泛型笔记
ParameterizedType
ParameterizedType represents a parameterized type such as Collection
源码:
public interface ParameterizedType extends Type {
/**
* Returns an array of {@code Type} objects representing the actual type
* arguments to this type.
Type[] getActualTypeArguments();
/**
* Returns the {@code Type} object representing the class or interface
* that declared this type.
/
Type getRawType();
/**
* Returns a {@code Type} object representing the type that this type
* is a member of. For example, if this type is {@code O<T>.I<S>},
* return a representation of {@code O<T>}.
/
Type getOwnerType();
}
要明白ParameterizedType 的含义,先看它的父类Type:
/**
* Type is the common superinterface for all types in the Java
* programming language. These include raw types, parameterized types,
* array types, type variables and primitive types.
*
* @since 1.5
*/
public interface Type {
/**
* Returns a string describing this type, including information
* about any type parameters.
*
* @implSpec The default implementation calls {@code toString}.
*
* @return a string describing this type
* @since 1.8
*/
default String getTypeName() {
return toString();
}
}
Type是一个表示Java语言中所有类型,包括原始类型, 参数化类型, 数组类型类型变量以及基本类型。
所以ParameterizedType表示参数化类型。
ParameterizedType有三个方法:
@getActualTypeArguments,@getRawType,@getOwnerType。多说无益处,直接看代码就明白了:
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestGenericInterface {
private class Food {
String foodName;
}
private interface Eat2<T> {
void eat(T things);
}
private interface Run {
void run();
}
private class Cat implements Eat2<Food>, Run {
@Override
public void run() {
}
@Override
public void eat(Food things) {
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<?> clazz2 = Cat.class;
Type[] genericInterfacesCat = clazz2.getGenericInterfaces();
ParameterizedType type = (ParameterizedType) genericInterfacesCat[0];
Type[] actualTypeArguments = type.getActualTypeArguments();
Type rawType = type.getRawType();
String typeName = type.getTypeName();
Type ownerType = type.getOwnerType();
System.out.println();
}
}
debug结果:

- type: type变量是
ParameterizedType类型, 值是TestGenericInterface$Eat2<TestGenericInterface$Food>, 不仅有接口Eat2的信息,也有接口泛型Food的信息; - rawType: rawType变量是
Type类型,值是TestGenericInterface$Eat2,仅包含接口Eat2的信息; - ownerType: 也是
Type类型,用来指示type变量在哪个类型的对象中使用, 这里是TestGenericInterface
getGenericInterfaces和getInterfaces
getGenericInterfaces
Returns the {@code Type}s representing the interfaces directly implemented by the class or interface represented by this object
getInterfaces:
Determines the interfaces implemented by the class or interface represented by this object.
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
/**
* @author longxingjian <longxingjian@kuaishou.com>
* Created on 2021-03-15
*/
public class TestGenericInterface {
private class Food {
String foodName;
}
private interface Eat {
void eat(String things);
}
private interface Eat2<T> {
void eat(T things);
}
private interface Run {
void run();
}
private class Dog implements Eat, Run {
@Override
public void run() {
}
@Override
public void eat(String things) {
}
}
private class Cat implements Eat2<Food>, Run {
@Override
public void run() {
}
@Override
public void eat(Food things) {
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<?> clazz = Dog.class;
Type[] genericInterfacesDog = clazz.getGenericInterfaces();
Class<?>[] interfacesDog = clazz.getInterfaces();
Class<?> clazz2 = Cat.class;
Type[] genericInterfacesCat = clazz2.getGenericInterfaces();
Class<?>[] interfacesCat = clazz.getInterfaces();
}
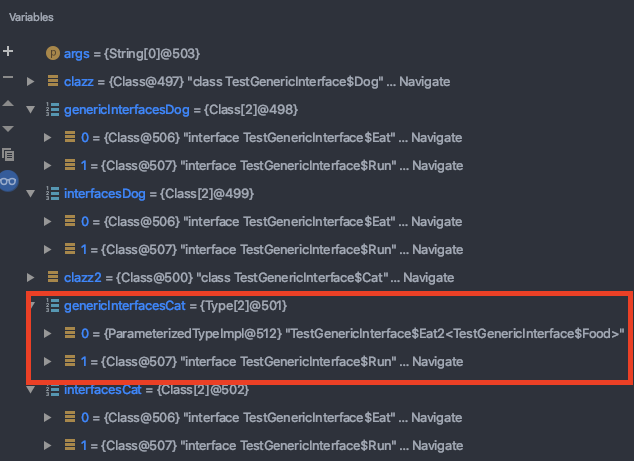
可以看出当Eat接口没有使用泛型参数时,getGenericInterfaces和getInterfaces的结果一样,都返回了该对象实现的接口类型;
当Eat2有泛型参数时,getGenericInterfaces返回了该对象实现接口的参数化类型,ParameterizedType,其中有泛型信息;而getInterfaces只能返回接口类型,没有泛型信息。
TALK IS CHEAP, SHOW ME THE CODE


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号