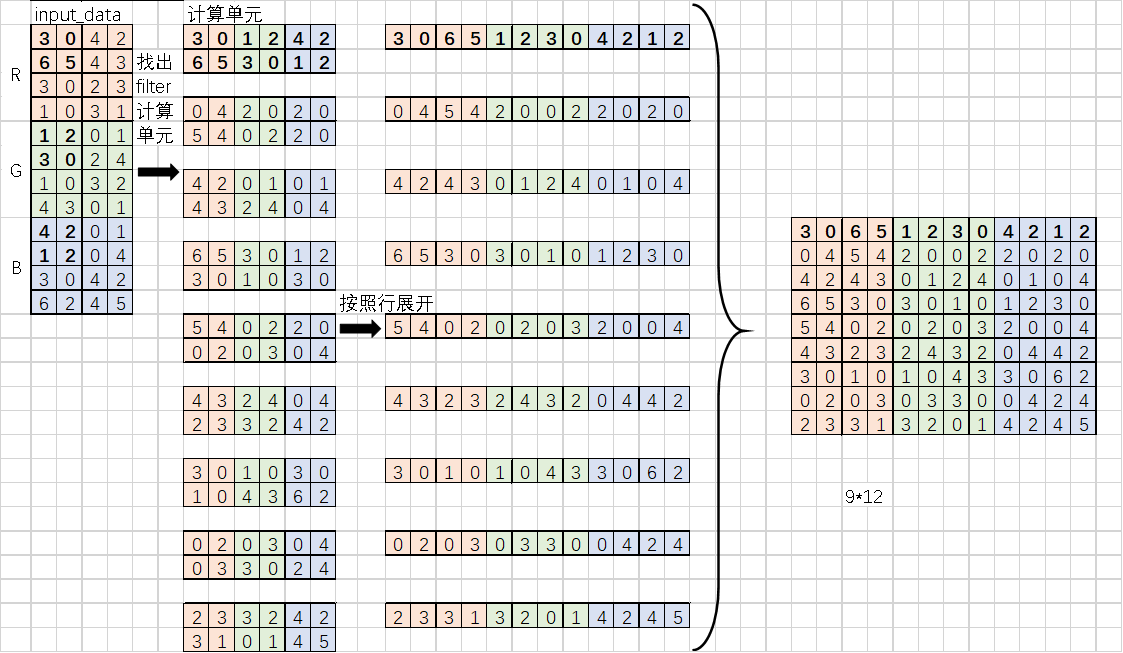
该函数大致的思路是:filter按照行列展开成一个2D矩阵即可,input_data按照计算的单元重新组合。因此需要写一个函数将图像转换成2D矩阵,该函数可以将图像展开成适合与滤波去做乘法的矩阵。
展开和计算的流程如下:
9.3 单元测试im2col
对filter计算有影响的因素有input_data,filter_h,filter_w,stride, padding;im2col会应该根据以上的因因素展开input_data,展开后的input_data一定是比之前要大的;
我们可以尝试计算一下input_data展开后的数据形状:
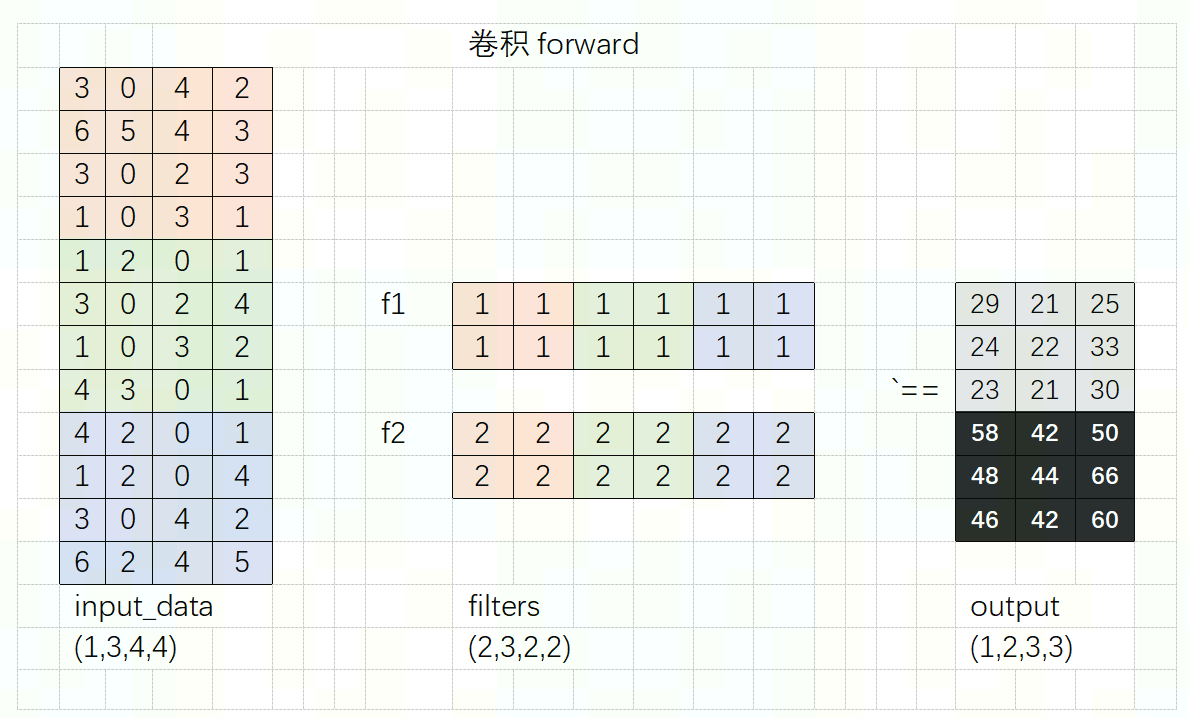
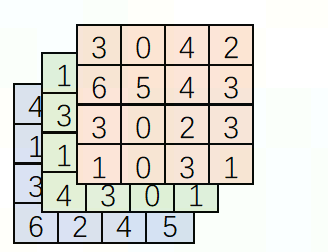
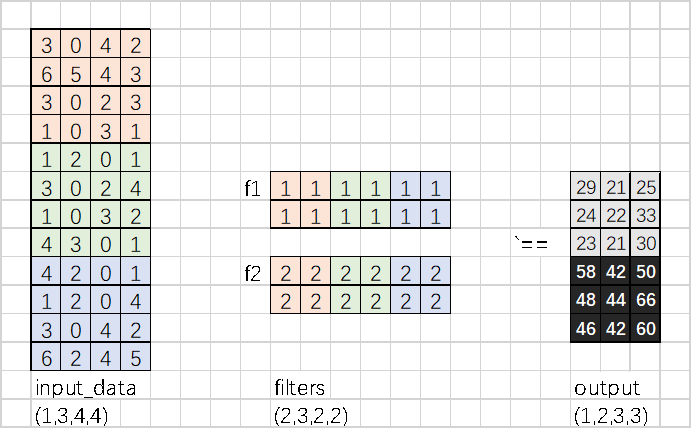
假设,输入数据为4*4*3大小的tensor; filter有两个为2*(2*2*3),filter_h=2,filter_w=2,stride=1, padding=0;这里可以计算出展开以后的大小:
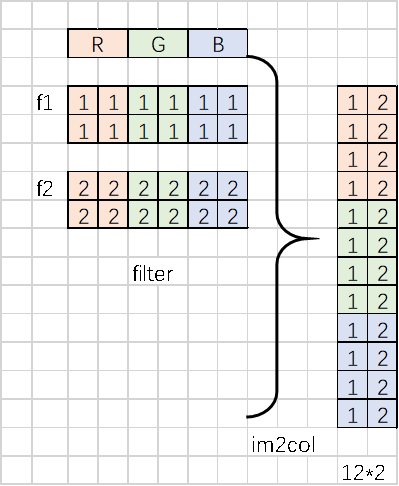
Filter为有两个,分别为f1和f2; shape=(2*2*3), 按照行展开成2D的矩阵以后如下图所示:
Input_data为4*4*3的tensor,如下图所示:
Input_data首先会找出filter对应的计算单元,这些还是需要padding\stride\filter_w\filter_h相关,找出计算的单元以后,按照行展开。最后得到的数据便是im2col的结果:
Input_data和filter这样展开以后,卷积计算就可以按照矩阵乘法的方式计算,避免了重复的for循环。如下图所示,黑色和灰色区域是计算的结果。不必担心矩阵过大是否会影响计算速度,Numpy对大规模矩阵乘法内部有优化加速,这样展开以后恰恰也能充分的利用numpy的特性。
Im2col的实现:
1 def im2col(input_data, filter_h, filter_w, stride=1, pad=0): 2 ''' 3 4 :param input_data: 输入数据由4维数组组成(N,C,H,W) 5 :param filter_h: filer的高 6 :param filter_w: filter的宽 7 :param stride: stride 8 :param pad: padding 9 :return: 2D矩阵 10 ''' 11 # 计算输出的大小 12 N, C, H, W = input_data.shape 13 out_h = (H + 2*pad - filter_h)//stride + 1 14 out_w = (W + 2*pad - filter_w)//stride + 1 15 # padding 16 img = np.pad(input_data, [(0,0), (0,0), (pad, pad), (pad, pad)], 'constant') 17 col = np.zeros((N, C, filter_h, filter_w, out_h, out_w)) 18 # 计算单元 19 for y in range(filter_h): 20 y_max = y + stride*out_h 21 for x in range(filter_w): 22 x_max = x + stride*out_w 23 col[:, :, y, x, :, :] = img[:, :, y:y_max:stride, x:x_max:stride] 24 # 重新排列 25 col = col.transpose(0, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3).reshape(N*out_h*out_w, -1) 26 return col
测试代码:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 # @File : test_im2col.py 3 # @Author: lizhen 4 # @Date : 2020/2/14 5 # @Desc : 测试im2col 6 import numpy as np 7 8 from src.common.util import im2col,col2im 9 10 if __name__ == '__main__': 11 raw_data = [3, 0, 4, 2, 12 6, 5, 4, 3, 13 3, 0, 2, 3, 14 1, 0, 3, 1, 15 16 1, 2, 0, 1, 17 3, 0, 2, 4, 18 1, 0, 3, 2, 19 4, 3, 0, 1, 20 21 4, 2, 0, 1, 22 1, 2, 0, 4, 23 3, 0, 4, 2, 24 6, 2, 4, 5 25 ] 26 27 input_data = np.array(raw_data) 28 input_data = input_data.reshape(1,3,4,4) 29 print(input_data.shape) 30 col1 = im2col(input_data=input_data,filter_h=2,filter_w=2,stride=1,pad=0)#input_data, filter_h, filter_w, stride=1, pad=0 31 print(col1) 32
========输出:可以发现和上面的绘图的结果是一致的 =====
(1, 3, 4, 4)
[[3. 0. 6. 5. 1. 2. 3. 0. 4. 2. 1. 2.]
[0. 4. 5. 4. 2. 0. 0. 2. 2. 0. 2. 0.]
[4. 2. 4. 3. 0. 1. 2. 4. 0. 1. 0. 4.]
[6. 5. 3. 0. 3. 0. 1. 0. 1. 2. 3. 0.]
[5. 4. 0. 2. 0. 2. 0. 3. 2. 0. 0. 4.]
[4. 3. 2. 3. 2. 4. 3. 2. 0. 4. 4. 2.]
[3. 0. 1. 0. 1. 0. 4. 3. 3. 0. 6. 2.]
[0. 2. 0. 3. 0. 3. 3. 0. 0. 4. 2. 4.]
[2. 3. 3. 1. 3. 2. 0. 1. 4. 2. 4. 5.]]
