https://www.cnblogs.com/gaoxiang12/p/5304272.html
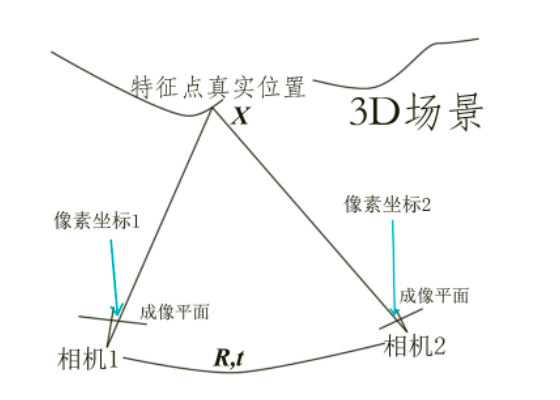

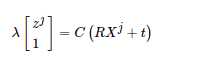
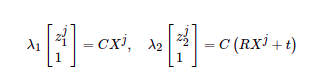

- 结点1:相机位姿结点:g2o::VertexSE3Expmap,来自<g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.h>;
- 结点2:特征点空间坐标结点:g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ,来自<g2o/types/sba/types_sba.h>;
- 边:重投影误差:g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV,来自<g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.h>;
这个是 EdgeProjectXYZ2UV 边的定义。它是一个Binary Edge,后面的模板参数表示,它的数据是2维的,来自Eigen::Vector2D,它连接的两个顶点必须是 VertexSBAPointXYZ, VertexSE3Expmap。 我们还能看到它的 computeError 定义,和前面给出的公式是一致的。注意到计算Error时,它调用了 g2o::CameraParameters 作为参数,所以我们在设置这条边时也需要给定一个相机参数。
/**
* BA Example
* Author: Xiang Gao
* Date: 2016.3
* Email: gaoxiang12@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn
*
* 在这个程序中,我们读取两张图像,进行特征匹配。然后根据匹配得到的特征,计算相机运动以及特征点的位置。这是一个典型的Bundle Adjustment,我们用g2o进行优化。
*/
// for std
#include <iostream>
// for opencv
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp>
#include <boost/concept_check.hpp>
// for g2o
#include <g2o/core/sparse_optimizer.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/robust_kernel.h>
#include <g2o/core/robust_kernel_impl.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/cholmod/linear_solver_cholmod.h>
#include <g2o/types/slam3d/se3quat.h>
#include <g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.h>
using namespace std;
// 寻找两个图像中的对应点,像素坐标系
// 输入:img1, img2 两张图像
// 输出:points1, points2, 两组对应的2D点
int findCorrespondingPoints( const cv::Mat& img1, const cv::Mat& img2, vector<cv::Point2f>& points1, vector<cv::Point2f>& points2 );
// 相机内参
double cx = 325.5;
double cy = 253.5;
double fx = 518.0;
double fy = 519.0;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
// 调用格式:命令 [第一个图] [第二个图]
if (argc != 3)
{
cout<<"Usage: ba_example img1, img2"<<endl;
exit(1);
}
// 读取图像
cv::Mat img1 = cv::imread( argv[1] );
cv::Mat img2 = cv::imread( argv[2] );
// 找到对应点
vector<cv::Point2f> pts1, pts2;
if ( findCorrespondingPoints( img1, img2, pts1, pts2 ) == false )
{
cout<<"匹配点不够!"<<endl;
return 0;
}
cout<<"找到了"<<pts1.size()<<"组对应特征点。"<<endl;
// 构造g2o中的图
// 先构造求解器
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
// 使用Cholmod中的线性方程求解器
g2o::BlockSolver_6_3::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverCholmod<g2o::BlockSolver_6_3::PoseMatrixType> ();
// 6*3 的参数
g2o::BlockSolver_6_3* block_solver = new g2o::BlockSolver_6_3( linearSolver );
// L-M 下降
g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* algorithm = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg( block_solver );
optimizer.setAlgorithm( algorithm );
optimizer.setVerbose( false );
// 添加节点
// 两个位姿节点
for ( int i=0; i<2; i++ )
{
g2o::VertexSE3Expmap* v = new g2o::VertexSE3Expmap();
v->setId(i);
if ( i == 0)
v->setFixed( true ); // 第一个点固定为零
// 预设值为单位Pose,因为我们不知道任何信息
v->setEstimate( g2o::SE3Quat() );
optimizer.addVertex( v );
}
// 很多个特征点的节点
// 以第一帧为准
for ( size_t i=0; i<pts1.size(); i++ )
{
g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ* v = new g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ();
v->setId( 2 + i );
// 由于深度不知道,只能把深度设置为1了
double z = 1;
double x = ( pts1[i].x - cx ) * z / fx;
double y = ( pts1[i].y - cy ) * z / fy;
v->setMarginalized(true);
v->setEstimate( Eigen::Vector3d(x,y,z) );
optimizer.addVertex( v );
}
// 准备相机参数
