2021牛客寒假算法训练营1题解(9/10)
2021牛客寒假训练营1题解
A、串
题目链接:A.串
相关:DP、快速幂
解法一:
f[i]:长度为i的含“us”的字符串个数
- 前
i-1个字符中含"us":26 * f[i-1] - 前
i-1个字符中含"u"不含"us":总数 - 不含"u"的 - 含"us"的 = \(26^{i-1}-25^{i-1}-f[i-1]\)
综上:$ f[i] = 26^{i-1} - 25^{i-1} + 25 * f[i-1]$
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e6+10, mod = 1e9+7;
int n;
long long a[N], ans = 1;
long long quick_pow(int a, int b)
{
long long res = 1;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1) res = res * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
a = (long long)a * a % mod;
}
return res % mod;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
a[2] = 1;
for(int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
{
//暂时不明白为什么要加一个mod
a[i] = (quick_pow(26, i-1) - quick_pow(25, i-1) + 25*a[i-1] + mod) % mod;
ans = (ans + a[i]) % mod;
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
解法二:
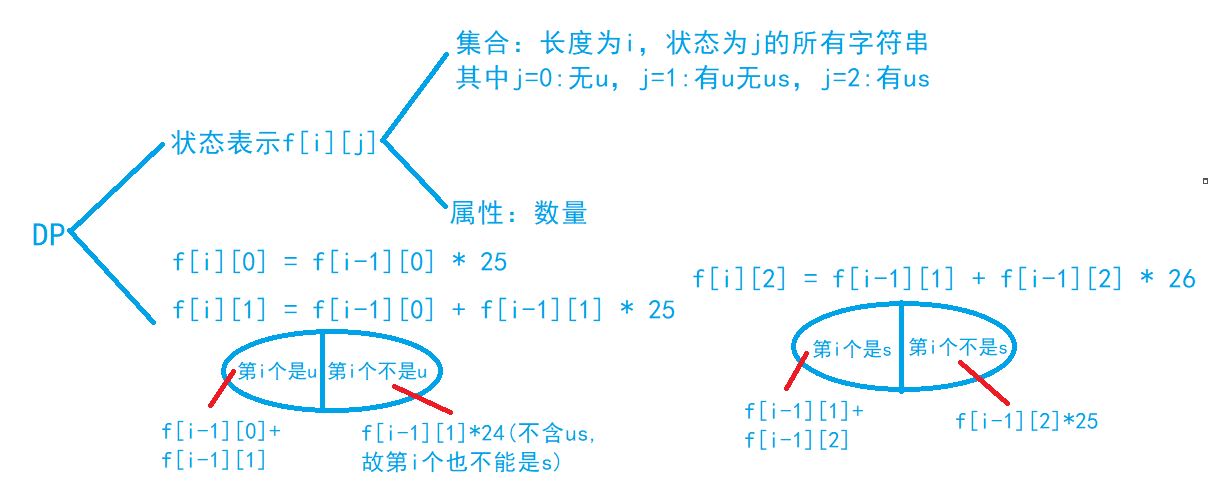
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e6+10, mod = 1e9+7;
int n;
long long ans, f[N][3];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
f[1][0] = 25;
f[1][1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
f[i][0] = (f[i-1][0] * 25) % mod;
f[i][1] = (f[i-1][0] + f[i-1][1] * 25) % mod;
f[i][2] = (f[i-1][1] + f[i-1][2] * 26) % mod;
ans = (ans + f[i][2]) % mod;
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
B、括号
题目链接:B.括号
相关:找规律、构造
写几对括号可以发现:
() :1 = 1
()() :3 = 2 + 1
()()():6 = 3 + 2 + 1
......
进一步观察可以发现:在第i对括号后面加1个')', 括号的数量就会加i .
