PMP SRC Algo - 微分几何相关基础
PMP SRC Algo - 微分几何相关基础
PMP主页为:http://www.pmp-library.org/
代码实现见:src/pmp/algorithms/DifferentialGeometry.cpp
cot和cos值的clamp
将cot和cos值进行了clamp操作,为什么??
cot的clamp能够避免数值过小,或过大。cos呢?
相关实现如下:
//! clamp cotangent values as if angles are in [3, 177]
inline double clamp_cot(const double v)
{
const double bound = 19.1; // 3 degrees
return (v < -bound ? -bound : (v > bound ? bound : v));
}
//! clamp cosine values as if angles are in [3, 177]
inline double clamp_cos(const double v)
{
const double bound = 0.9986; // 3 degrees
return (v < -bound ? -bound : (v > bound ? bound : v));
}
atan2是一个函数,double atan2(double y, double x) ,返回以弧度表示的 y/x 的反正切。计算时atan2 比 atan 稳定。返回的值 [-pi,+pi] 的弧度制。当x=0的时候也能够计算。具体如下:
inline Scalar angle(const Point& v0, const Point& v1)
{
return atan2(norm(cross(v0, v1)), dot(v0, v1));
}
三角形面积计算
利用两个向量的叉乘计算平行四边形的面积,然后再求三角形的面积,如下:
Scalar triangle_area(const Point& p0, const Point& p1, const Point& p2)
{
return Scalar(0.5) * norm(cross(p1 - p0, p2 - p0));
}
重心计算
三角形的重心就是三个顶点的算术平均。如下:
Point centroid(const SurfaceMesh& mesh, Face f)
{
Point c(0, 0, 0);
Scalar n(0);
for (auto v : mesh.vertices(f))
{
c += mesh.position(v);
++n;
}
c /= n;
return c;
}
mesh表面的重心是三角形的重心随面积的加权平均值,如下:
Point centroid(const SurfaceMesh& mesh)
{
Point center(0, 0, 0), c;
Scalar area(0), a;
for (auto f : mesh.faces())
{
a = triangle_area(mesh, f);
c = centroid(mesh, f);
area += a;
center += a * c;
}
center /= area;
return center;
}
边的cotan_weight

以上图为例,边xixj的cotan_weight,为\(\cot(\alpha_{ij}) + \cot(\beta_{ij})\).
具体实现如下,代码中对于边界边进行了额外处理:
double cotan_weight(const SurfaceMesh& mesh, Edge e)
{
double weight = 0.0;
const Halfedge h0 = mesh.halfedge(e, 0);
const Halfedge h1 = mesh.halfedge(e, 1);
const dvec3 p0 = (dvec3)mesh.position(mesh.to_vertex(h0));
const dvec3 p1 = (dvec3)mesh.position(mesh.to_vertex(h1));
if (!mesh.is_boundary(h0))
{
const dvec3 p2 =
(dvec3)mesh.position(mesh.to_vertex(mesh.next_halfedge(h0)));
const dvec3 d0 = p0 - p2;
const dvec3 d1 = p1 - p2;
const double area = norm(cross(d0, d1));
if (area > std::numeric_limits<double>::min()) // 对特殊情况进行了处理
{
const double cot = dot(d0, d1) / area;
weight += clamp_cot(cot);
}
}
// 对另一个角cot的求解和上面类似
// ......
assert(!std::isnan(weight));
assert(!std::isinf(weight));
return weight;
}
顶点的mixed的voronoi面积计算
关于voronoi面积,mixed voronoi面积的介绍可以参见:grassofsky:DGP - 2. Discrete differential geometry
简单 ,如下:
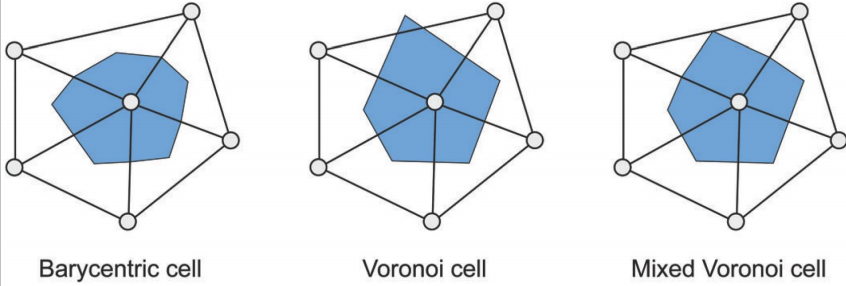
关于顶点周围三角形对mixed voronoi面积贡献分为三种情况:
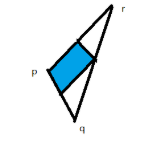
1-当顶点p对应的角为钝角时,贡献的面积为三角形面积的一半:
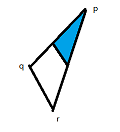
2-当q,或r为钝角是,共享的面积为三角形面积的1/4:
3-其他情况:
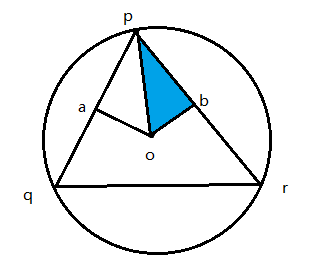
