基础学习
3D高斯渲染 (1-2)ros下 接受c++节点发送的位姿,python节点渲染图像返回
https://www.cnblogs.com/gooutlook/p/18385485
ros 自定义消息(图像+标志位+位姿)python和c++发布和接受
https://www.cnblogs.com/gooutlook/p/18412553
注意
1 高斯渲染原版本代码送入的是世界到相机的位姿,自己改的是相机到世界(slam发送来)
2 高斯加载colmap数据时候R矩阵是转置后的R也就是相机到世界。

本工程代码
为什么要做这个,因为之前的版本 图像和位姿是分开两个话题发送的,然后接收端依靠时间戳同步,但是可能会导致数据对齐且写代码复杂问题,这里直接自定义一个复合数据,图像和位姿以及id全部封装一起一起发。
编译
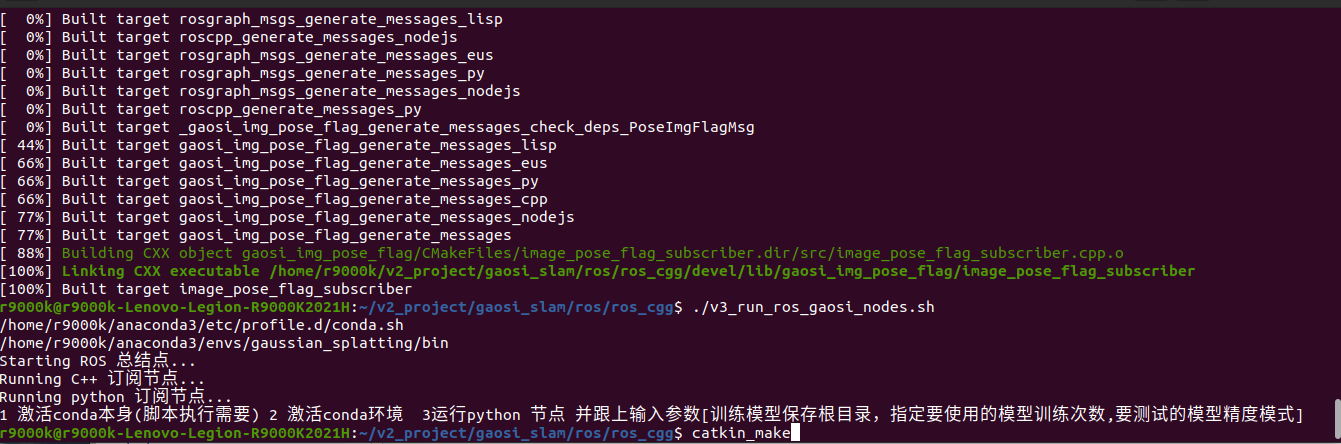
执行脚本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 | #!/bin/bash#外部给与执行权限#sudo chmod +x run_ros_nodes.sh# conda activate gaussian_splattingWORKSPACE_DIR="/home/r9000k/v2_project/gaosi_slam/ros/ros_cgg" # 修改1-1 自己创建的ros节点工程catkin_make根目录python_DIR="/home/r9000k/v2_project/gaosi_slam/ros/ros_cgg/src/gaosi_img_pose_flag/src" # 修改1-2 自己创建的python脚本位置data_dir="/home/r9000k/v2_project/data/NWPU"config_DIR="/home/dongdong/2project/0data/NWPU/FHY_config/GNSS_config.yaml" # 修改1-3 数据集conda_envs="/home/r9000k/anaconda3" # 修改2-1 自己的conda 安装路径# ROS_cv_briage_dir = "/home/r9000k/v1_software/opencv/catkin_ws_cv_bridge/devel/setup.bash" # 修改2-2 自己编译的cv_briage包节点,貌似不用也行 制定了依赖opencv3.4.9 而非自带4.2# echo $ROS_cv_briage_dirconda_envs_int=$conda_envs"/etc/profile.d/conda.sh" # 不用改 conda自带初始化文件echo $conda_envs_intconda_envs_bin=$conda_envs"/envs/gaussian_splatting/bin" # 不用改 conda自带python安装位置 脚本中需要指定是conda特定的环境python而不是系统默认的echo $conda_envs_binROS_SETUP="/opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash" #不用改 安装时候添加到系统路径了 不需要每次都source 这里留着#指定目录# 启动 ROS Master 不用改echo "Starting ROS 总结点..."gnome-terminal -- bash -c "\cd $WORKSPACE_DIR; source devel/setup.bash; \ roscore; \exec bash"# 等待 ROS Master 启动sleep 3echo "Running C++ 订阅节点..."gnome-terminal -- bash -c "\cd $WORKSPACE_DIR; source devel/setup.bash; \rosrun gaosi_img_pose_flag image_pose_flag_subscriber; \exec bash"# source /home/r9000k/v2_project/gaosi_slam/ros/ros_cgg/devel/setup.bash # 运行 python 渲染图节点# source conda_envs_int 和 source ROS_cv_briage_dir 非必要,但是考虑到脚本经常因为系统环境默认变量找不到导致的路径问题,这里还是强制给了也便于学习了解执行流程。echo "Running python 订阅节点..."echo "1 激活conda本身(脚本执行需要) 2 激活conda环境 3运行python 节点 并跟上输入参数[训练模型保存根目录,指定要使用的模型训练次数,要测试的模型精度模式]"gnome-terminal -- bash -c "\source $conda_envs_int; \ cd $WORKSPACE_DIR; source devel/setup.bash; \conda activate gaussian_splatting ; \cd $python_DIR; \python3 v1_image_pose_subscriber.py \-m $data_dir/gs_out/train1_out_sh0_num30000 \--iteration 30000 \--models baseline ;\exec bash" |
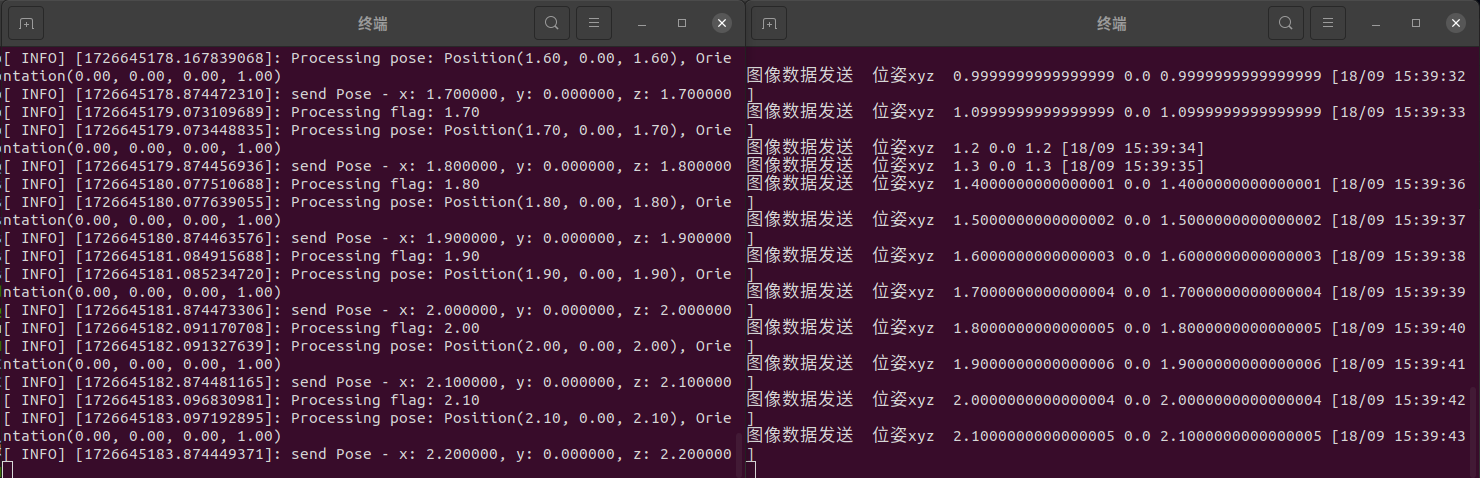
执行
创建消息

PoseImgFlagMsg.msg
1 2 3 4 5 | # PoseImgFlagMsg.msgstd_msgs/Time timestampsensor_msgs/Image imagestd_msgs/Float64 flaggeometry_msgs/Pose pose |
1 2 3 4 | std_msgs/Time timestamp 时间戳sensor_msgs/Image image 图像std_msgs/Float64 flag 请求的id, 某次请求渲染,可能要多张渲染图,同属于一个批次。geometry_msgs/Pose pose 图像位姿<br><br><br><br><br><br> |
编译
CMakeLists.txt
1 工程名字 gaosi_img_pose_flag
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 | cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0.2)project(gaosi_img_pose_flag)find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS roscpp geometry_msgs sensor_msgs cv_bridge message_filters # 消息同步 image_transport std_msgs # 自定义消息 message_generation # 自定义消息)# 自定义消息add_message_files( FILES PoseImgFlagMsg.msg)# 自定义消息generate_messages( DEPENDENCIES std_msgs sensor_msgs geometry_msgs)find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)find_package(Boost REQUIRED COMPONENTS filesystem)find_package(Eigen3 REQUIRED)catkin_package( CATKIN_DEPENDS roscpp geometry_msgs sensor_msgs cv_bridge std_msgs message_runtime DEPENDS Boost)include_directories( ${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS} ${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS} ${Boost_INCLUDE_DIRS} "/usr/local/include/eigen3")# # 编译发布节点# add_executable(image_pose_flag_publisher src/image_pose_flag_publisher.cpp)# # 自定义消息引用# add_dependencies(image_pose_flag_publisher ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})# target_link_libraries(image_pose_flag_publisher# ${catkin_LIBRARIES}# ${OpenCV_LIBRARIES}# ${Boost_LIBRARIES}# )add_executable(image_pose_flag_subscriber src/image_pose_flag_subscriber.cpp)add_dependencies(image_pose_flag_subscriber ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})target_link_libraries(image_pose_flag_subscriber ${catkin_LIBRARIES} ${OpenCV_LIBRARIES}) |
ros包名字 未来调用需要用到
1 | <name>gaosi_img_pose_flag</name> |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 | <?xml version="1.0"?><package format="2"> <name>gaosi_img_pose_flag</name> <version>0.0.1</version> <description> A package to publish and subscribe to images and GPS data using ROS. </description> <!-- Maintainer of the package --> <maintainer email="your_email@example.com">Your Name</maintainer> <!-- License of the package --> <license>MIT</license> <!-- Build tool required to build this package --> <buildtool_depend>catkin</buildtool_depend> <!-- Dependencies of the package during build and runtime --> <build_depend>roscpp</build_depend> <build_depend>sensor_msgs</build_depend> <build_depend>cv_bridge</build_depend> <build_depend>eigen</build_depend> <build_depend>geometry_msgs</build_depend> <build_depend>message_filters</build_depend> <build_depend>image_transport</build_depend> <!--自定义消息 --> <build_depend>message_generation</build_depend> <build_depend>message_runtime</build_depend> <build_depend>std_msgs</build_depend> <exec_depend>roscpp</exec_depend> <exec_depend>sensor_msgs</exec_depend> <exec_depend>cv_bridge</exec_depend> <exec_depend>eigen</exec_depend> <exec_depend>geometry_msgs</exec_depend> <exec_depend>message_filters</exec_depend> <exec_depend>image_transport</exec_depend> <!--自定义消息 --> <exec_depend>message_generation</exec_depend> <exec_depend>message_runtime</exec_depend> <exec_depend>std_msgs</exec_depend> <!-- Declare additional dependencies required for building this package --> <build_export_depend>roscpp</build_export_depend> <build_export_depend>sensor_msgs</build_export_depend> <build_export_depend>cv_bridge</build_export_depend> <build_export_depend>eigen</build_export_depend> <build_export_depend>geometry_msgs</build_export_depend> <build_export_depend>message_filters</build_export_depend> <build_export_depend>image_transport</build_export_depend> <!--自定义消息 --> <build_export_depend>message_generation</build_export_depend> <build_export_depend>message_runtime</build_export_depend> <build_export_depend>std_msgs</build_export_depend> <!-- Export information, can be used by other packages --> <export> <!-- Export any specific information here --> </export></package> |

