模板、知识点积累
模板、知识点基积累
一、读入字符串
inline string read()
{
char ch=getchar();
string st1="";
while (!(ch>='a' && ch<='z' || ch>='0' && ch <= '9' || ch >= 'A' && ch<='Z'))
ch=getchar();
while (ch>='a' && ch<='z' || ch>='0' && ch <= '9' || ch >= 'A' && ch<='Z')
st1+=ch,ch=getchar();
return st1;
}
二、读入数字
inline long long read()
{
long long x = 0, f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9')
{
if(ch == '-') f=-1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9')
{
x = ( x << 1 ) + ( x << 3 ) + ( ch ^ 48 );
ch = getchar();
}
return x * f;
}
三、字符串去空格+查找
string s;
getline(cin, s);
int index = 0;
//去空格
while( (index = s.find(' ',index)) != string::npos) s.erase(index,1);
//查找
if(s.find("***", 0) != string::npos)
{
}
四、求全排列函数
计算序列全排列的函数:
next_permutation(start, end)\\求当前排列的下一个排列prev_permutation(start, end)\\求当前排列的上一个排列
对于next_permutation()函数,其函数原型为:
#include <algorithm>
bool next_permutation(iterator start,iterator end)
//当当前序列不存在下一个排列时,函数返回false,否则返回true
//到达最大排列后,返回false,序列变为最小排列
对于next_permutation()函数,其函数实现原理为:
- 从后往前找到第一个a[k] < a[k+1]的位置k
- 在a[k+1] ~ a[n]中找到大于a[k]的最小的数a[t]
- 交换a[k]、a[t], 可以发现交换后:a[k+1] ~ a[n]仍是单调递减的
- 将a[k+1] ~ a[n]翻转
代码:
int k = n - 2;
while(a[k] > a[k+1]) k--;
int t = k + 1;
while(t + 1 < n && a[t+1] > a[k]) t++;
swap(a[t], a[k]);
reverse(a + k + 1, a + n);
五、对数计算
对数换底公式: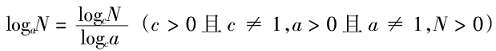
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double a=2; //以2为底
cout << log(4)/log(a)<<endl;
return 0;
}
exp(n)值为e^n次方;
另外log函数包括两种函数 一种以e为低的log()函数
另一种为以10为底的log10()函数;
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double a=9,b=10;
cout<<log(a)<<endl;
cout<<log(exp(a))<<endl;
cout<<log10(b)<<endl;
return 0;
}


