OO-封装,继承,多态,抽象
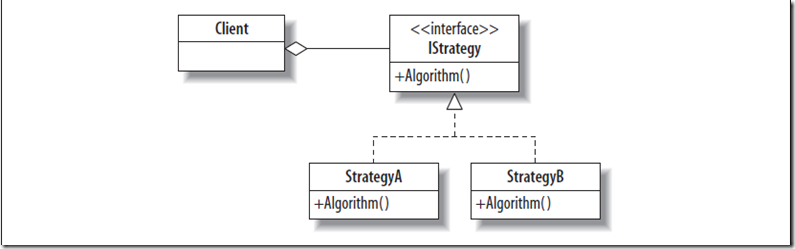
策略模式-strategy
c# 3.0 design patterns
Func和Action http://www.cnblogs.com/jams742003/archive/2009/10/31/1593393.html
Func<int ,bool> d= x=>x >10?true:false;
int? Nullable<int> hasvalue
To convert back to a non-nullable type, use the as operator. as will return null if it cannot convert the value. For example, int? val = DateTime.Now as int?;
Use the Strategy pattern when…
• Many related classes differ only in their behavior.
• There are different algorithms for a given purpose, and the selection criteria can be codified.
• The algorithm uses data to which the client should not have access.
装饰模式(Decorator)
动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责,就增加功能来说,装饰模式比生成子类更为灵活[DP]
The role of the Decorator pattern is to provide a way of attaching new state and behavior to an object dynamically.
The object does not know it is being “decorated,” which makes this a useful pattern for evolving systems.
A key implementation point in the Decorator pattern is that decorators both inherit the original class and contain an instantiation of it.
Given that the number of ways of decorating photos is endless, we can have many such new objects.
The beauty of this pattern is that:
• The original object is unaware of any decorations.
• There is no one big feature-laden class with all the options in it.
• The decorations are independent of each other.
• The decorations can be composed together in a mix-and-match fashion.
The Decorator pattern’s key feature is that it does not rely on inheritance for extending behavior.
作者:gracestoney
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/gracestoney/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
该文章也同时发布在我的csdn博客中-Gracestoney。