由此导出做法:
- 预处理出画几对括号会生成多少对括号:
a[i] = 1 + 2 + ... + i - 二分出小于等于k的最大
a[l] - 为了尽量让总长度短一些,倒序求出需要在第i对括号后面添加
rk[i]个')' - 输出答案
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e4+10;
int a[N], rk[N];
int main()
{
int k;
cin >> k;
//预处理
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) a[i] = a[i-1] + i;
//二分
int l = 0, r = N;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;
if(a[mid] <= k) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
//倒序求需添加的')'数量
int num = k - a[l];
for(int i = l; i && num; i--)
{
rk[i] = num / i;
num = max(0, num - i * (num / i));
}
//按题意输出答案
if(k)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= l; i++)
{
printf("()");
// cout << rk[i] << endl;
for(int j = 1; j <= rk[i]; j++) printf(")");
}
puts("");
}
else cout << "(" << endl;
return 0;
}
C、红和蓝
题目链接:C.红和蓝
参考题解:https://blog.nowcoder.net/n/32e7a9e7caa3422286109ab0b3fabf37
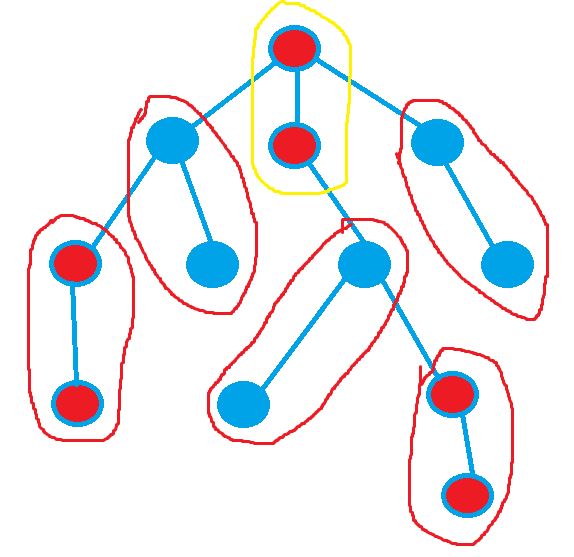
题意:给一颗树的节点染红蓝两种色,满足每个节点的相邻节点有且仅有一个节点的颜色和当前节点相同
首先考虑最特殊的节点——叶子节点,与叶子节点相邻的仅有其父节点一个节点,所以叶子节点一定和其父节点颜色相同。
将所有的叶子节点和其父节点标记后,剩余的树又会出现新的叶子结点,重复步骤使整棵树全部被标记,然后根据标记是否相同染上相应的颜色。
如果出现标记时父节点已经被标记(重复标记)或者仅有根节点一个节点则无法完成染色。
解法:两遍dfs(), 第一遍打标记,第二遍染颜色
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5+10;
int n;
int h[N], e[2 * N], ne[2 * N], idx;
//f[]:标记,color[]:颜色(1:R, 2:B)
int f[N], color[N], cnt;
bool flag = true;
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx++;
}
//第一遍dfs给所有点打上标记
//参数:x-当前节点,fa-当前节点的父节点
void dfs1(int x, int fa)
{
//记录儿子数量
int son = 0;
//遍历所有儿子
for(int i = h[x]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
//由于是双向边,“父节点也在儿子节点中”,特殊处理去掉
if(j == fa) continue;
son++;
dfs1(j, x);
}
//如果当前节点是叶子节点(儿子数量为0),或者当前节点并没有被标记
if(!son || !f[x])
{
//如果父节点已经有标记了,说明不可能完成染色
if(f[fa])
{
flag = false;
return;
}
//给当前节点和父节点打上相同的标记
f[x] = f[fa] = ++cnt;
}
}
//如果顺利给所有点打上标记,则第二遍dfs根据标记涂上颜色
//参数:x-当前节点,fa-当前节点的父节点
void dfs2(int x, int fa)
{
//遍历儿子节点
for(int i = h[x]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
//去掉儿子节点中的父节点
if(j == fa) continue;
//如果当前节点和子节点标记相同,则染上相同的颜色
//否则染上不同的颜色
if(f[j] == f[x]) color[j] = color[x];
else color[j] = color[x] ^ 1;
dfs2(j, x);
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for(int i = 0; i < n-1; i++)
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
add(a, b), add(b, a);
}
dfs1(1, 0);
if(f[0] != 0 || !flag)
{
cout << -1 << endl;
return 0;
}
color[1] = 1;
dfs2(1, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if(color[i] == 1) printf("R");
else printf("B");
