【转】SpringBoot之@EnableAutoConfiguration注解
首先Spring Boot项目中都会如下启动类:
@SpringBootApplication public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } }
从上面代码可以看出,注解@SpringBootApplication和SpringApplication.run()方法是最为重要的部分。这里主要来看看@SpringBootApplication注解部分。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan( excludeFilters = {@Filter( type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class} ), @Filter( type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class} )} ) public @interface SpringBootApplication { ... }
虽然定义使用了多个Annotation进行了原信息标注,但实际上重要的只有三个Annotation:
- @Configuration(@SpringBootConfiguration点开查看发现里面还是应用了@Configuration)
- @EnableAutoConfiguration
- @ComponentScan
如果在启动类使用这个三个注解,整个SpringBoot应用依然可以与之前的启动类功能一样。但每次写这3个比较啰嗦,所以写一个@SpringBootApplication方便点。
这三个注解中@Configuration和@ComponentScan对我们来说并不陌生,今天我们的主角是@EnableAutoConfiguration。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @AutoConfigurationPackage @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration"; Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; String[] excludeName() default {}; }
其中最关键的要属@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class),借助AutoConfigurationImportSelector,@EnableAutoConfiguration可以帮助SpringBoot应用将所有符合条件的@Configuration配置都加载到当前SpringBoot创建并使用的IoC容器。
借助于Spring框架原有的一个工具类:SpringFactoriesLoader的支持,@EnableAutoConfiguration可以智能的自动配置功效才得以大功告成!
在AutoConfigurationImportSelector类中可以看到通过 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()
把 spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar/META-INF/spring.factories中每一个xxxAutoConfiguration文件都加载到容器中,spring.factories文件里每一个xxxAutoConfiguration文件一般都会有下面的条件注解:
- @ConditionalOnClass : classpath中存在该类时起效
- @ConditionalOnMissingClass : classpath中不存在该类时起效
- @ConditionalOnBean : DI容器中存在该类型Bean时起效
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean : DI容器中不存在该类型Bean时起效
- @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate : DI容器中该类型Bean只有一个或@Primary的只有一个时起效
- @ConditionalOnExpression : SpEL表达式结果为true时
- @ConditionalOnProperty : 参数设置或者值一致时起效
- @ConditionalOnResource : 指定的文件存在时起效
- @ConditionalOnJndi : 指定的JNDI存在时起效
- @ConditionalOnJava : 指定的Java版本存在时起效
- @ConditionalOnWebApplication : Web应用环境下起效
- @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication : 非Web应用环境下起效
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\
SpringFactoriesLoader
SpringFactoriesLoader属于Spring框架私有的一种扩展方案(类似于Java的SPI方案java.util.ServiceLoader),其主要功能就是从指定的配置文件META-INF/spring-factories加载配置,spring-factories是一个典型的java properties文件,只不过Key和Value都是Java类型的完整类名,比如:
example.MyService=example.MyServiceImpl1,example.MyServiceImpl2
对于@EnableAutoConfiguration来说,SpringFactoriesLoader的用途稍微不同一些,其本意是为了提供SPI扩展的场景,而在@EnableAutoConfiguration场景中,它更多提供了一种配置查找的功能支持,即根据@EnableAutoConfiguration的完整类名org.springframework.boot.autoconfig.EnableAutoConfiguration作为查找的Key,获得对应的一组@Configuration类。
SpringFactoriesLoader是一个抽象类,类中定义的静态属性定义了其加载资源的路径public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories",此外还有三个静态方法:
- loadFactories:加载指定的factoryClass并进行实例化。
- loadFactoryNames:加载指定的factoryClass的名称集合。
- instantiateFactory:对指定的factoryClass进行实例化。
在loadFactories方法中调用了loadFactoryNames以及instantiateFactory方法。
public static <T> List<T> loadFactories(Class<T> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) { Assert.notNull(factoryClass, "'factoryClass' must not be null"); ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader; if (classLoaderToUse == null) { classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader(); } List<String> factoryNames = loadFactoryNames(factoryClass, classLoaderToUse); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Loaded [" + factoryClass.getName() + "] names: " + factoryNames); } List<T> result = new ArrayList<T>(factoryNames.size()); for (String factoryName : factoryNames) { result.add(instantiateFactory(factoryName, factoryClass, classLoaderToUse)); } AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(result); return result; }
loadFactories方法首先获取类加载器,然后调用loadFactoryNames方法获取所有的指定资源的名称集合、接着调用instantiateFactory方法实例化这些资源类并将其添加到result集合中。最后调用AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort方法进行集合的排序。
一个例子
上面介绍了很多原理的知识,下面结合一个例子来加深理解,例子展示的是当项目启动时如果某个类存在就自动配置这个Bean,并且这个属性可以在application.properties中配置
新建一个Maven项目,pom.xml文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.chm.test</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-hello</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>spring-boot-starter-hello</name> <!-- FIXME change it to the project's website --> <url>http://www.example.com</url> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId> <version>2.0.4.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <version>2.0.4.RELEASE</version> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
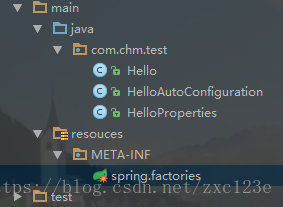
项目目录结构如下:
Hello.java
public class Hello { private String msg; public String sayHello() { return "hello " + msg; } public String getMsg() { return msg; } public void setMsg(String msg) { this.msg = msg; } }
HelloProperties.java
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "hello") //获取属性值 public class HelloProperties { private static final String MSG = "world"; private String msg = MSG ; public String getMsg() { return msg; } public void setMsg(String msg) { this.msg = msg; } }
HelloAutoConfiguration.java
@Configuration //为带有@ConfigurationProperties注解的Bean提供有效的支持。 // 这个注解可以提供一种方便的方式来将带有@ConfigurationProperties注解的类注入为Spring容器的Bean。 @EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class)//开启属性注入,通过@autowired注入 @ConditionalOnClass(Hello.class)//判断这个类是否在classpath中存在,如果存在,才会实例化一个Bean // The Hello bean will be created if the hello.enable property exists and has a value other than false // or the property doesn't exist at all. @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix="hello", value="enabled", matchIfMissing = true) public class HelloAutoConfiguration { @Autowired private HelloProperties helloProperties; @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(Hello.class)//容器中如果没有Hello这个类,那么自动配置这个Hello public Hello hello() { Hello hello = new Hello(); hello.setMsg(helloProperties.getMsg()); return hello; } }
spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.chm.test.HelloAutoConfiguration
最后使用mvn package将上面项目打包,使用mvn install:install-file命令将打包文件上传到本地Maven仓库进行测试。下面再新建一个Maven项目用于测试。
pom.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.chm.test</groupId> <artifactId>test-starter</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>test-starter</name> <!-- FIXME change it to the project's website --> <url>http://www.example.com</url> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target> <boot.version>2.0.4.RELEASE</boot.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.chm.test</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-hello</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <version>${boot.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <version>${boot.version}</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
App.java
@SpringBootApplication @RestController public class App { @Autowired private Hello hello; @RequestMapping("/") public String index() { return hello.sayHello(); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(App.class, args); } }
application.properties
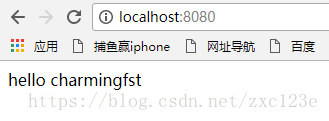
#可以不配置 hello.enabled=true hello.msg=charmingfst #以debug模式运行 debug=true
以debug模式运行,可以看到我们的配置:
启动项目,打开浏览器,运行结果如下: