A:计算256MB能够存放多少个int
1 int main() 2 { 3 cout<<256*1024*1024/4; 4 return 0; 5 }
ans=67108864
B:计算2021张1到10的卡片能够拼出1~n的最大的n
1 int cnt[10]; 2 int main() 3 { 4 for(int i=0;i<10;i++) cnt[i]=2021; 5 int k=1; 6 while(1){ 7 int t=k; 8 while(t) cnt[t%10]--,t/=10; 9 for(int i=0;i<10;i++) 10 if(cnt[i]<0){ 11 cout<<k-1; 12 return 0; 13 } 14 k++; 15 } 16 return 0; 17 }
ans=3181
C:给定一个20*21的棋盘,任选两点,问有多少条直线。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <cmath> 5 #define x first 6 #define y second 7 using namespace std; 8 typedef pair<double,double> PII; 9 const double eps=1e-6; 10 struct node{ 11 double k,b; 12 bool operator<(const node& t)const{ 13 if(fabs(k-t.k)<eps) return b<t.b; 14 return k<t.k; 15 } 16 }; 17 vector<node> v; 18 int main() 19 { 20 for(int x1=0;x1<20;x1++){ 21 for(int y1=0;y1<21;y1++){ 22 for(int x2=0;x2<20;x2++){ 23 for(int y2=0;y2<21;y2++){ 24 if(x1!=x2){ 25 double k=double(y2-y1) / (x2-x1); 26 double b=y1-k*x1; 27 v.push_back({k,b}); 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 sort(v.begin(),v.end()); 34 int res=1; 35 for(int i=1;i<v.size();i++){ 36 if(fabs(v[i].k-v[i-1].k)>eps||fabs(v[i].b-v[i-1].b)>eps) 37 res++; 38 } 39 cout<<res+20; 40 return 0; 41 }
ans=40257
D:给定一个很大的数,问差分成3个数相乘有多少种方案,1*2*2和2*2*1是不同的方案。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 typedef long long LL; 6 LL n=2021041820210418; 7 vector<LL> p; 8 int main() 9 { 10 LL t=n; 11 for(LL i=1;i<=n/i;i++){ 12 if(t%i==0){ 13 p.push_back(i); 14 if(t/i!=i) 15 p.push_back(t/i); 16 } 17 } 18 LL res=0; 19 for(int i=0;i<p.size();i++){ 20 for(int j=0;j<p.size();j++){ 21 for(int k=0;k<p.size();k++){ 22 if(p[i]*p[j]*p[k]==n){ 23 res++; 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 cout<<res; 29 return 0; 30 }
ans=2430
E:裸的最短路问题。(当时用的floyd,因为好写)