此时o点为三角形pqr的外接圆,那么角pqr,等于角pob,那么三角形pob的面积为:
结合上面的注解,可以更容易理解:double voronoi_area(const SurfaceMesh& mesh, Vertex v)的实现。
顶点的面积voronoi面积计算
此时计算的场景是barycentric cell对应的面积,每个三角形贡献的面积为其面积的1/3。
顶点的laplace(voronoi面积归一化后)结果计算
关于laplace的介绍可以参见:grassofsky:DGP - 2. Discrete differential geometry中的Cotangent Laplacian一节。代码实现中,对公式进行了拆解,如下:
Point laplace(const SurfaceMesh& mesh, Vertex v)
{
Point laplace(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
if (!mesh.is_isolated(v))
{
Scalar weight, sumWeights(0.0);
for (auto h : mesh.halfedges(v))
{
weight = cotan_weight(mesh, mesh.edge(h));
sumWeights += weight;
laplace += weight * mesh.position(mesh.to_vertex(h));
}
laplace -= sumWeights * mesh.position(v);
laplace /= Scalar(2.0) * voronoi_area(mesh, v);
}
return laplace;
}
顶点周围的角度和计算
角度和的计算通过代码很容易看懂。
内部顶点的最小,最大,平均,高斯曲率计算
平均曲率 = (最小曲率 + 最大曲率)/ 2
高斯曲率 = (最小曲率 x 最大曲率)
重心坐标计算
基本思路是,将3D空间中的点映射到2D,利用2D中的三角形面积比进行计算,具体实现代码如下:
template <typename Scalar>
const Vector<Scalar, 3> barycentric_coordinates(const Vector<Scalar, 3>& p,
const Vector<Scalar, 3>& u,
const Vector<Scalar, 3>& v,
const Vector<Scalar, 3>& w)
{
Vector<Scalar, 3> result(1.0 / 3.0); // default: barycenter
Vector<Scalar, 3> vu = v - u, wu = w - u, pu = p - u;
// 三角形两条边,vu,wu的叉乘结果为(nx,ny,nz),即三角形的法向量
// 然后求得法向量在哪个轴具有最大值
// 如果x轴最大,那么将三角形投影到yz平面,利用2D中的三角形面积比进行计算
// 如果y轴最大,那么将三角形投影到xz平面,利用2D中的三角形面积比进行计算
// 如果z轴最大,那么将三角形投影到xy平面,利用2D中的三角形面积比进行计算
// find largest absolute coodinate of normal
Scalar nx = vu[1] * wu[2] - vu[2] * wu[1],
ny = vu[2] * wu[0] - vu[0] * wu[2],
nz = vu[0] * wu[1] - vu[1] * wu[0], ax = fabs(nx), ay = fabs(ny),
az = fabs(nz);
unsigned char maxCoord;
if (ax > ay)
{
if (ax > az)
{
maxCoord = 0;
}
else
{
maxCoord = 2;
}
}
else
{
if (ay > az)
{
maxCoord = 1;
}
else
{
maxCoord = 2;
}
}
// solve 2D problem
switch (maxCoord)
{
case 0:
{
if (1.0 + ax != 1.0)
{
result[1] = 1.0 + (pu[1] * wu[2] - pu[2] * wu[1]) / nx - 1.0;
result[2] = 1.0 + (vu[1] * pu[2] - vu[2] * pu[1]) / nx - 1.0;
result[0] = 1.0 - result[1] - result[2];
}
break;
}
case 1:
{
if (1.0 + ay != 1.0)
{
result[1] = 1.0 + (pu[2] * wu[0] - pu[0] * wu[2]) / ny - 1.0;
result[2] = 1.0 + (vu[2] * pu[0] - vu[0] * pu[2]) / ny - 1.0;
result[0] = 1.0 - result[1] - result[2];
}
break;
}
case 2:
{
if (1.0 + az != 1.0)
{
result[1] = 1.0 + (pu[0] * wu[1] - pu[1] * wu[0]) / nz - 1.0;
result[2] = 1.0 + (vu[0] * pu[1] - vu[1] * pu[0]) / nz - 1.0;
result[0] = 1.0 - result[1] - result[2];
}
break;
}
}
return result;
}
作者: grassofsky
出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/grass-and-moon
本文版权归作者,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出, 原文链接 如有问题, 可邮件(grass-of-sky@163.com)咨询.



