性能战术的目标:对一定时间限制内到达系统的事件生成一个响应,这些事件可以是消息到达、定时器到时,系统状态的变化。
通俗来讲,就是减少系统的响应时间,减少空间的消耗

性能战术的分类以及基本的方法
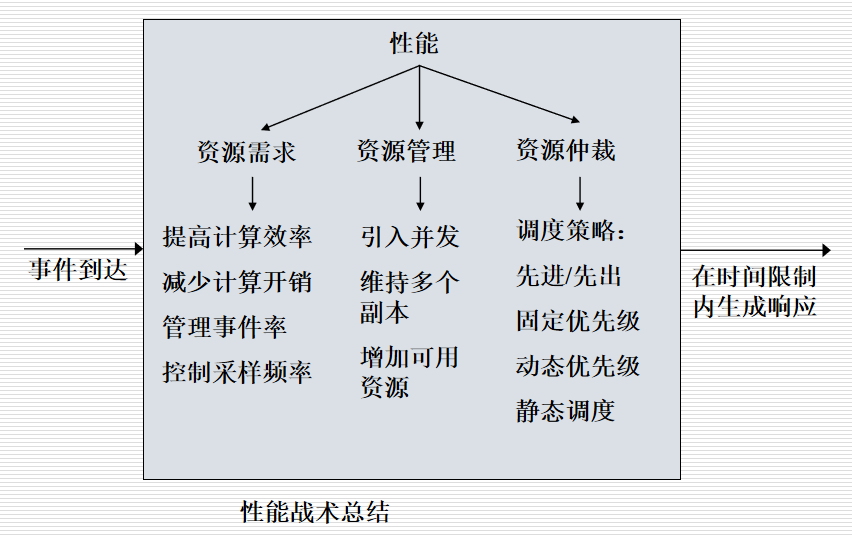
1.资源需求
- 减少处理一个事件流所需要的资源
- 提高计算效率,如改进关键算法
- 减少计算开销,比如保存上次计算
- 减少所处理事件的数量
- 管理事件率,减少需求
- 控制采样频率
-
 减少对变量的重复计算
减少对变量的重复计算for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {...} //替换为: for (int i = 0, length = list.size(); i < length; i++) {...}
- 控制资源的使用
- 限制执行时间
-
 超时
超时import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import com.sun.corba.se.impl.orbutil.closure.Future; import com.sun.corba.se.impl.orbutil.threadpool.TimeoutException; public class ThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { final ExecutorService exec = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1); Callable<String> call = new Callable<String>() { public String call() throws Exception { //开始执行耗时操作 Thread.sleep(1000 * 5); return "线程执行完成."; } }; try { Future<String> future = exec.submit(call); String obj = future.get(1000 * 1, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); //任务处理超时时间设为 1 秒 System.out.println("任务成功返回:" + obj); } catch (TimeoutException ex) { System.out.println("处理超时"); ex.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("处理失败."); e.printStackTrace(); } // 关闭线程池 exec.shutdown(); } }
-
- 限制队列大小,控制处理事件的数量
- 限制执行时间
针对这个问题,在之前的热词分析项目中,把首页直接表格显示所有数据库内容,改成了分页显示,并且跳页才查询,只查询当前页的记录

<table border="1" cellpadding="3" cellspacing="0" style="width: 80%;margin:auto">
<tr>
<td style="width:40px">序号</td>
<td style="width:40px">热词</td>
<td>热词解释</td>
<td>内容链接</td>
</tr>
<% List<WordBean> list = dao.select_page(pages,limit);
//List<WordBean> list =(List<WordBean>)session.getAttribute("list");
for(WordBean n:list){ %>
<tr>
<td><%=n.getId() %></td>
<td><%=n.getWord() %></td>
<td><%=n.getExplain() %></td>
<td><a href='<%=n.getLink() %>'><%=n.getLink() %></a></td>
</tr>
<%} %>
</table>

