2021牛客寒假算法训练营3题解(9/10)
2021牛客寒假训练营3题解
A.模数的世界
题目链接:A.模数的世界
相关:数论
参考题解:https://ac.nowcoder.com/discuss/594509?type=101&channel=-1&source_id=0
引用题解的结论(自己太菜,推不出来。。。):
对于最大值,可以猜想除非a == b == 0时最大值为0,此时x == y == p;否则最大值一定为p - 1
假设a >= b
-
当
b == 0 && a != 0时,x = (p - a) * (p - 1); y = (p - b) * (p - 1) -
当
a != 0 && b != 0时:由\(k_1 * (p-1) \% p = a\) 和\(k_2 * (p-1) \% p = b\) 可得
k1 = (p - a), k2 = (p - b)此时\(k_1 \leq k_2\),且\(k_1 和 k_2\)可能并不互质此时设
x = (m * p + k1) * (p - 1), y = k2 * (p - 1)注意到
k2!=0且 k2 必然和 p 互质,那么mp+nk2=1必有解。利用exgcd解出系数,并让m大于0,此时该式子等价于$ m*p\equiv1(mod\ k2) $。构造((k2 + 1 - k1) * m * p + k1) * (p - 1) = x, k2 * (p - 1) = y为解,可证满足上述方程,且二者gcd为p-1。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int t;
LL exgcd(LL a, LL b, LL &x, LL &y)
{
if(!b)
{
x = 1, y = 0;
return a;
}
int d = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y -= (a / b) * x;
return d;
}
int main()
{
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
LL a, b, p, ra, rb, k1, k2, x, y;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &a, &b, &p);
if(!a && !b) printf("0 %lld %lld\n", p, p);
else if(!a || !b)
{
ra = (p - a)*(p - 1);
rb = (p - b)*(p - 1);
printf("%lld %lld %lld\n", p - 1, ra, rb);
}
else
{
bool flag = false;
if(a < b) swap(a, b), flag = true;
k1 = p - a, k2 = p - b;
exgcd(p, k2, x, y);
if(x < 0) x = (x % k2 + k2) % k2;
ra = ((k2 + 1 - k1) * x * p + k1) * (p - 1);
rb = k2 * (p - 1);
if(flag) swap(ra, rb);
printf("%lld %lld %lld\n", p - 1, ra, rb);
}
}
return 0;
}
B.内卷
题目链接:B.内卷
相关:尺取法
待补。。。
C.重力坠击
题目链接:C.重力坠击
相关:搜索(DFS)、数学
题目数据不大,枚举每一个点,记录最大值即可。注意去重
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 11, M = 20;
int n, k, R, ans;
bool bat[N], back_bat[4][N];
struct Enemy
{
int x, y, r;
}e[N];
int check(int x, int y)
{
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if(!bat[i])
{
int a = e[i].x, b = e[i].y, r = e[i].r;
int dist = (a-x)*(a-x) + (b-y)*(b-y);
if(dist <= (r + R) * (r + R))
{
res++;
bat[i] = true;
}
}
return res;
}
void dfs(int num, int at)
{
if(num == k)
{
ans = max(ans, at);
return ;
}
for(int i = -7; i <= 7; i++)
for(int j = -7; j <= 7; j++)
{
memcpy(back_bat[num], bat, sizeof bat);
dfs(num+1, at + check(i, j));
memcpy(bat, back_bat[num], sizeof bat);
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> k >> R;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x, y, r;
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &r);
e[i] = {x, y, r};
}
dfs(0, 0);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
D. Happy New Year!
题目链接:D. Happy New Year!