c++ 发送位姿,获取渲染图
image_pose_flag_subscriber.cpp
简单版本 发送端没有手动漫游
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 | #include <ros/ros.h>#include <ros/time.h>#include <std_msgs/Time.h>#include <queue>#include <mutex>#include <thread>#include <iostream>#include <sensor_msgs/Image.h>#include <std_msgs/Float64.h>#include <geometry_msgs/Pose.h>#include <cv_bridge/cv_bridge.h>#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>#include <gaosi_img_pose_flag/PoseImgFlagMsg.h> // 更换为你包的名字#include <Eigen/Dense>#include <Eigen/Geometry> // For Quaterniond // Global variablesstd::queue<gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg::ConstPtr> data_queue;std::mutex queue_mutex;// 用于过于早位姿的节点Eigen::Quaterniond Q_c2w ;Eigen::Vector3d t_c2w;void publishPose(ros::Publisher& pose_pub, std_msgs::Float64 flag_,Eigen::Quaterniond &quat, Eigen::Vector3d &t){ cv::Mat image_; //std_msgs::Float64 flag_; geometry_msgs::Pose pose_msg; pose_msg.position.x = t[0]; // 示例位置 pose_msg.position.y = t[1]; pose_msg.position.z = t[2]; pose_msg.orientation.x = quat.x(); // 示例姿态 pose_msg.orientation.y = quat.y(); pose_msg.orientation.z = quat.z(); pose_msg.orientation.w = quat.w(); ROS_INFO("send Pose - x: %f, y: %f, z: %f", pose_msg.position.x, pose_msg.position.y, pose_msg.position.z); gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg pose_img_flag_msg; //pose_msg.image = *cv_bridge::CvImage(std_msgs::Header(), "bgr8", image_).toImageMsg(); pose_img_flag_msg.flag = flag_; pose_img_flag_msg.pose = pose_msg; // 设置当前时间戳 ros::Time current_time = ros::Time::now(); pose_img_flag_msg.timestamp = std_msgs::Time(); // 初始化时间戳 pose_img_flag_msg.timestamp.data = current_time; // 设置当前时间 // 发布PoseStamped消息 pose_pub.publish(pose_img_flag_msg);}// Callback function to handle incoming messagesvoid render_callback(const gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg::ConstPtr& msg){ std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex); data_queue.push(msg);}// Thread function to process the queuevoid processQueue(){ while (ros::ok()) { std::queue<gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg::ConstPtr> local_queue; { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex); std::swap(local_queue, data_queue); // Safely access the queue } while (!local_queue.empty()) { auto msg = local_queue.front(); local_queue.pop(); // 将ROS图像消息转换为OpenCV图像 cv_bridge::CvImagePtr cv_ptr = cv_bridge::toCvCopy(msg->image, sensor_msgs::image_encodings::BGR8); cv::imshow("Rec_Image", cv_ptr->image); cv::waitKey(1); // Process the message ROS_INFO("Processing flag: %.2f", msg->flag.data); ROS_INFO("Processing pose: Position(%.2f, %.2f, %.2f), Orientation(%.2f, %.2f, %.2f, %.2f)", msg->pose.position.x, msg->pose.position.y, msg->pose.position.z, msg->pose.orientation.x, msg->pose.orientation.y, msg->pose.orientation.z, msg->pose.orientation.w); } // Optional: Sleep to avoid busy waiting std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100)); }}void spinThread(){ ros::spin();// 处理回调函数积累消息}int main(int argc, char** argv){ ros::init(argc, argv, "image_pose_processor"); ros::NodeHandle nh; ros::Subscriber sub; ros::Publisher pose_pub; // Initialize the subscriber sub = nh.subscribe("render/image_pose_topic", 10, render_callback); pose_pub = nh.advertise<gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg>("slam/image_pose_topic", 10); // Start a thread to run ros::spin() std::thread spin_thread(spinThread); // 处理rospin的线程 // Create a thread to process the queue std::thread processing_thread(processQueue); // 处理接受消息的线程 Q_c2w = Eigen::Quaterniond::Identity();; t_c2w={0,0,0.1}; std::string control_mode="auto";// 自动 auto 手动 hand ros::Rate rate(1);// Hz 频率 if(control_mode=="auto"){ // 定时器每秒调用一次 ros::Rate rate(1); double i =0; while (ros::ok()) { i=i+0.1; if(i>3)i=0; t_c2w={i,0,i}; std_msgs::Float64 Msg_id; // 创建 Float64 消息 Msg_id.data = i;// 将 double 值赋给消息的 data 成员 // todo 从slam获取想要的位姿 publishPose(pose_pub,Msg_id,Q_c2w,t_c2w); rate.sleep(); } } // Join the processing thread before exiting if (processing_thread.joinable()) { processing_thread.join(); } // Join the spin thread before exiting if (spin_thread.joinable()) { spin_thread.join(); } return 0;} |
升级版本 发送端也可以手动漫游
image_pose_flag_subscriber.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 | #include <ros/ros.h>#include <ros/time.h>#include <std_msgs/Time.h>#include <queue>#include <mutex>#include <thread>#include <iostream>#include <sensor_msgs/Image.h>#include <std_msgs/Float64.h>#include <geometry_msgs/Pose.h>#include <cv_bridge/cv_bridge.h>#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>#include <gaosi_img_pose_flag/PoseImgFlagMsg.h> // 更换为你包的名字#include <Eigen/Dense>#include <Eigen/Geometry> // For Quaterniond // Global variablesstd::queue<gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg::ConstPtr> data_queue;std::mutex queue_mutex;int i = 0;double x = 0, y = 0, z = 0;double step_ = 0.1, step_theta = 1.0;double theta_x = 0, theta_y = 0, theta_z = 0;cv::Mat image_hand = cv::Mat::zeros(480, 640, CV_8UC3); // 用于过于早位姿的节点Eigen::Quaterniond Q_c2w ;Eigen::Vector3d t_c2w;Eigen::Quaterniond eulerToQuaternion(double pitch, double yaw, double roll) { // 使用 Eigen 的四元数构造函数直接创建四元数 Eigen::Quaterniond q = Eigen::AngleAxisd(roll, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX()) * Eigen::AngleAxisd(pitch, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY()) * Eigen::AngleAxisd(yaw, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ()); return q;}Eigen::Matrix3d eulerToRotationMatrix(double pitch, double yaw, double roll) { // 使用 Eigen 的四元数计算旋转矩阵 Eigen::Quaterniond q = eulerToQuaternion(pitch, yaw, roll); return q.toRotationMatrix();}std::string rond_num(double value,int weishu) { // Round the number to 2 decimal places double roundedValue = std::round(value * 100.0) / 100.0; // Use a string stream to format the number std::ostringstream oss; oss << std::fixed << std::setprecision(weishu) << roundedValue; return oss.str();}int GetHandsPose(Eigen::Quaterniond &Q_c2w, Eigen::Vector3d &t_c2w){ int state_=0; if (image_hand.empty()) { return state_; } cv::namedWindow("cgg_hand_control", cv::WINDOW_NORMAL); bool new_img = false; // 设置文字的参数 double font_scale = 0.5; // 大小 int thickness = 1; // 粗细 cv::Scalar color1(255, 0, 0); // 文字颜色 cv::Scalar color2(0, 0, 255); // 文字颜色 // // 设置文字 std::string text1 = "position_xyz: " + (rond_num(x,2)) + " , " + (rond_num(y ,2)) + " , " + (rond_num(z,2)); cv::putText(image_hand, text1, cv::Point(10, 60), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_scale, color1, thickness); std::string text2 = "theta_xyz: " + (rond_num(theta_x,2) ) + " , " + (rond_num(theta_y ,2)) + " , " + (rond_num(theta_z,2)); cv::putText(image_hand, text2, cv::Point(10, 120), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_scale, color2, thickness); cv::imshow("cgg_hand_control", image_hand); char key = (char)cv::waitKey(1); if (key == 27) { // 按下 'ESC' 键 std::cout << "退出" << std::endl; state_=-1; new_img=false; return state_; //break; } else if (key == 'w') { // 按下 'w' 键 std::cout << "x前进" << std::endl; x += step_; i++; new_img = true; } else if (key == 's') { // 按下 's' 键 std::cout << "x后退" << std::endl; x -= step_; i++; new_img = true; } else if (key == 'a') { // 按下 'a' 键 std::cout << "y前进" << std::endl; y += step_; i++; new_img = true; } else if (key == 'd') { // 按下 'd' 键 std::cout << "y后退" << std::endl; y -= step_; i++; new_img = true; } else if (key == 'q') { // 按下 'q' 键 std::cout << "z前进" << std::endl; z += step_; i++; new_img = true; } else if (key == 'e') { // 按下 'e' 键 std::cout << "z后退" << std::endl; z -= step_; i++; new_img = true; } else if (key == 'i') { // 按下 'i' 键 std::cout << "x旋转+" << std::endl; theta_x += step_theta; if (theta_x > 360 || theta_x < -360) theta_x = 0; i++; new_img = true; } else if (key == 'k') { // 按下 'k' 键 std::cout << "x旋转-" << std::endl; theta_x -= step_theta; if (theta_x > 360 || theta_x < -360) theta_x = 0; i++; new_img = true; } else if (key == 'j') { // 按下 'j' 键 std::cout << "y旋转+" << std::endl; theta_y += step_theta; if (theta_y > 360 || theta_y < -360) theta_y = 0; i++; new_img = true; } else if (key == 'l') { // 按下 'l' 键 std::cout << "y旋转-" << std::endl; theta_y -= step_theta; if (theta_y > 360 || theta_y < -360) theta_y = 0; i++; new_img = true; } else if (key == 'u') { // 按下 'u' 键 std::cout << "z旋转+" << std::endl; theta_z += step_theta; if (theta_z > 360 || theta_z < -360) theta_z = 0; i++; new_img = true; } else if (key == 'o') { // 按下 'o' 键 std::cout << "z旋转-" << std::endl; theta_z -= step_theta; if (theta_z > 360 || theta_z < -360) theta_z = 0; i++; new_img = true; } else{ new_img = false; state_=0; } if (new_img) { state_=1; // 示例角度(以弧度为单位) double pitch = M_PI*(theta_x/180); // 30度 double yaw = M_PI*(theta_y/180); // 45度 double roll = M_PI*(theta_z/180); // 60度 Q_c2w = eulerToQuaternion(pitch, yaw, roll); t_c2w={x,y,z}; } return state_; }void publishPose(ros::Publisher& pose_pub, std_msgs::Float64 flag_,Eigen::Quaterniond &quat, Eigen::Vector3d &t){ cv::Mat image_; //std_msgs::Float64 flag_; geometry_msgs::Pose pose_msg; pose_msg.position.x = t[0]; // 示例位置 pose_msg.position.y = t[1]; pose_msg.position.z = t[2]; pose_msg.orientation.x = quat.x(); // 示例姿态 pose_msg.orientation.y = quat.y(); pose_msg.orientation.z = quat.z(); pose_msg.orientation.w = quat.w(); ROS_INFO("send Pose - x: %f, y: %f, z: %f", pose_msg.position.x, pose_msg.position.y, pose_msg.position.z); gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg pose_img_flag_msg; //pose_msg.image = *cv_bridge::CvImage(std_msgs::Header(), "bgr8", image_).toImageMsg(); pose_img_flag_msg.flag = flag_; pose_img_flag_msg.pose = pose_msg; // 设置当前时间戳 ros::Time current_time = ros::Time::now(); pose_img_flag_msg.timestamp = std_msgs::Time(); // 初始化时间戳 pose_img_flag_msg.timestamp.data = current_time; // 设置当前时间 // 发布PoseStamped消息 pose_pub.publish(pose_img_flag_msg);}// Callback function to handle incoming messagesvoid render_callback(const gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg::ConstPtr& msg){ std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex); data_queue.push(msg);}// Thread function to process the queuevoid processQueue(){ while (ros::ok()) { std::queue<gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg::ConstPtr> local_queue; { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex); std::swap(local_queue, data_queue); // Safely access the queue } while (!local_queue.empty()) { auto msg = local_queue.front(); local_queue.pop(); // 将ROS图像消息转换为OpenCV图像 cv_bridge::CvImagePtr cv_ptr = cv_bridge::toCvCopy(msg->image, sensor_msgs::image_encodings::BGR8); cv::imshow("Rec_Image", cv_ptr->image); cv::waitKey(1); // Process the message ROS_INFO("Processing flag: %.2f", msg->flag.data); ROS_INFO("Processing pose: Position(%.2f, %.2f, %.2f), Orientation(%.2f, %.2f, %.2f, %.2f)", msg->pose.position.x, msg->pose.position.y, msg->pose.position.z, msg->pose.orientation.x, msg->pose.orientation.y, msg->pose.orientation.z, msg->pose.orientation.w); } // Optional: Sleep to avoid busy waiting std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100)); }}void spinThread(){ ros::spin();// 处理回调函数积累消息}int main(int argc, char** argv){ ros::init(argc, argv, "image_pose_processor"); ros::NodeHandle nh; ros::Subscriber sub; ros::Publisher pose_pub; // Initialize the subscriber sub = nh.subscribe("render/image_pose_topic", 10, render_callback); pose_pub = nh.advertise<gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg>("slam/image_pose_topic", 10); // Start a thread to run ros::spin() std::thread spin_thread(spinThread); // 处理rospin的线程 // Create a thread to process the queue std::thread processing_thread(processQueue); // 处理接受消息的线程 std_msgs::Float64 Msg_id; // 创建 Float64 消息 Msg_id.data =0; Q_c2w = Eigen::Quaterniond::Identity();; t_c2w={0,0,0.1}; std::string control_mode="hand";// 自动 auto 手动 hand ros::Rate rate(1);// Hz 频率 if(control_mode=="hand"){ int state_=0; while ( ros::ok()){ if(ros::ok() && state_==1){ Msg_id.data=Msg_id.data+1; //ros::spinOnce(); // 不能执行太快 否则来不及处理回调 必须配合ros::Rate rate(10); rate.sleep(); 单独卡求一个线程处理 publishPose(pose_pub,Msg_id,Q_c2w,t_c2w); } else if(state_==-1) {break;} //std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(20)); // 暂停以减少CPU使用率 rate.sleep(); state_= GetHandsPose(Q_c2w,t_c2w); } } else if(control_mode=="auto"){ // 定时器每秒调用一次 double i =0; while (ros::ok()) { i=i+0.1; if(i>3)i=0; t_c2w={i,0,i}; Msg_id.data = i;// 将 double 值赋给消息的 data 成员 // todo 从slam获取想要的位姿 publishPose(pose_pub,Msg_id,Q_c2w,t_c2w); rate.sleep(); } } // Join the processing thread before exiting if (processing_thread.joinable()) { processing_thread.join(); } // Join the spin thread before exiting if (spin_thread.joinable()) { spin_thread.join(); } return 0;} |
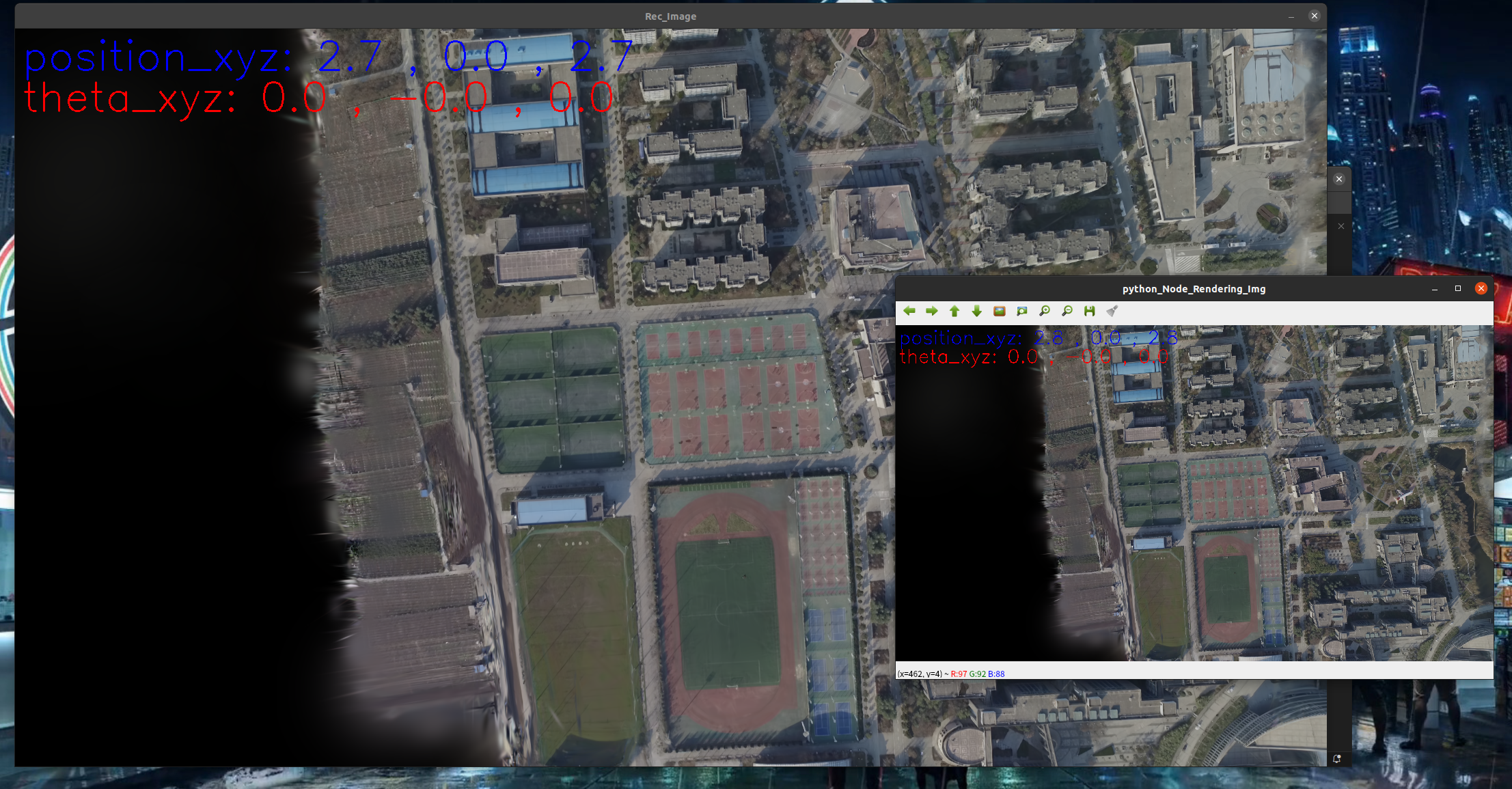
python接受位姿消息,渲染图像,返回图像,且可以手动漫游地图给与渲染图

v1_image_pose_subscriber.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 | # sudo apt-get install python3-rosdep python3-rosinstall python3-rospkgimport rospyimport cv2import numpy as npfrom sensor_msgs.msg import Image as ImageMsgfrom geometry_msgs.msg import PoseStamped,Posefrom cv_bridge import CvBridge, CvBridgeErrorfrom collections import dequefrom sensor_msgs.msg import Imagefrom std_msgs.msg import Float64from geometry_msgs.msg import Posefrom gaosi_img_pose_flag.msg import PoseImgFlagMsg # 更换为你包的名字import std_msgs.msg# import sys# directory = '/home/dongdong/2project/2_3DGaosi/reduced-3dgs/'# sys.path.append(directory)from API_render import *pose_queue = deque() # Queue to store pose messages with timestampsbridge = CvBridge()def pose_callback(msg): # Store the pose message with timestamp in the queue pose_queue.append((msg.timestamp, msg)) #print("收到位姿 x", msg.pose.position.x, "y", msg.pose.position.y, "z", msg.pose.position.z) # try: # # Convert ROS image message to OpenCV image # cv_image = bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(msg.image, desired_encoding="bgr8") # cv2.imshow("Received Image", cv_image) # cv2.waitKey(1) # except Exception as e: # rospy.logerr("Failed to convert image: %s", str(e)) # rospy.loginfo("Received flag: %.2f", msg.flag.data) # rospy.loginfo("Received pose: Position(%.2f, %.2f, %.2f), Orientation(%.2f, %.2f, %.2f, %.2f)", # msg.pose.position.x, msg.pose.position.y, msg.pose.position.z, # msg.pose.orientation.x, msg.pose.orientation.y, msg.pose.orientation.z, msg.pose.orientation.w)# 继承模式 直接使用而非拷贝def publish_image_with_pose_gaosi(dataset : ModelParams, iteration : int, pipeline : PipelineParams, ): # ============ 3d 初始化 ================= with torch.no_grad():# 丢不更新 防止高斯模型数据修改 print("dataset._model_path 训练渲染保存的模型总路径",dataset.model_path) print("dataset._source_path 原始输入SFM数据路径",dataset.source_path) print("dataset.sh_degree 球谐系数",dataset.sh_degree) print("dataset.white_background 是否白色背景",dataset.sh_degree) cam_info = Read_caminfo_from_colmap(dataset.source_path) height, width = cam_info["height"], cam_info["width"] Fovx,Fovy = cam_info["FovX"], cam_info["FovY"] img_opencv = np.ones((height, width, 3), dtype=np.uint8) * 0 cv2.namedWindow('python_Node_Rendering_Img', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL) # 加载渲染器 gaussians = GaussianModel(dataset.sh_degree) bg_color = [1,1,1] if dataset.white_background else [0, 0, 0] background = torch.tensor(bg_color, dtype=torch.float32, device="cuda") # 加载什么精度模型 model = args.models print("渲染实际加载的训练模型精度类型 (标准baseline 半精度quantised 半半精度half_float)",model) name = models_configuration[model]['name'] quantised = models_configuration[model]['quantised'] half_float = models_configuration[model]['half_float'] try: # 选择什么训练次数模型 model_path = dataset.model_path+"/point_cloud/iteration_"+str(iteration)+"/" model_path=os.path.join(model_path,name) print("渲染实际加载的训练模型",model_path) gaussians.load_ply(model_path, quantised=quantised, half_float=half_float) except: raise RuntimeError(f"Configuration {model} with name {name} not found!") # ============== rosros 节点 =============== i=0 x,y,z=0,0,0 # 手动控制的位置 t_x,t_y,t_z=0,0,0 # ros 收到的位置 后期会更新给x,y,z 保证手动控制给的位置是从上次的位姿开始的,而不会突变。 