单词搜索 II——leetcode212(DFS/DFS+字典树)
单词搜索 II
题目:单词搜索 II
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个单词(字符串)列表 words,找出所有同时在二维网格和字典中出现的单词。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过 相邻的单元格 内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母在一个单词中不允许被重复使用。
示例:
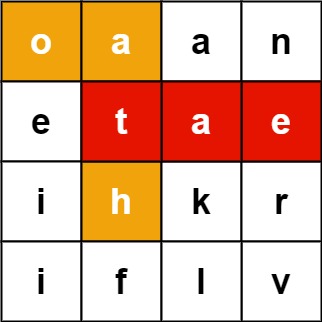
输入:board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"]
输出:["eat","oath"]题解
方法一: 单纯的DFS
会超时
方法二:DFS+前缀剪枝
用set集合存储字典中的前缀
dfs遍历时判断当前字符串在前缀结合中是否存在
如果存在,则继续,否则就退出。
时间复杂度和空间复杂度:10%

class Solution0 {
private Set<String> results;
private Set<String> prex;
private Set<String> wordSet;
private int[][] nag=new int[][]{{0,1},{0,-1},{-1,0},{1,0}};
public void dfs(char[][] board, int[][] book, int x, int y, StringBuilder sb){
if(!prex.contains(sb.toString())) return; //判断前缀中是否包含sb
if(wordSet.contains(sb.toString())) { //判断结果中是否包含sb
results.add(sb.toString());
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) {
int newx=x+nag[i][0], newy=y+nag[i][1];
if(newx<0 || newx>=board.length || newy<0 || newy>=board[0].length || book[newx][newy]==1) continue;
book[newx][newy]=1;
sb.append(board[newx][newy]);
dfs(board, book, newx, newy, sb);
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1);
book[newx][newy]=0;
}
}
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
int[][] book=new int[board.length][board[0].length];
results=new HashSet<>();
prex=new HashSet<>(); //前缀集合
wordSet=new HashSet<>(); //字典集合
for(int i=0;i<words.length;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<words[i].length();j++){
prex.add(words[i].substring(0, j+1));
}
wordSet.add(words[i]);
}
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<board.length;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<board[0].length;j++) {
book[i][j]=1;
sb.append(board[i][j]);
dfs(board, book, i, j, sb);
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1);
book[i][j]=0;
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(results);
}
}方法三:DFS+字典树

class Solution {
class Tree
{
String word;
Map<Character, Tree> children;
public Tree()
{
this.word="";
children=new HashMap<>();
}
//字典树插入
public void insert(String word){
Tree temp=this;
for(int i=0;i<word.length();i++) {
char c=word.charAt(i);
temp.children.putIfAbsent(c, new Tree());
temp=temp.children.get(c);
}
temp.word=word;
}
}
private Set<String> results;
private int[][] dirs=new int[][]{{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
public void dfs(char[][] board, Tree root, int x, int y, int[][] book) {
//字典树:判断board[x][y]是否是当前节点的下一个节点
if(!root.children.containsKey(board[x][y])) return;
Tree next=root.children.get(board[x][y]);
//判断当前节点是否是叶子节点
if(!next.word.equals("")){
results.add(next.word);
}
//DFS遍历四个方向的节点
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int newx=x+dirs[i][0], newy=y+dirs[i][1];
if(newx<0||newx>=board.length|| newy<0|| newy>=board[0].length || book[newx][newy]==1) continue;
book[newx][newy]=1;
dfs(board, next, newx, newy, book);
book[newx][newy]=0;
}
}
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
results=new HashSet<>();
int book[][]=new int[board.length][board[0].length];
Tree root=new Tree();
for (String word : words) {
root.insert(word);
}
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<board.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<board[0].length;j++) {
book[i][j]=1;
dfs(board, root, i, j, book);
book[i][j]=0;
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(results);
}
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· 葡萄城 AI 搜索升级:DeepSeek 加持,客户体验更智能
· 什么是nginx的强缓存和协商缓存
· 一文读懂知识蒸馏