利用expect测试ssh是否可以连接
前言
SHELL功能强大,但是却无法执行交互操作,比如SSH的登录。
在利用SSH进行自动化部署的开发中,测试远程服务器是否可以进行SSH连接是非常重要的操作。
在这项功能的开发中,我们使用基于TCL的脚本编程工具语言Expect来实现。
Expect的安装
yum install -y expect离线安装需要下载
expect-5.45-14.el7_1.x86_64.rpm
tcl-8.5.13-8.el7.x86_64.rpm
Expect脚本
创建checkssh.exp文件,并键入以下内容
#!/usr/bin/expect
set timeout 10
set host [ lindex $argv 0 ]
set uname [ lindex $argv 1 ]
set upass [ lindex $argv 2 ]
spawn ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no $uname@$host echo "SSH Connected"
expect {
timeout {puts "Timeout happened";exit 1}
eof {puts "$uname Logined $host Faild"; exit 1}
"password:" {send $upass\n;send_user "\nNetwork Connected"; exp_continue}
"Connected" {puts "$uname Logined $host Successed"; exit 0}
}调用脚本进行SSH连接测试
#调用checkssh.exp,并输入参数IP,USER,PWD
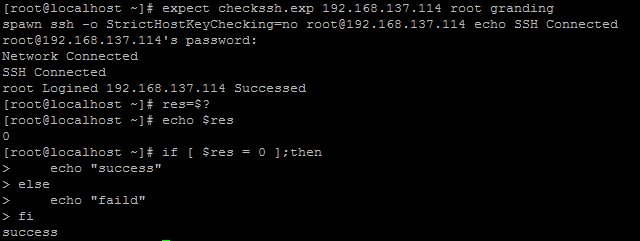
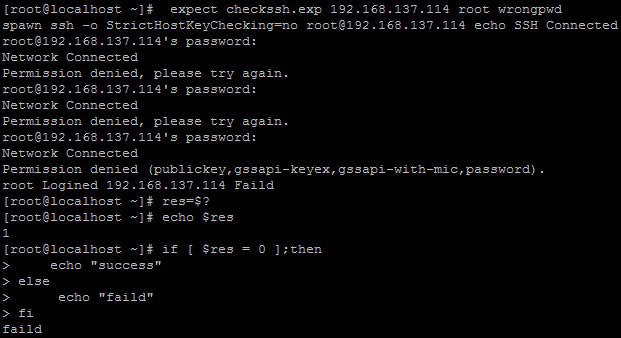
expect checkssh.exp 192.168.137.114 root granding
#执行完成后可调用$?系统变量判断连接状态
res=$?
#打印执行结果
echo $res
#可通过如下方式进行后续操作
if [ $res = 0 ];then
echo "success"
else
echo "faild"
fi密码正确
密码错误
将脚本嵌入SHELL中
新建脚本,并键入以下内容
#!/bin/bash
check_ssh(){
host=$1
uname=$2
upass=$3
expect <<EOF
set timeout 10
spawn ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no $uname@$host echo "SSH Connected"
expect {
timeout {puts "Timeout happened";exit 1}
eof {puts "$uname Logined $host Faild"; exit 1}
"password:" {send $upass\n;send_user "\nNetwork Connected"; exp_continue}
"Connected" {puts "$uname Logined $host Successed"; exit 0}
}
EOF
}
#调用check_ssh 并输入参数host,uname,upass
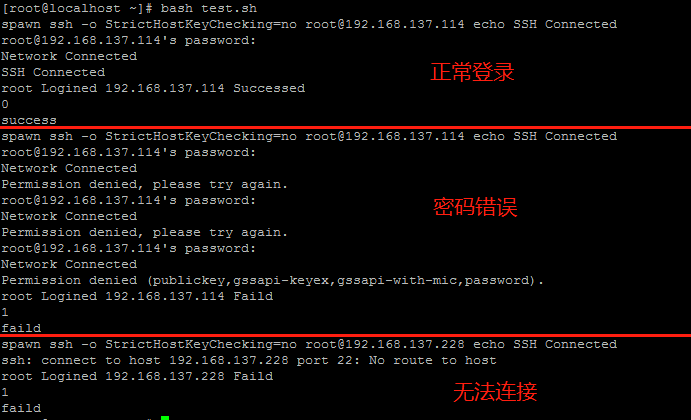
check_ssh 192.168.137.114 root granding
#执行完成后可调用$?系统变量判断连接状态
res=$?
#打印执行结果
echo $res
#可通过如下方式进行后续操作
if [ $res = 0 ];then
echo "success"
else
echo "faild"
fi
#输错密码的情况
#调用check_ssh 并输入参数host,uname,upass
check_ssh 192.168.137.114 root wrongpwd
#执行完成后可调用$?系统变量判断连接状态
res=$?
#打印执行结果
echo $res
#可通过如下方式进行后续操作
if [ $res = 0 ];then
echo "success"
else
echo "faild"
fi
#连接一个不存在的主机
#调用check_ssh 并输入参数host,uname,upass
check_ssh 192.168.137.228 root wrongpwd
#执行完成后可调用$?系统变量判断连接状态
res=$?
#打印执行结果
echo $res
#可通过如下方式进行后续操作
if [ $res = 0 ];then
echo "success"
else
echo "faild"
fi将check_ssh函数放入脚本中,正常调用即可
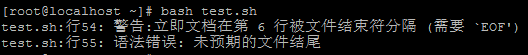
(注意:结尾的EOF前后不可有空格或其他字符,否则会报错)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号