step_=0.1 theta_x=0 # 旋转角度 theta_y=0 theta_z=0 step_theta=1 scale_c2w=1 t_c2w=np.array([0, 0, 0]) R_c2w = quaternion_to_rotation_matrix((0,0,0,1)) # 初始化消息 image = np.zeros((480, 640, 3), dtype=np.uint8) flag_ = Float64() flag_.data = 1.0 pose_=Pose() pose_.position.x =0 pose_.position.y =0 pose_.position.z =0 pose_.orientation.x =0 pose_.orientation.y =0 pose_.orientation.z =0 pose_.orientation.w =1 ImagePoseFlag_Msg = PoseImgFlagMsg() timestamp = rospy.Time.now()# 时间戳 同于数据同步 ImagePoseFlag_Msg.timestamp = std_msgs.msg.Time() # 初始化时间戳 ImagePoseFlag_Msg.timestamp.data = timestamp # 设置当前时间 ImagePoseFlag_Msg.image = bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(image, encoding="bgr8") ImagePoseFlag_Msg.flag.data = flag_ ImagePoseFlag_Msg.pose = pose_ # 用于构造渲染视角 view = Camera_view(img_id=i, R=R_c2w, t=t_c2w, scale=scale_c2w, FoVx=Fovx, FoVy=Fovy, image_width=width, image_height=height) #df = pd.DataFrame() # 初期渲染一张 img_opencv = render_img( view, gaussians, pipeline, background) # 用于增加文字信息后的可视化 image = img_opencv# 原始渲染图不能被污染 要发送slam回去,新创建图可视化 cv2.UMat转换后才可以 cv2.putText new_img=0 rate = rospy.Rate(20) # 1 Hz while not rospy.is_shutdown(): new_img=0 image = img_opencv# 原始渲染图不能被污染 要发送slam回去,新创建图可视化 cv2.UMat转换后才可以 cv2.putText # 设置文字的参数 font_scale = 2 # 大小 thickness = 2 # 粗细 text1 ="position_xyz: " + str(round(t_x, 2))+" , "+str(round(t_y, 2)) +" , "+ str(round(t_z, 2)) position1 = (10, 60) # 文字的位置 cv2.putText(image, text1, position1, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_scale, (255, 0, 0), thickness) text2 = "theta_xyz: " + str(round(theta_x, 2))+" , "+str(round(theta_y, 2)) +" , "+ str(round(theta_z, 2)) position2 = (10, 120) # 文字的位置 cv2.putText(image, text2, position2, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_scale, (0, 0, 255), thickness) cv2.imshow('python_Node_Rendering_Img', image) #cv2.imshow('Rendering_Img', img_opencv)# imshow 不需要额外 cv2.UMat转换 key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF if pose_queue: # 收到渲染请求 位姿队列不为空 i=i+1 # 记录 new_img=1 timestamp, rec_pose_msg = pose_queue.popleft() t_x = rec_pose_msg.pose.position.x t_y = rec_pose_msg.pose.position.y t_z = rec_pose_msg.pose.position.z qx = rec_pose_msg.pose.orientation.x qy = rec_pose_msg.pose.orientation.y qz = rec_pose_msg.pose.orientation.z qw = rec_pose_msg.pose.orientation.w x,y,z=t_x,t_y,t_z# 将收到的位姿更新给按键变量 确保按键从现有位置开始运动 scale_c2w=1 t_c2w=np.array([t_x, t_y, t_z]) quaternion = (qx,qy,qz,qw) R_c2w = quaternion_to_rotation_matrix(quaternion) # # 从旋转矩阵获取欧拉角 roll, pitch, yaw = rotation_matrix_to_euler_angles(R_c2w) theta_x,theta_y,theta_z = roll, pitch, yaw flag_ = rec_pose_msg.flag pose_ = rec_pose_msg.pose #print(f"绕 X 轴的角度 滚转会使物体的左侧和右侧倾斜 (roll): {roll:.2f}°") #print(f"绕 Y 轴的角度 俯仰会使物体的前端向上或向下移动 (pitch): {pitch:.2f}°") #print(f"绕 Z 轴的角度 偏航会使物体的前端向左或向右转动 (yaw): {yaw:.2f}°") else:# 如果没有收到渲染请求 是否手动给了渲染位姿 if key == 27: # 按下 'q' 键 print("退出") break elif key == ord('w'): # 按下 's' 键 print("x前进") x=x+step_ i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('s'): # 按下 's' 键 print("x后退") x=x-step_ i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('a'): # 按下 's' 键 print("y前进") y=y+step_ i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('d'): # 按下 's' 键 print("y后退") y=y-step_ i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('q'): # 按下 's' 键 print("z前进") z=z+step_ i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('e'): # 按下 's' 键 print("z后退") z=z-step_ i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('i'): # 按下 's' 键 print("x旋转+") theta_x=theta_x+step_theta if(theta_x>360 or theta_x<-360): theta_x=0 i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('k'): # 按下 's' 键 print("x旋转-") theta_x=theta_x-step_theta if(theta_x>360 or theta_x<-360): theta_x=0 i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('j'): # 按下 's' 键 print("y旋转+") theta_y=theta_y+step_theta if(theta_y>360 or theta_y<-360): theta_y=0 i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('l'): # 按下 's' 键 print("y旋转-") theta_y=theta_y-step_theta if(theta_y>360 or theta_y<-360): theta_y=0 i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('u'): # 按下 's' 键 print("z旋转+") theta_z=theta_z+step_theta if(theta_z>360 or theta_z<-360): theta_z=0 i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('o'): # 按下 's' 键 print("z旋转-") theta_z=theta_z-step_theta if(theta_z>360 or theta_z<-360): theta_z=0 i=i+1 new_img=1 if new_img==1: t_x,t_y,t_z = x,y,z# 将按键变量更新给收到的位姿变量 确保图像可以显示刷新当前位置 # # 示例角度(以弧度为单位) theta_x_pi = np.radians(theta_x) # 30度 theta_y_pi = np.radians(theta_y) # 45度 theta_z_pi = np.radians(theta_z) # 60度 # # 计算旋转矩阵 R_c2w = combined_rotation_matrix(theta_x_pi, theta_y_pi, theta_z_pi) # 相机到世界的旋转矩阵 # R_c2w = np.array([ # [1.0, 0.0, 0.0], # [0.0, 1.0, 0.0], # [0.0, 0.0, 1.0] # ]) # print("旋转矩阵 R:") # print(R) # 相机到世界的平移矩阵 也就是相机在世界坐标系下的位置 t_c2w=np.array([x, y, z]) scale_c2w=1 q_c2w=rotation_matrix_to_quaternion(R_c2w) #timestamp = rospy.Time.now() pose_.position.x =t_c2w[0] pose_.position.y =t_c2w[1] pose_.position.z =t_c2w[2] pose_.orientation.x =q_c2w[0] pose_.orientation.y =q_c2w[1] pose_.orientation.z =q_c2w[2] pose_.orientation.w =q_c2w[3] if new_img==1: view = Camera_view(img_id=i, R=R_c2w, t=t_c2w, scale=scale_c2w, FoVx=Fovx, FoVy=Fovy, image_width=width, image_height=height) #df = pd.DataFrame() img_opencv = render_img( view, gaussians, pipeline, background) #random_image = np.random.randint(0, 256, (480, 640, 3), dtype=np.uint8) try: ImagePoseFlag_Msg.timestamp.data = rospy.Time.now() ImagePoseFlag_Msg.pose = pose_ ImagePoseFlag_Msg.flag.data = flag_.data ImagePoseFlag_Msg.image = bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(image, "bgr8") pub_ImgPoseFlag.publish(ImagePoseFlag_Msg) # Publish pose and image #pose_pub.publish(pose_msg) #image_pub.publish(image_msg) print("图像数据发送", " 位姿xyz ", x, y, z) except CvBridgeError as e: rospy.logerr(f'CvBridge Error: {e}') rate.sleep()if __name__ == '__main__': # ============ 3d 初始化 ================= parser = ArgumentParser(description="渲染测试脚本") model = ModelParams(parser, sentinel=True) pipeline = PipelineParams(parser) parser.add_argument("--iteration", default=30000, type=int) parser.add_argument("--models", default='baseline',type=str) #'baseline','quantised' 'quantised_half' parser.add_argument("--quiet", action="store_true") #标记以省略写入标准输出管道的任何文本。 