return 0;
}
D、点一成零
题目链接:D.点一成零
参考题解:https://blog.nowcoder.net/n/4e45b3189c564001b186775f7ea43ec4
相关:维护size的并查集、快速幂求逆元
在初始状态下:有x个连通块,如果每个连通块只能点1个,总共有x!种, 而每个连通块有size个可以点,所以$ans = x! * (每个连通块1的个数的乘积) $
对于每次操作:
-
如果当前位置已经是‘1’,矩阵和答案均不会发生改变
-
如果当前位置是‘0’,先假设其是一个单独的连通块cnt++,先行更新答案$ ans = ans * cnt * 1$, 然后检查与其相邻的四个位置
-
如果该位置不是1,无影响
-
如果该位置是1,且与当前点已经在并查集的同一个连通块中了,无影响
-
如果该位置是1,且与当前点不在并查集的同一个连通块中,则要把当前点和该位置的连通块合并,更新答案:
连通块数量-1:\(ans = (ans / cnt) \% mod\) (分数取模),注意
cnt--将两个连通块的大小除去:\(ans = ans / size1,ans = ans / size2\)
将新的连通块大小乘进去:\(ans = ans * (size1 + size2)\)
-
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
typedef long long LL;
using namespace std;
const int N = 510, mod = 1e9+7;
int n, k;
char g[N][N];
int p[N*N], s[N*N];
int dx[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1}, dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
//快速幂,求逆元,用于分数取模
LL quick_pow(int a, int b)
{
LL res = 1;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1) res = (res * a) % mod;
b >>= 1;
a = (LL)a * a % mod;
}
return res;
}
//并查集操作
int find(int x)
{
if(p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
//并查集合并操作
void merge(int x, int y)
{
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
if(fx != fy) p[fx] = fy, s[fy] += s[fx];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
//下标从1开始,因为需要映射坐标到数字:x * n + y
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> g[i]+1;
n++;//映射的数最大为:n*n+n > n^2, n+1后映射最大为n*(n+1)+n < (n+1)^2
//初始化并查集
for(int i = 1; i <= n*n; i++)
{
p[i] = i;
s[i] = 1;
}
//遍历整个矩阵,将'1'的连通块通过并查集合并
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++)
if(g[i][j] == '1')
{
if(g[i+1][j] == '1') merge(i*n+j, (i+1)*n + j);
if(g[i-1][j] == '1') merge(i*n+j, (i-1)*n + j);
if(g[i][j+1] == '1') merge(i*n+j, i*n + j + 1);
if(g[i][j-1] == '1') merge(i*n+j, i*n + j - 1);
}
//遍历并查集,计算初始答案,并记录初始连通块数量cnt
int cnt = 0;
LL ans = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++)
if(p[i*n+j] == i*n+j && g[i][j] == '1')
{
cnt++;
ans = (ans * s[i*n+j]) % mod;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) ans = (ans * i) % mod;
//处理每个询问
cin >> k;
while(k--)
{
int x, y;
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
x++, y++;//坐标相应+1
//如果当前更改的位置已经为'1'则直接输出答案
if(g[x][y] == '1')
{
cout << ans << endl;
continue;
}
//当前位置不是'1',变为1,假设是单独的连通块,先更新答案
g[x][y] = '1';
cnt++;
ans = (ans * cnt) % mod;
//遍历与当前位置连通的4个位置
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int xx = x + dx[i], yy = y + dy[i];