9.3 卷积操作的实现
卷积操作也需要实现forward和backward函数。
Forward函数中用到了9.1\9.2的im2col
1 class Convolution: 2 def __init__(self, W, b, stride=1, pad=0): 3 ''' 4 conv的构造函数 5 :param W: 2D矩阵 6 :param b: 7 :param stride: 8 :param pad: 9 ''' 10 self.W = W 11 self.b = b 12 self.stride = stride 13 self.pad = pad 14 15 # 中间结果(backward的时候使用) 16 self.x = None 17 self.col = None 18 self.col_W = None 19 20 # 权重的梯度/偏置的梯度 21 self.dW = None 22 self.db = None 23 24 def forward(self, x): 25 ''' 26 使用im2col 将输入的x 转换成2D矩阵 27 然后 y= w*x+b 以矩阵的形式完成 28 最后返回y 29 :param x: x为4D tensor, 输入数据 30 :return: out=w*x+b 31 ''' 32 FN, C, FH, FW = self.W.shape 33 N, C, H, W = x.shape 34 out_h = 1 + int((H + 2 * self.pad - FH) / self.stride) 35 out_w = 1 + int((W + 2 * self.pad - FW) / self.stride) 36 37 col = im2col(x, FH, FW, self.stride, self.pad) 38 col_W = self.W.reshape(FN, -1).T 39 40 out = np.dot(col, col_W) + self.b 41 out = out.reshape(N, out_h, out_w, -1).transpose(0, 3, 1, 2) 42 43 self.x = x 44 self.col = col 45 self.col_W = col_W 46 47 return out 48 49 def backward(self, dout): 50 ''' 51 反馈过程中也需要将2D 矩阵转换为4D tensor 52 :param dout: 梯度差 53 :return: 54 ''' 55 FN, C, FH, FW = self.W.shape 56 dout = dout.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(-1, FN) 57 58 self.db = np.sum(dout, axis=0) 59 self.dW = np.dot(self.col.T, dout) 60 self.dW = self.dW.transpose(1, 0).reshape(FN, C, FH, FW) 61 62 dcol = np.dot(dout, self.col_W.T) 63 dx = col2im(dcol, self.x.shape, FH, FW, self.stride, self.pad) 64 65 return dx 66
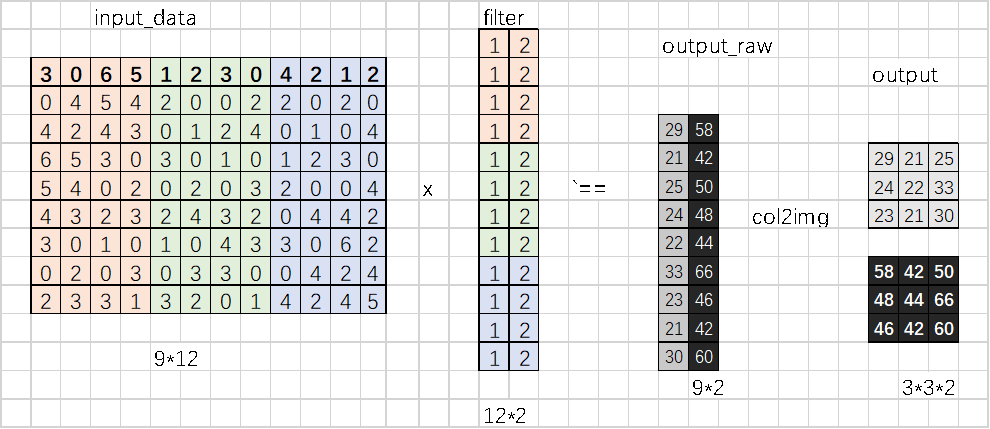
9.4单元测试卷积操作
输入:input_data\filters
输出:output
测试代码:
1 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 # @File : test_im2col.py 4 # @Author: lizhen 5 # @Date : 2020/2/14 6 # @Desc : 测试im2col 7 import numpy as np 8 9 from src.common.util import im2col,col2im 10 from src.common.layers import Convolution 11 12 13 if __name__ == '__main__': 14 raw_data = [3, 0, 4, 2, 15 6, 5, 4, 3, 16 3, 0, 2, 3, 17 1, 0, 3, 1, 18 19 1, 2, 0, 1, 20 3, 0, 2, 4, 21 1, 0, 3, 2, 22 4, 3, 0, 1, 23 24 4, 2, 0, 1, 25 1, 2, 0, 4, 26 3, 0, 4, 2, 27 6, 2, 4, 5 28 ] 29 30 raw_filter=[ 31 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 32 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 33 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 34 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 35 36 ] 37 38 39 40 input_data = np.array(raw_data) 41 filter_data = np.array(raw_filter) 42 43 x = input_data.reshape(1,3,4,4)# NCHW 44 W = filter_data.reshape(2,3,2,2) # NHWC 45 b = np.zeros(2) 46 # b = b.reshape((2,1)) 47 # col1 = im2col(input_data=x,filter_h=2,filter_w=2,stride=1,pad=0)#input_data, filter_h, filter_w, stride=1, pad=0 48 # print(col1) 49 50 print("input_data.shape=%s"%str(input_data.shape)) 51 print("W.shape=%s"%str(W.shape)) 52 print("b.shape=%s"%str(b.shape)) 53 conv = Convolution(W,b) # def __init__(self, W, b, stride=1, pad=0) 54 out = conv.forward(x) 55 print("bout.shape=%s"%str(out.shape)) 56 print(out)
Conv的输出结果,与上图的结果一致。