args = get_combined_args(parser) # 从cfg_args加载路径 safe_state(args.quiet) #render_sets_handMode(model.extract(args), args.iteration, pipeline.extract(args)) # ============== rosros 节点初始化 =============== rospy.init_node('node2', anonymous=True) rospy.Subscriber('slam/image_pose_topic', PoseImgFlagMsg, pose_callback) global pub_ImgPoseFlag pub_ImgPoseFlag = rospy.Publisher('render/image_pose_topic', PoseImgFlagMsg, queue_size=10) publish_image_with_pose_gaosi(model.extract(args), args.iteration, pipeline.extract(args)) |
API_render.py
修改自己的高斯渲染工程代码路径
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 | import sysdirectory = '/home/r9000k/v2_project/gaosi_slam/reduced-3dgs'sys.path.append(directory)import cv2import numpy as npimport torchfrom scene import Sceneimport osfrom tqdm import tqdmfrom os import makedirsfrom gaussian_renderer import renderimport torchvisionfrom utils.general_utils import safe_statefrom argparse import ArgumentParserfrom arguments import ModelParams, PipelineParams, get_combined_argsfrom gaussian_renderer import GaussianModelimport pandas as pdimport torchfrom torch import nnimport numpy as npfrom utils.graphics_utils import getWorld2View2, getProjectionMatrixfrom scene.colmap_loader import *from scene.dataset_readers import *# 要选的视角class Camera_view(nn.Module): def __init__(self, img_id, R, FoVx, FoVy, image_width,image_height, t=np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0]), scale=1.0 ): super(Camera_view, self).__init__() self.img_id = img_id # 相机到世界 也就是相机在世界坐标系下的位姿 self.R = R # 相机到世界 源代码 self.t = t # 相机到世界 self.scale = scale # 尺度 展示没有 self.FoVx = FoVx self.FoVy = FoVy self.image_width = image_width self.image_height = image_height self.zfar = 100.0 self.znear = 0.01 # 相机到世界 sRt_c2w = np.zeros((4, 4)) #标准的矩阵转置 sRt_c2w[:3, :3] = self.R sRt_c2w[:3, 3] = self.scale*self.t sRt_c2w[3, 3] = 1.0 # 3D高斯渲染 需要的是 一个3D高斯球(x,y,z) 投影到相机像素画面 ,也就是世界到相机的变换矩阵, 所以需要对相机到世界矩阵sRt转置取逆 # 3D世界到3D相机坐标系 变换矩阵 # 高斯渲染 计算从世界坐标系到相机视图坐标系的变换矩阵,并将其移动到 GPU sRt_w2c=np.linalg.inv(sRt_c2w) # 世界到相机 self.world_view_transform = torch.tensor(np.float32(sRt_w2c)).transpose(0, 1).cuda() # 世界到相机 ''' #将3D相机坐标投影到2D相机像素平面的投影矩阵 # 真实相机成像模型中 该矩阵是由 fx fy cx cy构造的 # 虚拟渲染相机模型中 该矩阵是由 znear 默认0.01 近平面 zfar 默认100 远平面 视场角FoVx FoVy构造的。计算视场角FoVx=fx/(W/2),FoVy=fy/(H/2) # 两者关系: # 虚拟渲染相机用fx和fy表示的话 ,最后都是变为统一的形式。 (相机前方为z正轴的坐标系) u=fx*x/z-W/2 v=fy*y/z-H/2 w=-zfar*n/z (像素坐标不关心投影后的z值,无用舍去,所以最终znear和zfar对像素坐标u,v没有影响。) # 真实采集相机参数 fx fy cx=实际物理值 cy=实际物理值 成像分辨率 W*H # 渲染虚拟相机参数 fx fy cx=W/2 cy=H/2 成像分辨率 W*H ''' self.projection_matrix = getProjectionMatrix(znear=self.znear, zfar=self.zfar, fovX=self.FoVx, fovY=self.FoVy).transpose(0, 1).cuda() # 3D世界点投影到2D相机像素坐标 变换矩阵 world_view_transform 世界到相机 projection_matrix 相机到像素 合起来 世界到像素投影 ''' unsqueeze(0):为张量添加一个额外的维度,以便进行批量操作。 .bmm(...):执行批量矩阵乘法,将世界到视图的变换与投影矩阵相乘,得到一个合成的变换矩阵。 .squeeze(0):移除之前添加的额外维度。 ''' self.full_proj_transform = (self.world_view_transform.unsqueeze(0).bmm(self.projection_matrix.unsqueeze(0))).squeeze(0) self.inverse_full_proj_transform = self.full_proj_transform.inverse()# 后面貌似没用到 self.camera_center = self.world_view_transform.inverse()[3, :3] # 先求逆矩阵 相机到世界 然后取出t 世界计算相机中心位置 世界坐标系下的 # 考虑到R在层层计算中精度损失行列式不为1,从而影响t的计算,可以考虑直接用原始传来的t。 # 但是得保证数据采集时候 相机姿态方向没有转动过。飞机即使垂直朝下,也会因为气流扰动相机云台抖动有轻微R的变化。 #self.world_view_transform_c2w = torch.tensor(np.float32(sRt_c2w)).transpose(0, 1).cuda() # 自己定义的 未必用到 #self.camera_center = self.world_view_transform_c2w[3, :3] # 如果要忽略R的计算导致的误差 直接用原始的t_c2w def __del__(self): # 如果几个数据使用.cuda() 创建的,会自动存到显卡内存,多次渲染积累造成内存爆满,每次用完需要指定回收释放。否则不会随着程序(cpu)关闭而销毁。 # 删除张量并释放 GPU 内存 del self.world_view_transform del self.full_proj_transform del self.inverse_full_proj_transform del self.camera_center torch.cuda.empty_cache() #print("cuda占用回收.")#训练中间只会保存 原始模型 。 训练结束最后一次会保存原始模型baseline 精度减半模型quantised 精度减半减半模型 quantised_half,三种不同模型供测试。# 要测试的模型类型。标准的、基准的模型 “baseline”和将模型的权重或激活值量化为半精度(16-bit)格式“quantised_half”之间的选择#功能:量化可以显著降低计算量和内存消耗,但可能会引入一些精度损失。具体来说,“quantised_half”可能指的是将模型参数或中间激活值量化为16-bit浮点数(half precision),从而减少存储需求并提高计算效率。#半浮点量化 如果采用半浮点量化,则码本条目以及位置参数将以半精度存储。这意味着使用 16 位而不是 32 位,因此存储的是 float16 而不是 float32。# #但是,由于格式.ply不允许 float16 类型的数字,因此参数将指针转换为 int16 并以此形式存储。models_configuration = { 'baseline': { 'quantised': False, 'half_float': False, 'name': 'point_cloud.ply' }, 'quantised': { 'quantised': True, 'half_float': False, 'name': 'point_cloud_quantised.ply' }, 'quantised_half': { 'quantised': True, 'half_float': True, 'name': 'point_cloud_quantised_half.ply' },}def measure_fps(iteration, views, gaussians, pipeline, background, pcd_name): fps = 0 for _, view in enumerate(views): render(view, gaussians, pipeline, background, measure_fps=False) for _, view in enumerate(views): fps += render(view, gaussians, pipeline, background, measure_fps=True)["FPS"] fps *= 1000 / len(views) return pd.Series([fps], index=["FPS"], name=f"{pcd_name}_{iteration}")def rotation_matrix_x(theta_x): """ 创建绕x轴旋转的旋转矩阵 """ c, s = np.cos(theta_x), np.sin(theta_x) return np.array([ [1, 0, 0], [0, c, -s], [0, s, c] ])def rotation_matrix_y(theta_y): """ 创建绕y轴旋转的旋转矩阵 """ c, s = np.cos(theta_y), np.sin(theta_y) return np.array([ [c, 0, s], [0, 1, 0], [-s, 0, c] ])def rotation_matrix_z(theta_z): """ 创建绕z轴旋转的旋转矩阵 """ c, s = np.cos(theta_z), np.sin(theta_z) return np.array([ [c, -s, 0], [s, c, 0], [0, 0, 1] ])def combined_rotation_matrix(theta_x, theta_y, theta_z): """ 