Tinyply 源码阅读
Tinyply 源码阅读
ply格式介绍见:http://paulbourke.net/dataformats/ply/
tinyply项目路径为:https://github.com/ddiakopoulos/tinyply/
这里先放一个ply的示例:
ply
format ascii 1.0
comment author: anonymous
comment object: another cube
element vertex 8
property float32 x
property float32 y
property float32 z
property uint8 red { 顶点颜色開始 }
property uint8 green
property uint8 blue
element face 7
property list uint8 int32 vertex_index { 每一个面片的顶点个数 }
element edge 5 { 物体里有5条边 }
property int32 vertex1 { 边的第一个顶点的索引 }
property int32 vertex2 { 第二个顶点的索引 }
property uint8 red { 边颜色開始 }
property uint8 green
property uint8 blue
end_header
0 0 0 255 0 0 { 顶点列表開始 }
0 0 1 255 0 0
0 1 1 255 0 0
0 1 0 255 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 255
1 0 1 0 0 255
1 1 1 0 0 255
1 1 0 0 0 255
3 0 1 2 { 面片列表開始,从一个三角形開始 }
3 0 2 3 { 还有一个三角形 }
4 7 6 5 4 { 如今是一些四边形 }
4 0 4 5 1
4 1 5 6 2
4 2 6 7 3
4 3 7 4 0
0 1 255 255 255 { 边列表開始,从白边開始 }
1 2 255 255 255
2 3 255 255 255
3 0 255 255 255
2 0 0 0 0 { 以一个黑线结束 }
主要数据结构
- Type,定义支持的数据类型;
- PropertyInfo,包装对应数据类型所占字节大小,以及对应的文本表示;
- Buffer
- PolyData?用来存储element对应的具体数据;
- PlyProperty,定义property对应的名字,以及类型,是不是list,以及list的大小;
- PlyElement,定义element对应的名字, 以及关联的PlyProperty
- PlyFile,文件解析的具体实现;
- PlyFileImple: 文件解析的实现类,包括写入,读取;
- PlyDataCursor: 用于数据定位;
- ParsingHelper:用于辅助parsing;
- PropertyLookup:方便查找element,对应的property所占内存大小;
- PlyFileImple: 文件解析的实现类,包括写入,读取;
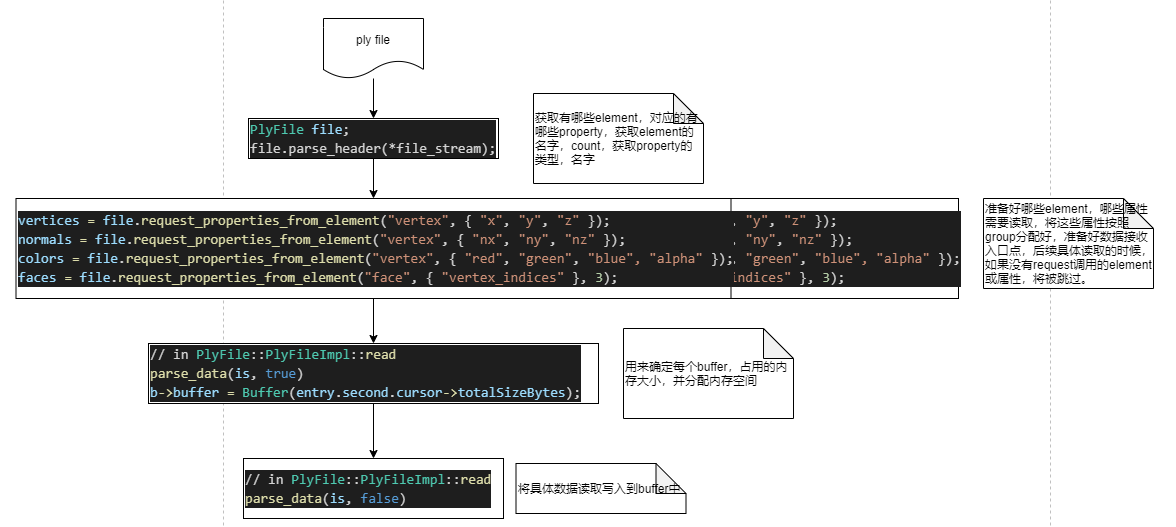
文件解析流程
header解析:
//parse_header处理的token分别为:
// comment, format, element, property, obj_info, end_header
// read_header_element 构建:PlyElement对象,并附上name,和size的值
// read_header_property 将上一步构建的plyelement中填上,property(property type,和name)标识
bool PlyFile::PlyFileImpl::parse_header(std::istream & is)
{
std::string line;
bool success = true;
while (std::getline(is, line))
{
std::istringstream ls(line);
std::string token;
ls >> token;
if (token == "ply" || token == "PLY" || token == "") continue;
else if (token == "comment") read_header_text(line, comments, 8);
else if (token == "format") read_header_format(ls);
else if (token == "element") read_header_element(ls);
else if (token == "property") read_header_property(ls);
else if (token == "obj_info") read_header_text(line, objInfo, 9);
else if (token == "end_header") break;
else success = false; // unexpected header field
}
return success;
}
准备element对应的property描述:
std::shared_ptr<PlyData> PlyFile::PlyFileImpl::request_properties_from_element(const std::string & elementKey,
const std::vector<std::string> propertyKeys,
const uint32_t list_size_hint)
{
if (elements.empty()) throw std::runtime_error("header had no elements defined. malformed file?");
if (elementKey.empty()) throw std::invalid_argument("`elementKey` argument is empty");
if (propertyKeys.empty()) throw std::invalid_argument("`propertyKeys` argument is empty");
std::shared_ptr<PlyData> out_data = std::make_shared<PlyData>();
const int64_t elementIndex = find_element(elementKey, elements);
std::vector<std::string> keys_not_found;
// Sanity check if the user requested element is in the pre-parsed header
// 由element.name + property.name组成的唯一标识,并建立与ParsingHelper之间的关系
// ParsingHelper内部的data用来存储具体数值的buffer空间(此时buffer空间被没有分配大小)
if (elementIndex >= 0)
{
// We found the element
const PlyElement & element = elements[elementIndex];
// Each key in `propertyKey` gets an entry into the userData map (keyed by a hash of
// element name and property name), but groups of properties (requested from the
// public api through this function) all share the same `ParsingHelper`. When it comes
// time to .read(), we check the number of unique PlyData shared pointers
// and allocate a single buffer that will be used by each property key group.
// That way, properties like, {"x", "y", "z"} will all be put into the same buffer.
ParsingHelper helper;
helper.data = out_data;
helper.data->count = element.size; // how many items are in the element?
helper.data->isList = false;
helper.data->t = Type::INVALID;
helper.cursor = std::make_shared<PlyDataCursor>();
helper.list_size_hint = list_size_hint;
// Find each of the keys
for (const auto & key : propertyKeys)
{
const int64_t propertyIndex = find_property(key, element.properties);
if (propertyIndex < 0) keys_not_found.push_back(key);
}
if (keys_not_found.size())
{
std::stringstream ss;
for (auto & str : keys_not_found) ss << str << ", ";
throw std::invalid_argument("the following property keys were not found in the header: " + ss.str());
}
for (const auto & key : propertyKeys)
{
const int64_t propertyIndex = find_property(key, element.properties);
const PlyProperty & property = element.properties[propertyIndex];
helper.data->t = property.propertyType;
helper.data->isList = property.isList;
auto result = userData.insert(std::pair<uint32_t, ParsingHelper>(hash_fnv1a(element.name + property.name), helper));
if (result.second == false)
{
throw std::invalid_argument("element-property key has already been requested: " + element.name + " " + property.name);
}
}
// Sanity check that all properties share the same type
std::vector<Type> propertyTypes;
for (const auto & key : propertyKeys)
{
const int64_t propertyIndex = find_property(key, element.properties);
const PlyProperty & property = element.properties[propertyIndex];
propertyTypes.push_back(property.propertyType);
}
if (std::adjacent_find(propertyTypes.begin(), propertyTypes.end(), std::not_equal_to<Type>()) != propertyTypes.end())
{
throw std::invalid_argument("all requested properties must share the same type.");
}
}
else throw std::invalid_argument("the element key was not found in the header: " + elementKey);
return out_data;
}
读取具体的element对应的property内容:
void PlyFile::PlyFileImpl::read(std::istream & is)
{
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<PlyData>> buffers;
for (auto & entry : userData) buffers.push_back(entry.second.data);
// Discover if we can allocate up front without parsing the file twice
// list_hints用于性能优化的目的
uint32_t list_hints = 0;
for (auto & b : buffers) for (auto & entry : userData) {list_hints += entry.second.list_size_hint;(void)b;}
// No list hints? Then we need to calculate how much memory to allocate
if (list_hints == 0)
{
// 第一遍parse_data用来分配需要的内存空间
parse_data(is, true);
}
// Count the number of properties (required for allocation)
// e.g. if we have properties x y and z requested, we ensure
// that their buffer points to the same PlyData
std::unordered_map<PlyData*, int32_t> unique_data_count;
for (auto & ptr : buffers) unique_data_count[ptr.get()] += 1;
// Since group-requested properties share the same cursor,
// we need to find unique cursors so we only allocate once
std::sort(buffers.begin(), buffers.end());
buffers.erase(std::unique(buffers.begin(), buffers.end()), buffers.end());
// 分配buffer对应的空间
// We sorted by ptrs on PlyData, need to remap back onto its cursor in the userData table
for (auto & b : buffers)
{
for (auto & entry : userData)
{
if (entry.second.data == b && b->buffer.get() == nullptr)
{
// If we didn't receive any list hints, it means we did two passes over the
// file to compute the total length of all (potentially) variable-length lists
if (list_hints == 0)
{
b->buffer = Buffer(entry.second.cursor->totalSizeBytes);
}
else
{
// otherwise, we can allocate up front, skipping the first pass.
const size_t list_size_multiplier = (entry.second.data->isList ? entry.second.list_size_hint : 1);
auto bytes_per_property = entry.second.data->count * PropertyTable[entry.second.data->t].stride * list_size_multiplier;
bytes_per_property *= unique_data_count[b.get()];
b->buffer = Buffer(bytes_per_property);
}
}
}
}
// Populate the data
// 此时,读取具体的数值
parse_data(is, false);
// In-place big-endian to little-endian swapping if required
if (isBigEndian)
{
for (auto & b : buffers)
{
uint8_t * data_ptr = b->buffer.get();
const size_t stride = PropertyTable[b->t].stride;
const size_t buffer_size_bytes = b->buffer.size_bytes();
switch (b->t)
{
case Type::INT16: endian_swap_buffer<int16_t, int16_t>(data_ptr, buffer_size_bytes, stride); break;
case Type::UINT16: endian_swap_buffer<uint16_t, uint16_t>(data_ptr, buffer_size_bytes, stride); break;
case Type::INT32: endian_swap_buffer<int32_t, int32_t>(data_ptr, buffer_size_bytes, stride); break;
case Type::UINT32: endian_swap_buffer<uint32_t, uint32_t>(data_ptr, buffer_size_bytes, stride); break;
case Type::FLOAT32: endian_swap_buffer<uint32_t, float>(data_ptr, buffer_size_bytes, stride); break;
case Type::FLOAT64: endian_swap_buffer<uint64_t, double>(data_ptr, buffer_size_bytes, stride); break;
default: break;
}
}
}
}
parse_data的实现:
void PlyFile::PlyFileImpl::parse_data(std::istream & is, bool firstPass)
{
std::function<void(PropertyLookup & f, const PlyProperty & p, uint8_t * dest, size_t & destOffset, std::istream & is)> read;
std::function<size_t(PropertyLookup & f, const PlyProperty & p, std::istream & is)> skip;
const auto start = is.tellg();
uint32_t listSize = 0;
size_t dummyCount = 0;
std::string skip_ascii_buffer;
// Special case mirroring read_property_binary but for list types; this
// has an additional big endian check to flip the data in place immediately
// after reading. We do this as a performance optimization; endian flipping is
// done on regular properties as a post-process after reading (also for optimization)
// but we need the correct little-endian list count as we read the file.
auto read_list_binary = [this](const Type & t, void * dst, size_t & destOffset, const size_t & stride, std::istream & _is) noexcept
{
destOffset += stride;
_is.read((char*)dst, stride);
if (isBigEndian)
{
switch (t)
{
case Type::INT16: *(int16_t*)dst = endian_swap<int16_t, int16_t>(*(int16_t*)dst); break;
case Type::UINT16: *(uint16_t*)dst = endian_swap<uint16_t, uint16_t>(*(uint16_t*)dst); break;
case Type::INT32: *(int32_t*)dst = endian_swap<int32_t, int32_t>(*(int32_t*)dst); break;
case Type::UINT32: *(uint32_t*)dst = endian_swap<uint32_t, uint32_t>(*(uint32_t*)dst); break;
default: break;
}
}
return stride;
};
if (isBinary)
{
read = [this, &listSize, &dummyCount, &read_list_binary](PropertyLookup & f, const PlyProperty & p, uint8_t * dest, size_t & destOffset, std::istream & _is) noexcept
{
if (!p.isList)
{
return read_property_binary(f.prop_stride, dest + destOffset, destOffset, _is);
}
read_list_binary(p.listType, &listSize, dummyCount, f.list_stride, _is); // the list size
return read_property_binary(f.prop_stride * listSize, dest + destOffset, destOffset, _is); // properties in list
};
skip = [this, &listSize, &dummyCount, &read_list_binary](PropertyLookup & f, const PlyProperty & p, std::istream & _is) noexcept
{
if (!p.isList)
{
_is.read((char*)scratch, f.prop_stride);
return f.prop_stride;
}
read_list_binary(p.listType, &listSize, dummyCount, f.list_stride, _is); // the list size (does not count for memory alloc)
auto bytes_to_skip = f.prop_stride * listSize;
_is.ignore(bytes_to_skip);
return bytes_to_skip;
};
}
else
{
read = [this, &listSize, &dummyCount](PropertyLookup & f, const PlyProperty & p, uint8_t * dest, size_t & destOffset, std::istream & _is) noexcept
{
if (!p.isList)
{
read_property_ascii(p.propertyType, f.prop_stride, dest + destOffset, destOffset, _is);
}
else
{
read_property_ascii(p.listType, f.list_stride, &listSize, dummyCount, _is); // the list size
for (size_t i = 0; i < listSize; ++i)
{
read_property_ascii(p.propertyType, f.prop_stride, dest + destOffset, destOffset, _is);
}
}
};
skip = [this, &listSize, &dummyCount, &skip_ascii_buffer](PropertyLookup & f, const PlyProperty & p, std::istream & _is) noexcept
{
skip_ascii_buffer.clear();
if (p.isList)
{
read_property_ascii(p.listType, f.list_stride, &listSize, dummyCount, _is); // the list size (does not count for memory alloc)
for (size_t i = 0; i < listSize; ++i) _is >> skip_ascii_buffer; // properties in list
return listSize * f.prop_stride;
}
_is >> skip_ascii_buffer;
return f.prop_stride;
};
}
//“userData”表是一种简单的数据结构,用于从ply文件中获取用户想要的数据,
// 但内部循环哈希查找并不理想。属性查找表将表向下展开为一个为解析优化的二维数组。
// 第一个索引是元素,第二个索引是属性。
std::vector<std::vector<PropertyLookup>> element_property_lookup = make_property_lookup_table();
size_t element_idx = 0;
size_t property_idx = 0;
ParsingHelper * helper {nullptr};
// This is the inner import loop
for (auto & element : elements)
{
for (size_t count = 0; count < element.size; ++count)
{
property_idx = 0;
for (auto & property : element.properties)
{
// property lookup 存储了属性元素占用的空间,或list元素占用的空间
PropertyLookup & lookup = element_property_lookup[element_idx][property_idx];
if (!lookup.skip)
{
helper = lookup.helper;
if (firstPass)
{
helper->cursor->totalSizeBytes += skip(lookup, property, is);
// These lines will be changed when tinyply supports
// variable length lists. We add it here so our header data structure
// contains enough info to write it back out again (e.g. transcoding).
if (property.listCount == 0) property.listCount = listSize;
if (property.listCount != listSize) throw std::runtime_error("variable length lists are not supported yet.");
}
else
{
read(lookup, property, helper->data->buffer.get(), helper->cursor->byteOffset, is);
}
}
else
{
skip(lookup, property, is);
}
property_idx++;
}
}
element_idx++;
}
// Reset istream position to the start of the data
if (firstPass) is.seekg(start, is.beg);
}
文件解析流程小结
版权说明
作者: grassofsky
出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/grass-and-moon
本文版权归作者,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出, 原文链接 如有问题, 可邮件(grass-of-sky@163.com)咨询.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号