[LeetCode] 1028. Recover a Tree From Preorder Traversal 从先序遍历还原二叉树
We run a preorder depth first search on the rootof a binary tree.
At each node in this traversal, we output D dashes (where D is the depth of this node), then we output the value of this node. (If the depth of a node is D, the depth of its immediate child is D+1. The depth of the root node is 0.)
If a node has only one child, that child is guaranteed to be the left child.
Given the output S of this traversal, recover the tree and return its root.
Example 1:
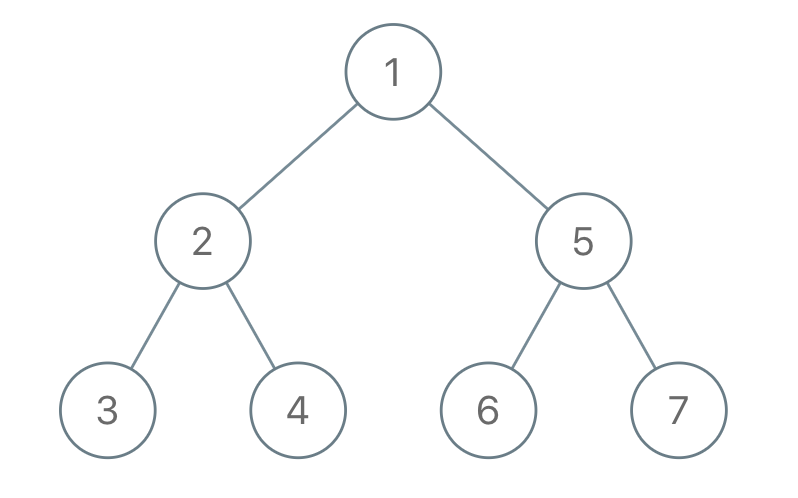
Input: "1-2--3--4-5--6--7"
Output: [1,2,5,3,4,6,7]
Example 2:
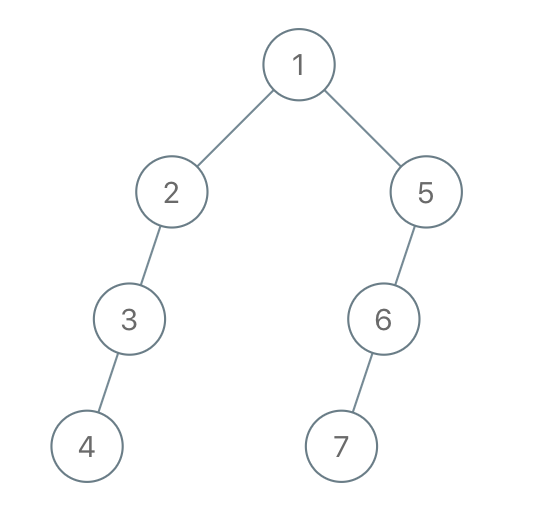
Input: "1-2--3---4-5--6---7"
Output: [1,2,5,3,null,6,null,4,null,7]
Example 3:
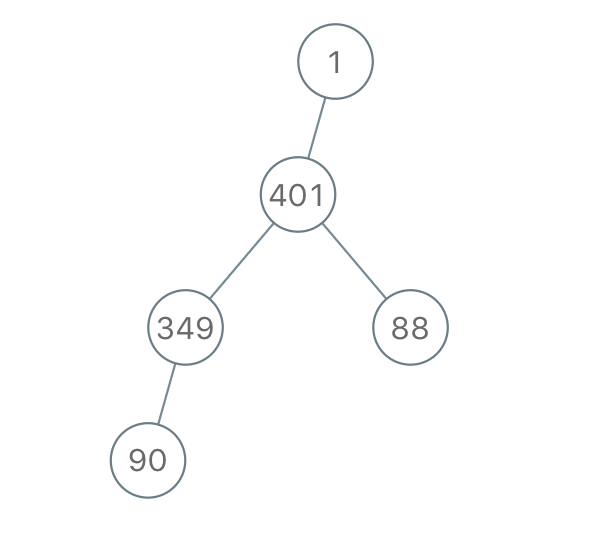
Input: "1-401--349---90--88"
Output: [1,401,null,349,88,90]
Note:
- The number of nodes in the original tree is between
1and1000. - Each node will have a value between
1and10^9.