通过绕x、y、z轴的旋转角度创建组合旋转矩阵 """ Rx = rotation_matrix_x(theta_x) Ry = rotation_matrix_y(theta_y) Rz = rotation_matrix_z(theta_z) # 旋转矩阵的组合顺序:绕z轴 -> 绕y轴 -> 绕x轴 R = Rz @ Ry @ Rx return R# # 示例角度(以弧度为单位)# theta_x = np.radians(30) # 30度# theta_y = np.radians(45) # 45度# theta_z = np.radians(60) # 60度# # 计算旋转矩阵# R = combined_rotation_matrix(theta_x, theta_y, theta_z)# print("旋转矩阵 R:")# print(R)def quaternion_to_rotation_matrix(q): qx, qy, qz, qw = q R = np.array([ [1 - 2*(qy**2 + qz**2), 2*(qx*qy - qz*qw), 2*(qx*qz + qy*qw)], [2*(qx*qy + qz*qw), 1 - 2*(qx**2 + qz**2), 2*(qy*qz - qx*qw)], [2*(qx*qz - qy*qw), 2*(qy*qz + qx*qw), 1 - 2*(qx**2 + qy**2)] ]) return Rdef rotation_matrix_to_euler_angles(R): sy = np.sqrt(R[0, 0]**2 + R[1, 0]**2) singular = sy < 1e-6 if not singular: x = np.arctan2(R[2, 1], R[2, 2]) y = np.arctan2(-R[2, 0], sy) z = np.arctan2(R[1, 0], R[0, 0]) else: x = np.arctan2(-R[1, 2], R[1, 1]) y = np.arctan2(-R[2, 0], sy) z = 0 return np.degrees(x), np.degrees(y), np.degrees(z)# # 示例四元数# quaternion = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) # 替换为你自己的四元数# # 转换为旋转矩阵# R = quaternion_to_rotation_matrix(quaternion)# print("旋转矩阵 R:")# print(R)# # 从旋转矩阵获取欧拉角# roll, pitch, yaw = rotation_matrix_to_euler_angles(R)# print(f"绕 X 轴的角度 (roll): {roll:.2f}°")# print(f"绕 Y 轴的角度 (pitch): {pitch:.2f}°")# print(f"绕 Z 轴的角度 (yaw): {yaw:.2f}°")def rotation_matrix_to_quaternion(R): """ Convert a rotation matrix to a quaternion. Parameters: R (numpy.ndarray): A 3x3 rotation matrix. Returns: numpy.ndarray: A quaternion in the form of [w, x, y, z]. """ assert R.shape == (3, 3), "Input must be a 3x3 rotation matrix." # Calculate the trace of the matrix trace = np.trace(R) if trace > 0: s = np.sqrt(trace + 1.0) * 2 # s=4*qw qw = 0.25 * s qx = (R[2, 1] - R[1, 2]) / s qy = (R[0, 2] - R[2, 0]) / s qz = (R[1, 0] - R[0, 1]) / s else: # Find the largest diagonal element if R[0, 0] > R[1, 1] and R[0, 0] > R[2, 2]: s = np.sqrt(1.0 + R[0, 0] - R[1, 1] - R[2, 2]) * 2 # s=4*qx qw = (R[2, 1] - R[1, 2]) / s qx = 0.25 * s qy = (R[0, 1] + R[1, 0]) / s qz = (R[0, 2] + R[2, 0]) / s elif R[1, 1] > R[2, 2]: s = np.sqrt(1.0 + R[1, 1] - R[0, 0] - R[2, 2]) * 2 # s=4*qy qw = (R[0, 2] - R[2, 0]) / s qx = (R[0, 1] + R[1, 0]) / s qy = 0.25 * s qz = (R[1, 2] + R[2, 1]) / s else: s = np.sqrt(1.0 + R[2, 2] - R[0, 0] - R[1, 1]) * 2 # s=4*qz qw = (R[1, 0] - R[0, 1]) / s qx = (R[0, 2] + R[2, 0]) / s qy = (R[1, 2] + R[2, 1]) / s qz = 0.25 * s return np.array([qw, qx, qy, qz])# # 示例# R = np.array([[0, -1, 0],# [1, 0, 0],# [0, 0, 1]]) # 90度绕Z轴旋转的矩阵# quaternion = rotation_matrix_to_quaternion(R)#print("Quaternion:", quaternion)# 渲染单个视角图像并转化opencv图像def render_img(view, gaussians, # 模型 pipeline, background, ): #for idx, view in enumerate(tqdm(views, desc="Rendering progress")): # view 拷贝 # gaussians 继承 pipeline 拷贝 background 继承 rendering = render(view, gaussians, pipeline, background)["render"] #fps = render(view, gaussians, pipeline, background, measure_fps=True)["FPS"] #gt = view.original_image[0:3, :, :] # 将渲染图像转换为 NumPy 数组 rendering_np = rendering.cpu().numpy() # 如果张量是 (C, H, W) 形式,需要调整为 (H, W, C) if rendering_np.shape[0] == 3: rendering_np = np.transpose(rendering_np, (1, 2, 0)) # 将 RGB 转换为 BGR #opencv_img = rendering_np[..., ::-1] # 后续调用convert_image 一次性完成 #print("转化前 ",opencv_img.dtype) opencv_img = convert_image(rendering_np) #高斯输出是 float32(imshow虽然可以直接显示出来) 但是opencv和ros发送需要8UC3 图像 #print("转化后",opencv_img.dtype) # 及时清空显卡数据缓存 #del rendering #del rendering_np #torch.cuda.empty_cache() # # 显示图像 # cv2.imshow('Rendering', opencv_img) # cv2.waitKey(0) # 等待用户按键 return opencv_imgdef convert_image(image_32fc3): # 确保图像类型是 float32 if image_32fc3.dtype != np.float32: raise TypeError("输入图像必须是 32FC3 类型") # 将 32FC3 图像转换为 8UC3 图像 # 将浮点值缩放到 0-255 范围 image_8uc3 = cv2.convertScaleAbs(image_32fc3, alpha=(255.0 / np.max(image_32fc3))) # 转换为 BGR 颜色空间 image_bgr8 = cv2.cvtColor(image_8uc3, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) return image_bgr8# 从slam读取相机参数def Read_caminfo_from_orbslam(path): # wait to do pass# 从colmap读取相机参数def Read_caminfo_from_colmap(path): cam_intrinsics={} cam_extrinsics={} # 自带的代码 ''' from scene.colmap_loader import * from scene.dataset_readers import * ''' try: cameras_extrinsic_file = os.path.join(path, "sparse/0", "images.bin") cameras_intrinsic_file = os.path.join(path, "sparse/0", "cameras.bin") cam_extrinsics = read_extrinsics_binary(cameras_extrinsic_file) cam_intrinsics = read_intrinsics_binary(cameras_intrinsic_file) except: cameras_extrinsic_file = os.path.join(path, "sparse/0", "images.txt") cameras_intrinsic_file = os.path.join(path, "sparse/0", "cameras.txt") cam_extrinsics = read_extrinsics_text(cameras_extrinsic_file) cam_intrinsics = read_intrinsics_text(cameras_intrinsic_file) ''' 加载相机内参 read_intrinsics_text() # Camera list with one line of data per camera: # CAMERA_ID, MODEL, WIDTH, HEIGHT, PARAMS[] # Number of cameras: 1 1 PINHOLE 1920 1080 1114.0581411159471 1108.508409747483 960 540 ''' cam_id=1 # 从1开始。以一个相机模型 这里默认colmap一般只有一个相机. 