React Native入门 认识Flexbox布局
Flexbox布局是由W3C在09年提出的在Web端取代CSS盒子模型的一种布局方式。
ReactNative实现了Flexbox布局的大部分功能。
Flexbox布局所使用的属性,基本可以分为两大类:
- 决定子组件排列规则的属性,例如:flexDirection , flexWrap, justifyContent, alignItems等。
- 决定自身的显示规则的属性,例如:alignSelf, flex等
[1] flexDirection
设置子组件的排列顺序,默认column(纵向排列),其他row(横向排列)
代码:
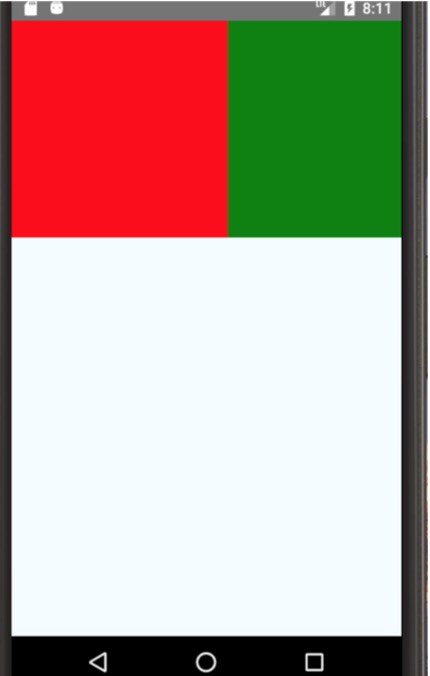
type Props = {}; export default class App extends Component<Props> { render() { return ( <View style={styles.container}> <View style={styles.view1}></View> <View style={styles.view2}></View> </View> ); } } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, //justifyContent: 'center', //alignItems: 'center', flexDirection: 'row', //这里显式声明为row,将横向排列,否则默认纵向排列 backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF', }, welcome: { fontSize: 20, textAlign: 'center', margin: 10, }, instructions: { textAlign: 'center', color: '#333333', marginBottom: 5, }, view1: { height: 150, width: 150, backgroundColor: 'red' }, view2: { height: 150, width: 150, backgroundColor: 'green' } });
如图:

[2]flexWrap
设置是否换行,默认值nowrap(不换行),其他wrap
当我们将两个子View的宽换为200时,绿框将溢出屏幕,而只显示一半
view1: { height: 200, width: 200, backgroundColor: 'red' }, view2: { height: 200, width: 200, backgroundColor: 'green'
如图:
将container样式改为wrap, 溢出的绿框将会另起一行。

[3] justifyContent
justifyContent 属性表示该组件的子组件横向排列的其父容器的哪个位置。
取值有:flex-start, flex-end, center, space-between, space-around
container: { flex: 1, //justifyContent: 'center', //alignItems: 'center', flexDirection: 'row', flexWrap: 'wrap', justifyContent: 'space-around', //修改的这一行 backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF', },
flex-start:贴左
flex-end: 贴右
center: 子组件群横向居中
space-between:空白在子组件中间
space-around:空白在子组件周围(每个子组件的两边)
[4] alignItems
属性表示该组件的子组件纵向排列的其父容器的哪个位置。
取值:flex-start, flex-end, center, baseline, stretch
center: 子组件群父容器的纵向向居中
flex-start:贴父容器顶
flex-end: 贴父容器底
baseline:现象与flex-start一致(待补)
stretch: 现象与flex-start一致(待补)
[5] alignSelf
表明某个特定组件的排列情况
取值:flex-start, flex-end, center, stretch
center: 当前组件基于父组件的布局后进行居中(父布局时横向排列,则纵向居中;横向排列,则纵向居中)
flex-start:当前组件基于父组件的布局后进行贴左(同上)
flex-end:当前组件基于父组件的布局后进行贴右(同上)
[6] flex
flex属性可以让组件动态的去计算和配置自己所占用的空间大小,取值是数值
代码:
container: { flex: 1, //这个父布局的flex必须要,它代表的是它在其父布局的比重,没有将是一片空白 backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF', }, welcome: { fontSize: 20, textAlign: 'center', margin: 10, }, instructions: { textAlign: 'center', color: '#333333', marginBottom: 5, }, view1: { flex: 1, backgroundColor: 'red' }, view2: { flex: 1, backgroundColor: 'green' }
结果:

可以看出flex,类似与Android 的weight(比重),将父布局的子布局的flex元素取出对比来计算出其实际大小。
当将绿色组件的flex属性改为2时,绿组件占父布局的三分之二,可见flex越大,所占父布局的空间越大
本文作者:明月照江江
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/gradyblog/p/8981604.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】