签到题
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
string s;
int main()
{
int x;
cin >> x;
if(x % 10) cout << x-1+10 << endl;
else cout << (x/1000)*1000 + 100 + ((x % 100)/10 - 1) << endl;
return 0;
}
E.买礼物
题目链接:E.买礼物
相关:线段树
第一次线段树实战演练,掌握十分不牢靠
由题意分析可得:实际是要模拟一下链表的操作,用last[i]记录a[i]前面第一个等于自己的位置,不存在则置0;用ne[i]记录a[i]后面第一个等于自己的位置,不存在则置n+1。
对于购买操作:
void del(int x)
{
ne[last[x]] = ne[x];
last[ne[x]] = last[x];
last[x] = 0;
ne[x] = n+1;
}
对于询问操作:
查询区间[l, r]中最小的ne[i],判断其是否小于等于r,小于等于则输出1, 否则输出0。(也可以查询最大的last[i]是否大于等于l)
如果每次询问都是暴力查询,则会TLE, 所以要用到线段树维护区间的最小ne[],实现单点修改,区间查询。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5+10, M = 1e6+10, INF = 0X3f3f3f3f;
int n, q;
int a[N];
int last[N], ne[N], pos[M];
struct Node
{
int l, r, v;
}tr[4 * N];
void pushup(int u)
{
tr[u].v = min(tr[u << 1].v, tr[u << 1 | 1].v);
}
void build(int u, int l, int r)
{
tr[u] = {l, r};
if(l == r)
{
tr[u].v = ne[l];
return;
}
int mid = l + r >> 1;
build(u << 1, l, mid);
build(u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
pushup(u);
}
void modify(int u, int x, int v)
{
if(tr[u].l == x && tr[u].r == x) tr[u].v = v;
else
{
int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1;
if(x <= mid) modify(u << 1, x, v);
else modify(u << 1 | 1, x, v);
pushup(u);
}
}
int query(int u, int l, int r)
{
if(tr[u].l >= l && tr[u].r <= r) return tr[u].v;
int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1;
int v = INF;
if(l <= mid) v = query(u << 1, l, r);
if(r > mid) v = min(v, query(u << 1 | 1, l, r));
return v;
}
void del(int x)
{
ne[last[x]] = ne[x];
last[ne[x]] = last[x];
last[x] = 0;
ne[x] = n+1;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
last[i] = 0, ne[i] = n+1;
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
if(pos[a[i]])
{
last[i] = pos[a[i]];
ne[pos[a[i]]] = i;
}
pos[a[i]] = i;
}
build(1, 1, n);
/* puts("");
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++)
cout << tr[i].l <<',' << tr[i].r << ':' << tr[i].v << endl;*/
while(q--)
{
int op, x, l, r;
scanf("%d", &op);
if(op == 1)
{
scanf("%d", &x);
modify(1, x, n+1);
modify(1, last[x], ne[x]);
del(x);
}
else
{
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
printf("%d\n", query(1, l, r) <= r ? 1 : 0);
}
}
return 0;
}
F.匹配串
题目链接:F.匹配串
相关:字符串
因为每个字符串都至少含有一个'#',所以答案只有0和-1。
可以预处理出每个字符串第一个'#'的前缀和最后一个'#'的后缀,然后逐一比对,如果每个前后缀都是最长的那个前后缀的子串,那么答案为-1, 否则为0。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1e6+10;
int n;
string s[N];
int lma = 0, rma = 0;
vector<PII> l_r;
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> s[i];;
int a = 0, b = s[i].length() - 1;
for(int j = 0; j <= b; j++)
if(s[i][j] == '#')
{
a = j-1;
break;
}
for(int j = b; ~j; j--)
if(s[i][j] == '#')
{
b = b - j;
break;
}
l_r.push_back({a, b});
lma = max(lma, a);
rma = max(rma, b);
}
for(int i = 0; i <= lma; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++)
if(s[j][i] != s[j+1][i] && i <= l_r[j].first && i <= l_r[j+1].first)
{
cout << 0 << endl;
return 0;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= rma; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < n-1; j++)
if(s[j][s[j].length()-i] != s[j+1][s[j+1].length()-i] && i <= l_r[j].second && i <= l_r[j+1].second)
{
cout << 0 << endl;
return 0;
}
cout << -1 << endl;
return 0;
}
G.糖果
题目链接:G.糖果
相关:搜索(dfs、bfs)、连通块
根据题意将每个小朋友作为顶点,两人是朋友则连一条无向边,建图。题目即可转化为求每个连通块的点数和最大糖果数,答案即为:
\(\sum{点数*最大糖果数}\)
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
typedef long long LL;
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6+10;
int n, m, a[N];
int h[N], e[N*2], ne[N*2], idx;
bool st[N];
LL ans;
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx++;
}
void dfs(int x, int &ma, int &num)
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(x);
ma = max(a[x], ma);
num++;
st[x] = true;
while(q.size())
{
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(!st[j])
{
num++;
ma = max(ma, a[j]);
q.push(j);
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int u, v;
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
add(u, v), add(v, u);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int ma = 0, num = 0;
if(!st[i]) dfs(i, ma, num);
// cout << ma << ' ' << num << endl;
ans += (LL)ma * num;
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
H.数字串
题目链接:H.数字串
相关:字符串处理、模拟
考虑两种情况即可:字符是否可以拆分(如:k为11,可拆分为aa),两个字符是否可以合并(如:aa为11,可合并为k)
两种情况任意一种被执行一次即可
特别注意:10、20不可拆分,也不可参与合并
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
string s, t, ans;
bool ok;
string ctn(char c)
{
return to_string(c - 'a' + 1);
}
string ntc(string n)
{
string res = "";
res += 'a' + stod(n) - 1;
return res;
}
int main()
{
cin >> s;
int ls = s.length();
for(int i = 0; i < ls; i++)
{
if(!ok)
{
char c = s[i];
t += ctn(c);
// cout << c << ' ' << t << ' ' << ans << endl;
if(t.length() == 2 && (t[0]-'0') * 10 + (t[1]-'0') <= 26 && t[1] != '0')
{
//分
if(c > 'j')
{
string t0 = "", t1 = "";
t0 += t[0];
t1 += t[1];
ans += ntc(t0);
ans += ntc(t1);
// cout << "ok:" << ok << ' ' << t0 << ' ' << t1 << ' ' << ans << endl;
}
else ans += ntc(t); //合
ok = true;
}
else if(t.length() == 3 && t[2] != '0')
{
string t0 = "", t1 = "";
t0 += t[0];
t0 += t[1];
t1 += t[2];
// cout << t0 << ' ' << t1 << endl;
ans += ntc(t0);
ans += ntc(t1);
ok = true;
// cout << ok << ' ' << ans << endl;
}
else if(t[0] > '2' || t.length() == 2 && t[1] == '0')
{
ans += s[i];
t = "";
}
else if((t[0]-'0') * 10 + (t[1]-'0') > 26 || t.length() == 3 && t[2] == '0')
{
ans += s[i-1];
ans += s[i];
t = "";
}
}
else ans += s[i];
}
// cout << ok << endl;
if(ok) cout << ans << endl;
else cout << -1 << endl;
return 0;
}
I.序列的美观度
题目链接:I.序列的美观度
相关:动态规划、优化
感觉和最长上升子序列很像,然后推出来的DP做法是对的,但是时间复杂度为O(N2),很明显超时了,需要优化
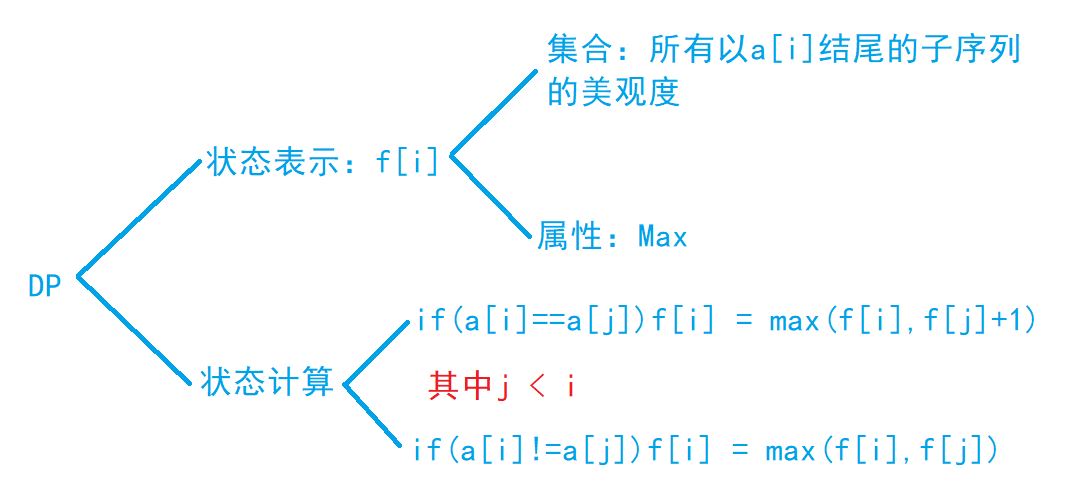
对于两种情况:
a[i] != a[j]:f[i] = max(f[i], f[j]),是用f[1]~f[i-1]中的最大值来更新f[i], 所以在求每个f[i]的时候可以用一个ma变量来存最大值,这样状态转移方程即可变为:f[i] = maa[i] == a[j]:f[i] = max(f[i], f[j]+1),这里可以直接去a[i]前最后一个与其相等的位置的f[j]来更新,然后我们可以通过一个pos[]数组来记录前一个和当前位置值相等的位置,这样状态转移方程即可变为:f[i] = max(ma, f[pos[a[i]]] + 1)
经过这两个优化,时间复杂度变为O(n)
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6+10;
int n, ans;
int a[N], pos[N], f[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
int ma = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
if(!pos[a[i]]) f[i] = ma;
else f[i] = max(f[pos[a[i]]] + 1, ma);
ma = max(ma, f[i]);
pos[a[i]] = i;
}
cout << ma << endl;
return 0;
}
J.加法和乘法
题目链接:J.加法和乘法
相关:博弈论、找规律
- 对加法:奇数+奇数=偶数,奇数+偶数=奇数,偶数+偶数=偶数
- 对乘法:奇数*奇数=奇数,奇数*偶数=偶数,偶数*偶数=偶数
关键在于最后一次操作,如果n为奇数,则n-1为偶数,牛妹进行最后一次,反之牛牛进行最后一次操作
首先,对于以后一次操作,无论剩余的两个数的奇偶性,一定可以变成一个偶数,所以如果牛妹是最后一次操作(n为奇数)则必赢
对于牛牛最后一次操作(n为偶数),当且仅当最后两个数至少有一个奇数时,牛牛才能赢。所以对于牛妹,最优策略是想办法把奇数全部消去;对牛牛,最优策略是想办法保留至少一个奇数。根据上面的加乘法规律可得,奇数可以消去但无法增加,最多可以一次消去2个。
在n为偶数的情况下,牛妹一共可以操作\((n-2)/2\)次,在不考虑奇偶数个数的情况下,牛妹最多只能消去n-2个奇数,所以当给出的数中奇数个数大于n-2时,牛牛可以获胜。
注意特判n=1的情况。
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n, ji;
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
if(x & 1) ji++;
}
if(n == 1 && ji || !(n&1) && ji > n-2) puts("NiuNiu");
else puts("NiuMei");
return 0;
}