但是可能存在GNSS照片和视频抽离的帧,2个相机模型参数 cam_parameters=cam_intrinsics[cam_id] print("相机id",cam_parameters.id) print("相机模型",cam_parameters.model) print("图像宽度",cam_parameters.width) print("图像高度",cam_parameters.height) print("相机内参 fx ",cam_parameters.params[0]) print("相机内参 fy ",cam_parameters.params[1]) FovY=0 FovX=0 if cam_parameters.model=="SIMPLE_PINHOLE": focal_length_x = cam_parameters.params[0] FovY = focal2fov(focal_length_x, cam_parameters.height) FovX = focal2fov(focal_length_x, cam_parameters.width) elif cam_parameters.model=="PINHOLE": focal_length_x = cam_parameters.params[0] focal_length_y = cam_parameters.params[1] FovY = focal2fov(focal_length_y, cam_parameters.height) FovX = focal2fov(focal_length_x, cam_parameters.width) else: assert False, "Colmap camera model not handled: only undistorted datasets (PINHOLE or SIMPLE_PINHOLE cameras) supported!" cam_info = { "width": cam_parameters.width, "height": cam_parameters.height, "fx": cam_parameters.params[0], "fy": cam_parameters.params[1], "FovX": FovX, "FovY": FovY } return cam_infodef render_sets_handMode(dataset : ModelParams, iteration : int, pipeline : PipelineParams, ): with torch.no_grad(): print("dataset._model_path 训练渲染保存的模型总路径",dataset.model_path) print("dataset._source_path 原始输入SFM数据路径",dataset.source_path) print("dataset.sh_degree 球谐系数",dataset.sh_degree) print("dataset.white_background 是否白色背景",dataset.sh_degree) cam_info = Read_caminfo_from_colmap(dataset.source_path) height, width = cam_info["height"], cam_info["width"] Fovx,Fovy = cam_info["FovX"], cam_info["FovY"] img_opencv = np.ones((height, width, 3), dtype=np.uint8) * 0 cv2.namedWindow('Rendering_Img', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL) # 加载渲染器 gaussians = GaussianModel(dataset.sh_degree) bg_color = [1,1,1] if dataset.white_background else [0, 0, 0] background = torch.tensor(bg_color, dtype=torch.float32, device="cuda") # 加载什么精度模型 model = args.models print("渲染实际加载的训练模型精度类型 (标准baseline 半精度quantised 半半精度half_float)",model) name = models_configuration[model]['name'] quantised = models_configuration[model]['quantised'] half_float = models_configuration[model]['half_float'] try: # 选择什么训练次数模型 model_path = dataset.model_path+"/point_cloud/iteration_"+str(iteration)+"/" model_path=os.path.join(model_path,name) print("渲染实际加载的训练模型",model_path) gaussians.load_ply(model_path, quantised=quantised, half_float=half_float) except: raise RuntimeError(f"Configuration {model} with name {name} not found!") i=0 # 渲染的图像计数 id x=0 # 位置 y=0 z=0 step_=0.1 theta_x=0 # 旋转角度 theta_y=0 theta_z=0 step_theta=1 while True: new_img=0 image = img_opencv # 原始渲染图不能被污染 要发送slam回去,新创建图可视化 cv2.UMat转换后才可以 cv2.putText # 设置文字的参数 font_scale = 2 # 大小 thickness = 2 # 粗细 text1 ="position_xyz: " + str(round(x, 2))+" , "+str(round(y, 2)) +" , "+ str(round(z, 2)) position1 = (10, 60) # 文字的位置 cv2.putText(image, text1, position1, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_scale, (255, 0, 0), thickness) text2 = "theta_xyz: " + str(round(theta_x, 2))+" , "+str(round(theta_y, 2)) +" , "+ str(round(theta_z, 2)) position2 = (10, 120) # 文字的位置 cv2.putText(image, text2, position2, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_scale, (0, 0, 255), thickness) cv2.imshow('Rendering_Img', image) #cv2.imshow('Rendering_Img', img_opencv)# imshow 不需要额外 cv2.UMat转换 key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF if key == 27: # 按下 'q' 键 print("退出") break elif key == ord('w'): # 按下 's' 键 print("x前进") x=x+step_ i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('s'): # 按下 's' 键 print("x后退") x=x-step_ i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('a'): # 按下 's' 键 print("y前进") y=y+step_ i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('d'): # 按下 's' 键 print("y后退") y=y-step_ i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('q'): # 按下 's' 键 print("z前进") z=z+step_ i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('e'): # 按下 's' 键 print("z后退") z=z-step_ i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('i'): # 按下 's' 键 print("x旋转+") theta_x=theta_x+step_theta if(theta_x>360 or theta_x<-360): theta_x=0 i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('k'): # 按下 's' 键 print("x旋转-") theta_x=theta_x-step_theta if(theta_x>360 or theta_x<-360): theta_x=0 i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('j'): # 按下 's' 键 print("y旋转+") theta_y=theta_y+step_theta if(theta_y>360 or theta_y<-360): theta_y=0 i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('l'): # 按下 's' 键 print("y旋转-") theta_y=theta_y-step_theta if(theta_y>360 or theta_y<-360): theta_y=0 i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('u'): # 按下 's' 键 print("z旋转+") theta_z=theta_z+step_theta if(theta_z>360 or theta_z<-360): theta_z=0 i=i+1 new_img=1 elif key == ord('o'): # 按下 's' 键 print("z旋转-") theta_z=theta_z-step_theta if(theta_z>360 or theta_z<-360): theta_z=0 i=i+1 new_img=1 if new_img==1: # # 示例角度(以弧度为单位) theta_x_pi = np.radians(theta_x) # 30度 theta_y_pi = np.radians(theta_y) # 45度 theta_z_pi = np.radians(theta_z) # 60度 # # 计算旋转矩阵 R_c2w = combined_rotation_matrix(theta_x_pi, theta_y_pi, theta_z_pi) # 相机到世界的旋转矩阵 # R_c2w = np.array([ # [1.0, 0.0, 0.0], # [0.0, 1.0, 0.0], # [0.0, 0.0, 1.0] # ]) # print("旋转矩阵 R:") # print(R) # 相机到世界的平移矩阵 也就是相机在世界坐标系下的位置 t_c2w=np.array([x, y, z]) scale_c2w=1 view = Camera_view(img_id=i, R=R_c2w, t=t_c2w, scale=scale_c2w, FoVx=Fovx, FoVy=Fovy, image_width=width, image_height=height) #df = pd.DataFrame() img_opencv = render_img( view, gaussians, pipeline, background) # python ./render.py -m /home/dongdong/2project/0data/NWPU/gs_out/train1_out_sh1_num7000 --iteration 7010 # if __name__ == "__main__":# # Set up command line argument parser# parser = ArgumentParser(description="渲染测试脚本")# model = ModelParams(parser, sentinel=True)# pipeline = PipelineParams(parser)# parser.add_argument("--iteration", default=30000, type=int)# parser.add_argument("--models", default='baseline',type=str) #'baseline','quantised' 'quantised_half' # parser.add_argument("--quiet", action="store_true") #标记以省略写入标准输出管道的任何文本。# args = get_combined_args(parser) # 从cfg_args加载路径# safe_state(args.quiet)# render_sets_handMode(model.extract(args), args.iteration, pipeline.extract(args)) |
分类:
1_6 nerf和高斯
, 1_1_0SLAM工具集合





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
2023-09-18 pytorch(2) softmax回归
2023-09-18 pytorch(3)损失函数
2023-09-18 pytorch(1)安装