<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@page import="com.bean.WordBean" %> <%@page import="com.dao.WordDao" %> <%@page import="java.util.List" %> <%@page import="java.util.ArrayList" %> <% WordDao dao = new WordDao(); int pages=0; //待显示页面 int count=0; //总条数 int totalpages=0; //总页数 int limit=10; //每页显示记录条数 count = dao.select_count(); //由记录总数除以每页记录数得出总页数 totalpages = (int)Math.ceil(count/(limit*1.0)); //获取跳页时传进来的当前页面参数 String strPage = request.getParameter("pages"); //判断当前页面参数的合法性并处理非法页号(为空则显示第一页,小于0则显示第一页,大于总页数则显示最后一页) if (strPage == null) { pages = 1; } else { try{ pages = java.lang.Integer.parseInt(strPage); }catch(Exception e){ pages = 1; } if (pages < 1){ pages = 1; } if (pages > totalpages){ pages = totalpages; } } %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <style type="text/css"> body{ background: #ffffff; font-family: 华文行楷; } tr:nth-child(2n) { background:#f5fafc; } </style> <meta charset="UTF-8"> </head> <body style="height: 100%; margin: 0;"> <div style="text-align:center" class="results"> <table border="1" cellpadding="3" cellspacing="0" style="width: 80%;margin:auto"> <tr> <td style="width:40px">序号</td> <td style="width:40px">热词</td> <td>热词解释</td> <td>内容链接</td> </tr> <% List<WordBean> list = dao.select_page(pages,limit); //List<WordBean> list =(List<WordBean>)session.getAttribute("list"); for(WordBean n:list){ %> <tr> <td><%=n.getId() %></td> <td><%=n.getWord() %></td> <td><%=n.getExplain() %></td> <td><a href='<%=n.getLink() %>'><%=n.getLink() %></a></td> </tr> <%} %> </table> <form name="f1" method="POST" action="select.jsp" onSubmit="return checknum()"> <table border="0" align="center" > <tr> <td>第<%=pages%>页 共<%=totalpages%>页 <a href="select.jsp?pages=1">首页</a></td> <td><a href="select.jsp?pages=<%=(pages<1)?pages:(pages-1) %>"> 上一页</a></td> <td><a href="select.jsp?pages=<%=(pages>=totalpages)?totalpages:(pages+1)%>"> 下一页</a></td> <td><a href="select.jsp?pages=<%=totalpages%>">最后一页</a></td> <td>转到第:<input type="text" name="page" size="8">页<input type="submit" value="GO" name="cndok"></td> </tr> </table> </form> </div> </body> </html>
2.资源管理
- 引入并发
-
 java并发流操作
java并发流操作List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list..stream().parallel().forEach(list1 ->{ // 调用方法 method }); //其中list1为list一个子集。然后通过java流(steam)操作并发(parellel),同时开启多个线程去执行方法(method);所以当一个线程执行完成之后会继续执行集合中另外的子集,直到list循环结束。
-
- 维持数据或计算的多个副本
- 增加可用资源
3.资源仲裁
- 先进先出,同等看待每个资源
- 固定优先级,事先为某个事件分配优先级
- 动态优先级,运行时分配优先级
- 静态调度,非运行时确定资源的分配顺序
-
 优先级设置
优先级设置import java.util.concurrent.*; public class SimplePriority implements Runnable { private int countDown=5; private volatile double d; private int priority; public SimplePriority(int priority) { this.priority=priority; } public String toString() { return Thread.currentThread()+" : "+countDown; } public void run() { Thread.currentThread().setPriority(priority); while(true) { for(int i=1;i<100;i++) { d+=(Math.PI+Math.E)/(double)i; if(i%10==0) Thread.yield(); } System.out.println(this); if(--countDown==0) return; } } public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService exec=Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i=0;i<5;i++) exec.execute(new SimplePriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY)); exec.execute(new SimplePriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY)); exec.shutdown(); } }
-
参考
超时代码https://blog.csdn.net/u011494923/article/details/86570565
优先级https://blog.csdn.net/nice789987/article/details/17288557
性能优化https://www.cnblogs.com/wangjwei/p/10909979.html
java并发https://www.cnblogs.com/dfys/p/10874377.html