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int N=2050; 6 const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; 7 int f[N][N]; 8 int gcd(int a,int b){ 9 return b==0?a:gcd(b,a%b); 10 } 11 int main() 12 { 13 memset(f,0x3f,sizeof f); 14 for(int i=1;i<=2021;i++){ 15 for(int j=1;j<=2021;j++){ 16 if(abs(i-j)<=21){ 17 int tmp=i*j/gcd(i,j); 18 f[i][j]=tmp; 19 f[j][i]=tmp; 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 for(int k=1;k<=2021;k++){ 24 for(int i=1;i<=2021;i++){ 25 for(int j=1;j<=2021;j++){ 26 if(f[i][k]!=INF&&f[k][j]!=INF){ 27 f[i][j]=min(f[i][j],f[i][k]+f[k][j]); 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 cout<<f[1][2021]; 33 return 0; 34 }
ans=10266837
F:时间显示
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 int main() 6 { 7 long long n; 8 cin>>n; 9 n/=1000; 10 n%=24*60*60; 11 int h=n/(60*60); 12 n%=60*60; 13 int m=n/60; 14 n%=60; 15 int s=n; 16 printf("%02d:%02d:%02d",h,m,s); 17 return 0; 18 }
G:背包问题,但是需要加上一个偏移量
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int N=110; 6 const int M=2e5+10,B=M/2; 7 int w[N]; 8 bool f[N][M]; 9 int main() 10 { 11 int n,m=0; 12 cin>>n; 13 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>w[i],m+=w[i]; 14 f[0][0+B]=1; 15 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 16 for(int j=-m;j<=m;j++){ 17 f[i][j+B]=f[i-1][j+B]; 18 if(j-w[i]>=-m) f[i][j+B]|=f[i-1][j-w[i]+B]; 19 if(j+w[i]<=m) f[i][j+B]|=f[i-1][j+w[i]+B]; 20 } 21 } 22 int res=0; 23 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 24 if(f[n][i+B]) 25 res++; 26 cout<<res; 27 return 0; 28 }
H:杨辉三角形。
说实话挺复杂的,将杨辉三角形斜着看。
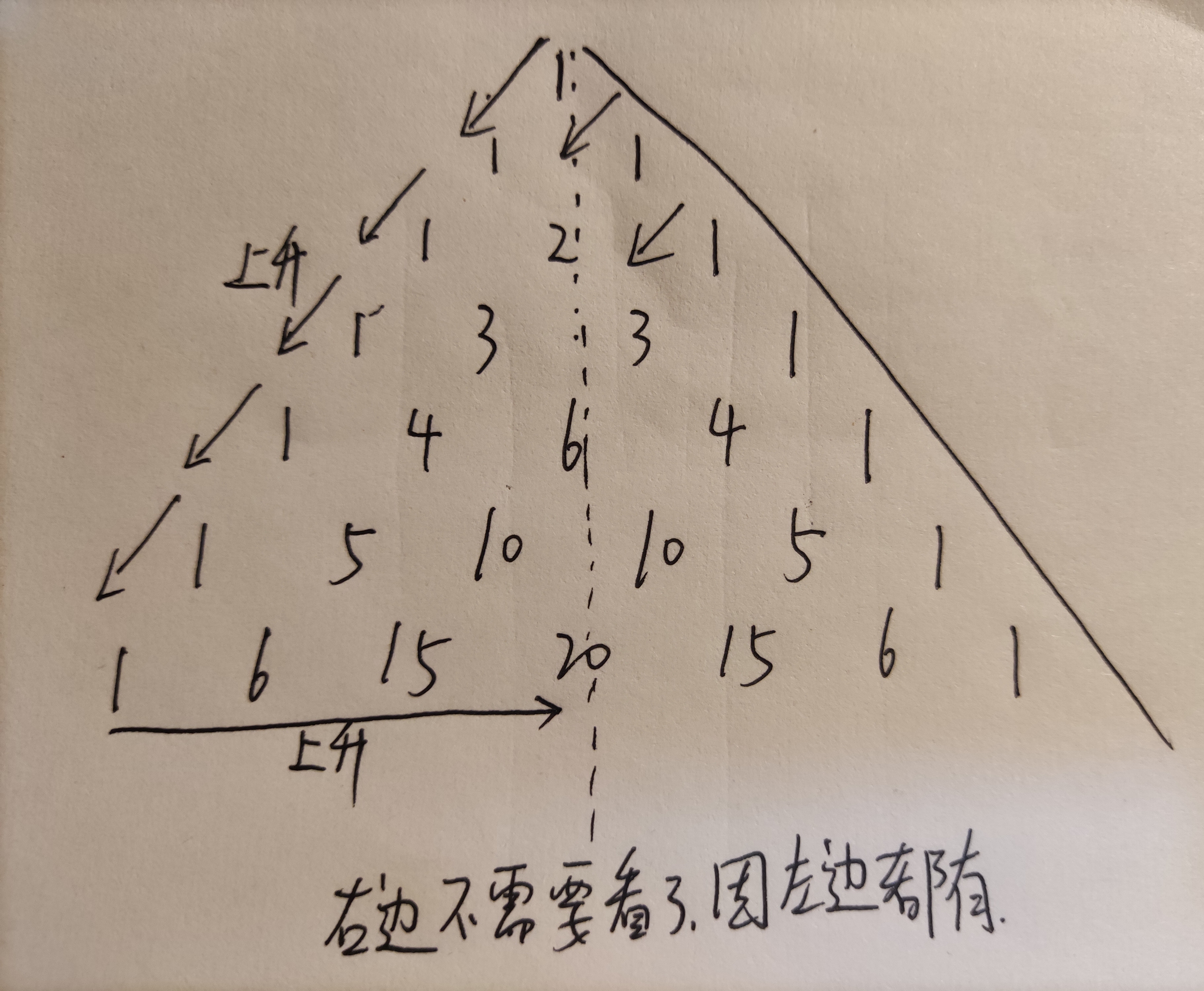
右半边可以直接不看了,因为右边的左边都有,所以一定更先出现。
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
1 6 15 20 15 6 1
越靠近中间列的增加的越快。
我们得先从中间开始找n,对于每一列找到大于等于n的最小的数,若他是n的话则他就是答案了。
否则找前面一列的,可以发现答案是必然存在的(看第二列)。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 typedef long long LL; 6 LL n; 7 LL C(LL a,LL b){ 8 LL res=1; 9 for(int i=a,j=1;j<=b;i--,j++){ 10 res=res*i/j; 11 if(res>n) return res; 12 } 13 return res; 14 } 15 bool check(LL k){ 16 LL l=2*k,r=n;//左端点为第2*k行,右端点为第n行 17 while(l<r){ 18 LL mid=l+r>>1; 19 if(C(mid,k)>=n) r=mid; 20 else l=mid+1; 21 } 22 if(C(r,k)!=n) return false; 23 cout<<r*(r+1)/2 + k+1; 24 return true; 25 } 26 int main() 27 { 28 cin>>n; 29 if(n==1){ 30 cout<<1<<endl; 31 return 0; 32 } 33 for(int i=16;;i--){ 34 if(check(i)){ 35 break; 36 } 37 } 38 return 0; 39 }
I:非常复杂的一道题。
因为n,m<=1e5,若是直接排序n*m*logn,肯定会超时的。
可以通过栈来解这道题。

在翻转的过程中虚线部份就已经确定了。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #define x first 5 #define y second 6 using namespace std; 7 typedef pair<int, int> PII; 8 const int N=1e5+10; 9 PII stk[N]; 10 int top=0; 11 int ans[N]; 12 int main() 13 { 14 int n,m; 15 cin>>n>>m; 16 while(m--){ 17 int p,q; 18 cin>>p>>q; 19 if(p==0){ 20 while(top&&stk[top].x==0) q=max(q,stk[top--].y); 21 while(top>=2&&q>=stk[top-1].y) top-=2; 22 stk[++top]={0,q}; 23 }else if(top){ 24 while(top&&stk[top].x==1) q=min(q,stk[top--].y); 25 while(top>=2&&q<=stk[top-1].y) top-=2; 26 stk[++top]={1,q}; 27 } 28 } 29 //以上是找出正确的操作。 30 int k=n,l=1,r=n; 31 for(int i=1;i<=top;i++){ 32 if(stk[i].x==0){ 33 while(r>stk[i].y&&l<=r) ans[r--]=k--; 34 }else if(stk[i].x==1){ 35 while(l<stk[i].y&&l<=r) ans[l++]=k--; 36 } 37 if(l>r) break; 38 } 39 if(top%2)//若是没放完的话 40 while(l<=r) ans[l++]=k--; 41 else 42 while(l<=r) ans[r--]=k--; 43 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 44 cout<<ans[i]<<" "; 45 return 0; 46 }
J:巨难的一道题。
1、括号序列合法的充要条件:左括号和右括号数目相等,且任意前缀左括号数目>=右括号数目
2、向不合法的括号序列中添加括号能否单独考虑左右括号?
可以,因为若是不存在左括号和右括号放在同一个空隙里的话,必然是可以的。
若是存在左括号与右括号放到同一个空隙里的话只有可能是" ))))((( "这种情况。
3、此时可以单独考虑左括号,那么如何保证考虑左括号的时候不会有重复的情况?
比如 ) ) 能够添加成 ( ( ) ) ,但是这会有两种解释一是在0前面添加两个左括号,或者在0前面以及1前面各添加一个左括号。
可以发现右括号将整个序列分成了3个左括号段,一个括号序列被每一段左括号的数目唯一确定。我们固定只能在) 前面添加(。
4、计算向序列中添加左括号的方案数。
DP。
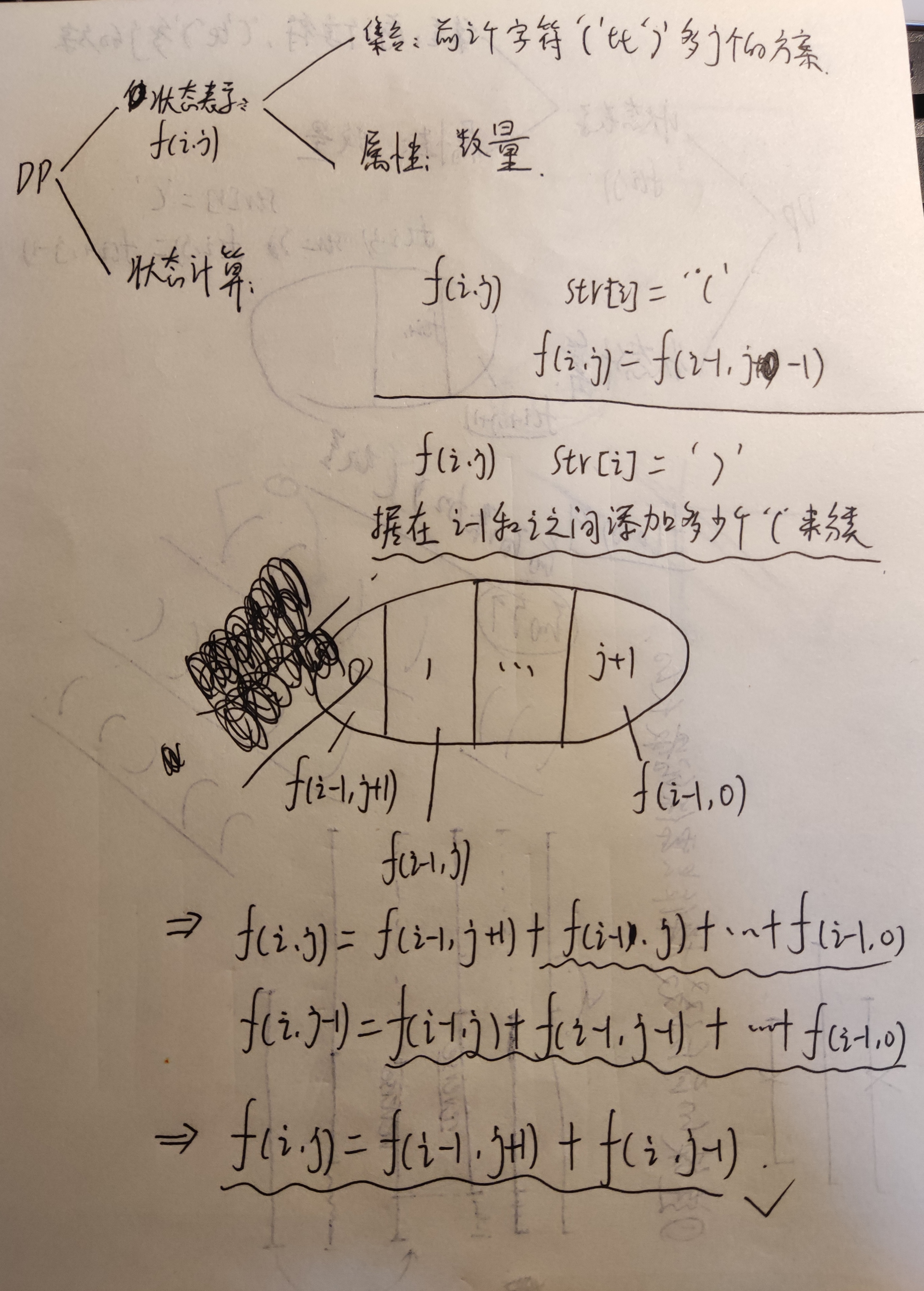
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 typedef long long LL; 6 const int N=5010,mod=1e9+7; 7 char str[N]; 8 LL f[N][N]; 9 LL n; 10 LL calc(){ 11 memset(f,0,sizeof f); 12 f[0][0]=1; 13 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 14 if(str[i]=='('){ 15 for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) 16 f[i][j]=f[i-1][j-1]; 17 }else if(str[i]=')'){ 18 f[i][0]=(f[i-1][0]+f[i-1][1])%mod; 19 for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) 20 f[i][j]=(f[i-1][j+1]+f[i][j-1])%mod; 21 } 22 } 23 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){ 24 if(f[n][i]) 25 return f[n][i]; 26 } 27 return -1; 28 } 29 int main() 30 { 31 cin>>str+1; 32 n=strlen(str+1); 33 LL l=calc(); 34 reverse(str+1,str+1+n); 35 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 36 if(str[i]=='(') str[i]=')'; 37 else str[i]='('; 38 LL r=calc(); 39 cout<<l*r%mod; 40 return 0; 41 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号