int f1 = find(x * n + y);
//如果是'1',且在并查集中不在同一个连通块中,更新答案,并将其连通
if(g[xx][yy] == '1')
{
int f2 = find(xx * n + yy);
if(f1 != f2)
{
ans = ans * quick_pow(cnt, mod-2) % mod;
ans = ans * quick_pow(s[f1], mod-2) % mod;
ans = ans * quick_pow(s[f2], mod-2) % mod;
ans = ans * (s[f1] + s[f2]) % mod;
merge(f1, f2);
cnt--;
}
}
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
E、三棱锥之刻
题目链接:E.三棱锥之刻
相关:立体几何
因为是正三棱锥,所以求出1面的面积,乘4即可
对一个面: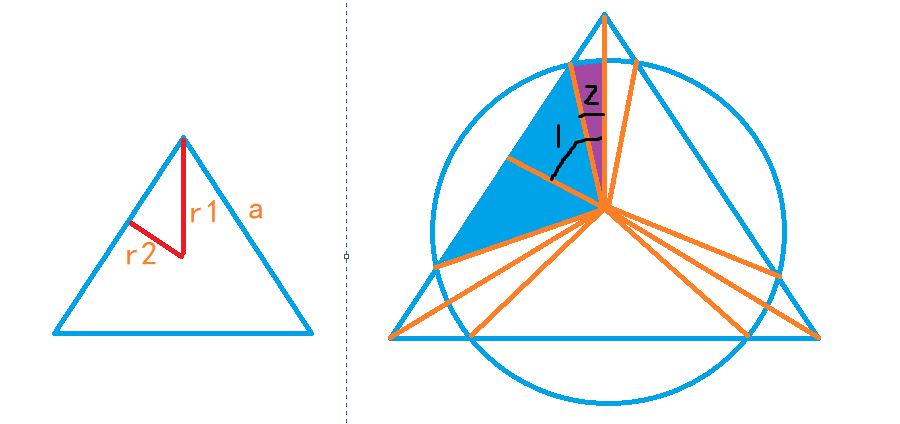
首先计算几个要用到的数据:
- 中心到面的距离$ h = \sqrt[2]{6} * a / 12$
- $ r1 = (a * cos30^\circ) / 2 = \sqrt[2]{3} * a / 3$
- \(r2 = r1 / 2 = \sqrt[2]{3} * a / 6\)
- 从中心可以够着的区域(圆)的半径$ R = \sqrt[2]{r^2 - h^2}$
分四种情况:
-
当$ r \leq h$ 时:无法够到四个面,面积为0
-
当\(r \geq h 且 R \leq r2\)时:够着的区域为三角形内部的整圆,\(s = \pi * R^2 = \pi * \sqrt[2]{r^2 - h^2}\)
-
当\(R \geq r1\)时:所有区域都能够着,\(s = a^2 * \sqrt[2]{3} / 4\)
-
当\(r2 < R < r1\)时:够着的区域为3个图中的蓝色三角形+6个图中的紫色扇形
$ ssan(三角形面积) = 底边*(r2) /2 = r2 * \sqrt[2]{r^2 - h^2 - (r2)^2}$
\(angle(扇形弧度) = \pi / 3 - acos((r2) / R)\)
\(sshan(扇形面积) = l*R / 2 = angle * R^2 /2\)
\(s = 3 * ssan + 6 * sshan\)
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const double pi = 3.1415926;
double a, r, h, r1, r2, R;
int main()
{
cin >> a >> r;
h = a * sqrt(6) / 12.0;
r1 = a * sqrt(3) / 3.0;
r2 = a * sqrt(3) / 6.0;
R = sqrt(r * r - h * h);
if(r <= h) cout << 0 << endl;
else if(r > h && R <= r2)
{
double s = pi * (r * r - h * h);
printf("%.5lf\n", 4 * s);
}
else if(R >= r1)
{
double s = sqrt(3) * a * a / 4;
printf("%.5lf\n", 4 * s);
}
else
{
double ssan = sqrt(r*r - h*h - r2*r2) * r2;
double angle = pi / 3 - acos(r2 / R);
double sshan = angle * R * R / 2.0;
double s = 3 * ssan + 6 * sshan;
printf("%.5lf\n", 4 * s);
}
return 0;
}
F、对答案一时爽
题目链接:F.对答案一时爽
相关:签到题
分析题意可得:两人均全错时分数最低为:0,当一人全对时最高分为:n + same
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int n, same;
char a[N], b[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> b[i];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) if(a[i] == b[i]) same++;
cout << n + same << ' ' << 0 << endl;
return 0;
}
G、好玩的数字游戏
题目链接:G.好玩的数字游戏
相关:大模拟
待补。。。。。。
H、幂塔个位数的计算
题目链接:H.幂塔个位数的计算
参考题解:https://blog.nowcoder.net/n/d4fef62909f2421890d32c00d1403c0c
相关:找规律
写数据找规律:
对a^i:枚举a的不同个位数对不同i的结果的个位数
0:{0} 0 0 ...... 5:{5} 5 5 ......
1:{1} 1 1 ...... 6:{6} 6 6 ......
2:{2 4 8 6} 2 4 8 6 ...... 7:{7 9 3 1} 7 9 3 1 ......
3:{3 9 7 1} 3 9 7 1 ...... 8:{8 4 2 6} 8 4 2 6 ......
4:{4 6} 4 6 ...... 9:{9 1} 9 1 ......
-
对a的个位数是2的,循环节为4
对\(a^a\): 若\(a\%4 == 2\) —— 4;若\(a\%4 == 0\) —— 6;
对\(a^{a^a}\): 因为\(a = 10x+2\),为偶数,偶数个2相乘 % 4 == 偶数个0相乘 % 4== 0 —— 6。
-
对a的个位数是8的,循环节为4
对\(a^a\): 若\(a\%4 == 2\) —— 4;若\(a\%4 == 0\) —— 6;
对\(a^{a^a}\): 因为\(a = 10x+8\),为偶数,偶数个2相乘 % 4 == 偶数个0相乘 % 4 == 0 —— 6。
-
对a的个位数是的3,循环节为4
对\(a^a\): 若\(a\%4 == 3\) —— 7;若\(a\%4 == 1\) —— 3;
对\(a^{a^a}\): 因为\(a = 10x+3\),为奇数,奇数个3相乘 % 4 == 3——7,偶数个1相乘 % 4 == 1 —— 3。
-
对a的个位数是的7,循环节为4
对\(a^a\): 若\(a\%4 == 3\) —— 3;若\(a\%4 == 1\) —— 7;
对\(a^{a^a}\): 因为$a = 10x+$7,为奇数,奇数个3相乘 % 4 == 3——3,偶数个1相乘 % 4 == 1 —— 7。
-
对a的个位数是的4,循环节为2
对\(a^a\): 若\(a\%2 == 0\) —— 6;
对\(a^{a^a}\): 因为\(a = 10x+4\),为偶数,偶数个0相乘 % 2 == 0——6。
-
对a的个位数是的9,循环节为2
对\(a^a\): 若$a%2 == $1 —— 9;
对\(a^{a^a}\): 因为\(a = 10x+9\),为奇数,奇数个1相乘 % 2 == 1——9。
综上所述:
对a的个位数是0、1、5、6、9的,幂塔个位数都为a本身的个位数
对a的个位数是4的。幂塔个位数均为6
对a的个位数是2、8的,若幂塔层数为2,则由a%4的结果决定(0-6, 2-4);若层数大于2,则个位数均为6
对a的个位数是3的,无论幂塔层数,个位数仅由a%4的结果决定(3-7, 1-3)
对a的个位数是3的,无论幂塔层数,个位数仅由a%4的结果决定(3-3, 1-7)
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5+10;
char s1[N], s2[N];
int main()
{
cin >> s1+1 >> s2+1;
s1[0] = '0', s2[0] = '0';
int l1 = strlen(s1), l2 = strlen(s2);
//a:个位数
int a = s1[l1 - 1] - '0';
//b:a%4
int b = ((s1[l1 - 2] - '0') * 10 + (s1[l1 - 1] - '0')) % 4;
int n = s2[l2 - 1] - '0';
//当n == 1的时候,直接输出a,记得结束程序
if(l2 == 2 && n == 1) {cout << a << endl; return 0;}
if(a == 0 || a == 1 || a == 5 || a == 6 || a == 9) cout << a << endl;
if(a == 4) cout << 6 << endl;
if(a == 2 || a == 8)
if(l2 == 2 && n == 2 && b) cout << 4 << endl; //n==2且a%4==2时
else cout << 6 << endl;
if(a == 3)
if(b == 1) cout << 3 << endl;//a%4 == 1时
else cout << 7 << endl;
if(a == 7)
if(b == 1) cout << 7 << endl;//a%4 == 1时
else cout << 3 << endl;
return 0;
}
I、限制不互素对的排列
题目链接:I.限制不互素对的排列
相关:找规律、构造
由题意可得出的性质:
- 当所有偶数连续排列时,可以构成含
n/2 - 1对相邻且gcd > 1的排列 - 要求最大值为
n/2对,而满足gcd(奇数,偶数) > 1的最小数对为(6, 3),故可将6放置偶数末尾,当对数不够时再将3放置在6后面 - 将剩余的数从大到小依次排列即可
- 由2可导出:当
n < 6 && (n / 2 - 1) < k时,无法构造
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5+10;
int n, k;
bool st[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> k;
if(n < 6 && n / 2 - 1 < k) cout << -1 << endl;
else
{
int i = 2, j = 0;
for(i = 2, j = 0; i <= n && j <= k; i += 2)
if(i != 6)
{
printf("%d ", i);
st[i] = true;
j++;
}
if(j < k + 1)
{
printf("6 ");
st[6] = true;
j++;
}
if(j < k + 1)
{
printf("3 ");
st[3] = true;
}
int t = 1;
while(t <= n) if(!st[t++]) printf("%d ", t-1);
}
return 0;
}
J、一群小青蛙呱嘣呱嘣呱
题目链接:J.一群小青蛙呱嘣呱嘣呱
题解参考:https://blog.nowcoder.net/n/96ba5fe158194f0a8e37bd6e767ee0e2
相关:线性筛法、最小公倍数、快速幂
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <math.h>
typedef long long LL;
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e8+10, mod = 1e9+7;
int n;
int primes[N], cnt;
bool st[N];
LL quick_pow(int a, int b)
{
LL ans = 1;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1) ans = ans * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
a = (LL)a * a % mod;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
LL ans = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n / 2; i++)
{
if(!st[i])
{
primes[cnt++] = i;
if(i == 2) ans = (ans * quick_pow(2, floor(log(n/3) / log(2)))) % mod;
else ans = (ans * quick_pow(i, floor(log(n/2) / log(i)))) % mod;
}
for(int j = 0; primes[j] <= n / (2 * i); j++)
{
st[primes[j] * i] = true;
if(i % primes[j] == 0) break;
}
}
if(ans == 1) puts("empty");
else cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}