g2o::CameraParameters* camera = new g2o::CameraParameters( fx, Eigen::Vector2d(cx, cy), 0 );
camera->setId(0);
optimizer.addParameter( camera );
// 准备边
// 第一帧
vector<g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV*> edges;
for ( size_t i=0; i<pts1.size(); i++ )
{
g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV* edge = new g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV();
edge->setVertex( 0, dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ*> (optimizer.vertex(i+2)) );
edge->setVertex( 1, dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSE3Expmap*> (optimizer.vertex(0)) );
edge->setMeasurement( Eigen::Vector2d(pts1[i].x, pts1[i].y ) );
edge->setInformation( Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity() );
edge->setParameterId(0, 0);
// 核函数
edge->setRobustKernel( new g2o::RobustKernelHuber() );
optimizer.addEdge( edge );
edges.push_back(edge);
}
// 第二帧
for ( size_t i=0; i<pts2.size(); i++ )
{
g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV* edge = new g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV();
edge->setVertex( 0, dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ*> (optimizer.vertex(i+2)) );
edge->setVertex( 1, dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSE3Expmap*> (optimizer.vertex(1)) );
edge->setMeasurement( Eigen::Vector2d(pts2[i].x, pts2[i].y ) );
edge->setInformation( Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity() );
edge->setParameterId(0,0);
// 核函数
edge->setRobustKernel( new g2o::RobustKernelHuber() );
optimizer.addEdge( edge );
edges.push_back(edge);
}
cout<<"开始优化"<<endl;
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(10);
cout<<"优化完毕"<<endl;
//我们比较关心两帧之间的变换矩阵
g2o::VertexSE3Expmap* v = dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSE3Expmap*>( optimizer.vertex(1) );
Eigen::Isometry3d pose = v->estimate();
cout<<"Pose="<<endl<<pose.matrix()<<endl;
// 以及所有特征点的位置
for ( size_t i=0; i<pts1.size(); i++ )
{
g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ* v = dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ*> (optimizer.vertex(i+2));
cout<<"vertex id "<<i+2<<", pos = ";
Eigen::Vector3d pos = v->estimate();
cout<<pos(0)<<","<<pos(1)<<","<<pos(2)<<endl;
}
// 估计inlier的个数
int inliers = 0;
for ( auto e:edges )
{
e->computeError();
// chi2 就是 error*\Omega*error, 如果这个数很大,说明此边的值与其他边很不相符
if ( e->chi2() > 1 )
{
cout<<"error = "<<e->chi2()<<endl;
}
else
{
inliers++;
}
}
cout<<"inliers in total points: "<<inliers<<"/"<<pts1.size()+pts2.size()<<endl;
optimizer.save("ba.g2o");
return 0;
}
int findCorrespondingPoints( const cv::Mat& img1, const cv::Mat& img2, vector<cv::Point2f>& points1, vector<cv::Point2f>& points2 )
{
cv::ORB orb;
vector<cv::KeyPoint> kp1, kp2;
cv::Mat desp1, desp2;
orb( img1, cv::Mat(), kp1, desp1 );
orb( img2, cv::Mat(), kp2, desp2 );
cout<<"分别找到了"<<kp1.size()<<"和"<<kp2.size()<<"个特征点"<<endl;
cv::Ptr<cv::DescriptorMatcher> matcher = cv::DescriptorMatcher::create( "BruteForce-Hamming");
double knn_match_ratio=0.8;
vector< vector<cv::DMatch> > matches_knn;
matcher->knnMatch( desp1, desp2, matches_knn, 2 );
vector< cv::DMatch > matches;
for ( size_t i=0; i<matches_knn.size(); i++ )
{
if (matches_knn[i][0].distance < knn_match_ratio * matches_knn[i][1].distance )
matches.push_back( matches_knn[i][0] );
}
if (matches.size() <= 20) //匹配点太少
return false;
for ( auto m:matches )
{
points1.push_back( kp1[m.queryIdx].pt );
points2.push_back( kp2[m.trainIdx].pt );
}
return true;
}