这道题让我们根据一棵二叉树的先序遍历的结果来重建这棵二叉树,之前有过根据三种遍历方式-先序,中序,后序中的两个来重建二叉树 Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal 和 Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal,因为一种遍历方式得到的结点值数组是无法唯一的重建出一棵二叉树的。这里为了能够只根据先序遍历的结果来唯一的重建出二叉树,提供了每个结点值的深度,用短杠的个数来表示,根结点的深度为0,前方没有短杠,后面的数字前方只有一个短杠的就是根结点的左右子结点,然后紧跟在一个短杠后面的两个短杠的数字就是根结点左子结点的左子结点,以此类推。而且题目还说了,若某个结点只有一个子结点,那么一定是左子结点,这就保证了树结构的唯一性。其实这道题还是蛮有难度的,输入只给了一个字符串,我们不但要把结点值和深度分别提取出来,还要正确的组成树的结构。由于先序遍历的特点,左右子结点的位置可能相隔很远,就拿例子1来说吧,根结点1的左结点2是紧跟在后面的,但是根结点1的右子结点5却在很后面,而且有时候也不一定存在右子结点,博主刚开始想的是先查找右子结点的位置,然后调用递归,但是发现不好查找,为啥呢,因为 C++ 中好像没有 whole match 的查找功能,这里需要要查找一个杠,且前后位置都不能是杠,后来觉得若树的深度很大的话,这种处理方式貌似不是很高效。得换一个角度来想问题,我们在写非递归的先序遍历的时候,使用了栈来辅助遍历,这里同样也可以利用栈的后入先出的特点来做。
遍历输入字符串,先提取短杠的个数,因为除了根结点之外,所有的深度值都是在结点值前面的,所有用一个 for 循环先提取出短杠的个数 level,然后提取结点值,也是用一个 for 循环,因为结点值可能是个多位数,有了结点值之后我们就可以新建一个结点了。下一步就比较 tricky 了,因为先序遍历跟 DFS 搜索一样有一个回到先前位置的过程,比如例子1中,当我们遍历到结点5的时候,此时是从叶结点4回到了根结点的右子结点5,现在栈中有4个结点,而当前深度为1的结点5是要连到根结点的,所以栈中的无关结点就要移除,需要把结点 2,3,4 都移除,就用一个 while 循环,假如栈中元素个数大于当前的深度 level,就移除栈顶元素。那么此时栈中就只剩根结点了,就可以连接了。此时我们的连接策略是,假如栈顶元素的左子结点为空,则连在左子结点上,否则连在右子结点上,因为题目中说了,假如只有一个子结点,一定是左子结点。然后再把当前结点压入栈即可,字符串遍历结束后,栈中只会留有一个结点(题目中限定了树不为空),就是根结点,直接返回即可,参见代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* recoverFromPreorder(string S) {
vector<TreeNode*> st;
int i = 0, level = 0, val = 0, n = S.size();
while (i < n) {
for (level = 0; i < n && S[i] == '-'; ++i) {
++level;
}
for (val = 0; i < n && S[i] != '-'; ++i) {
val = 10 * val + (S[i] - '0');
}
TreeNode *node = new TreeNode(val);
while (st.size() > level) st.pop_back();
if (!st.empty()) {
if (!st.back()->left) st.back()->left = node;
else st.back()->right = node;
}
st.push_back(node);
}
return st[0];
}
};
虽然博主最开始想的递归方法不太容易实现,但其实这道题也是可以用递归来做的,这里我们需要一个全局变量 cur,表示当前遍历字符串S的位置,递归函数还要传递个当前的深度 level。在递归函数中,首先还是要提取短杠的个数,但是这里有个很 tricky 的地方,我们在统计短杠个数的时候,不能更新 cur,因为 cur 是个全局变量,当统计出来的短杠个数跟当前的深度不相同,就不能再继续处理了,如果此时更新了 cur,而没有正确的复原的话,就会出错。博主成功入坑,检查了好久才找出原因。当短杠个数跟当前深度相同时,我们继续提取出结点值,然后新建出结点,对下一层分别调用递归函数赋给新建结点的左右子结点,最后返回该新建结点即可,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* recoverFromPreorder(string S) {
int cur = 0;
return helper(S, cur, 0);
}
TreeNode* helper(string& S, int& cur, int level) {
int cnt = 0, n = S.size(), val = 0;
while (cur + cnt < n && S[cur + cnt] == '-') ++cnt;
if (cnt != level) return nullptr;
cur += cnt;
for (; cur < n && S[cur] != '-'; ++cur) {
val = 10 * val + (S[cur] - '0');
}
TreeNode *node = new TreeNode(val);
node->left = helper(S, cur, level + 1);
node->right = helper(S, cur, level + 1);
return node;
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/1028
类似题目:
Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/recover-a-tree-from-preorder-traversal/





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号