void keyframe::set_cam_pose(const Mat44_t& cam_pose_cw) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx_pose_);
cam_pose_cw_ = cam_pose_cw;
const Mat33_t rot_cw = cam_pose_cw_.block<3, 3>(0, 0);
const Vec3_t trans_cw = cam_pose_cw_.block<3, 1>(0, 3);
const Mat33_t rot_wc = rot_cw.transpose();
cam_center_ = -rot_wc * trans_cw;
cam_pose_wc_ = Mat44_t::Identity();
cam_pose_wc_.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = rot_wc;
cam_pose_wc_.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = cam_center_;
}
0-1 R构造和四元数转换
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
int main()
{
// 定义三个角度(弧度制)
double yaw = 0.1; // 绕Z轴的角度
double pitch = 0.2; // 绕Y轴的角度
double roll = 0.3; // 绕X轴的角度
// 尺度因子 s
double s = 2.0;
// 构造旋转矩阵 R
Eigen::Matrix3d R;
R = Eigen::AngleAxisd(yaw, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ())
* Eigen::AngleAxisd(pitch, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY())
* Eigen::AngleAxisd(roll, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
// 输出旋转矩阵 R
std::cout << "Rotation matrix R:\n" << R << std::endl;
// 将旋转矩阵 R 转换为四元数 q
Eigen::Quaterniond q(R);
// 输出四元数 q
std::cout << "Quaternion q:\n" << q.coeffs().transpose() << std::endl;
// 将四元数 q 乘以尺度因子 s
q.coeffs() *= s;
// 输出乘以尺度因子后的四元数 q
std::cout << "Scaled Quaternion q:\n" << q.coeffs().transpose() << std::endl;
// 将乘以尺度因子后的四元数 q 转换回旋转矩阵 R_new
Eigen::Matrix3d R_new = q.toRotationMatrix();
// 输出转换后的旋转矩阵 R_new
std::cout << "Scaled Rotation matrix R_new:\n" << R_new << std::endl;
// 求解四元数 q 的逆
Eigen::Quaterniond q_inv = q.conjugate() / q.norm();
// 输出四元数 q 的逆
std::cout << "Quaternion q inverse:\n" << q_inv.coeffs().transpose() << std::endl;
// 求解旋转矩阵 R 的逆(即转置矩阵)
Eigen::Matrix3d R_inv = R.transpose();
// 输出旋转矩阵 R 的逆
std::cout << "Rotation matrix R inverse:\n" << R_inv << std::endl;
return 0;
}
尺度 sss,四元数 qqq,和位移向量 ttt 构造位姿变换矩阵 TTT
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
int main()
{
// 定义尺度因子 s
double s = 2.0;
// 定义四元数 q (示例为单位四元数)
Eigen::Quaterniond q(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0); // (w, x, y, z)
// 定义位移向量 t
Eigen::Vector3d t(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);
// 构造旋转矩阵 R
Eigen::Matrix3d R = q.toRotationMatrix();
// 构造尺度矩阵 S
Eigen::Matrix3d S = s * Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();
// 构造位姿变换矩阵 T
Eigen::Matrix4d T = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity();
T.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = S * R; // 前三行前三列为 sR
T.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = t; // 前三行第四列为 t
// 输出位姿变换矩阵 T
std::cout << "Transformation matrix T:\n" << T << std::endl;
return 0;
}
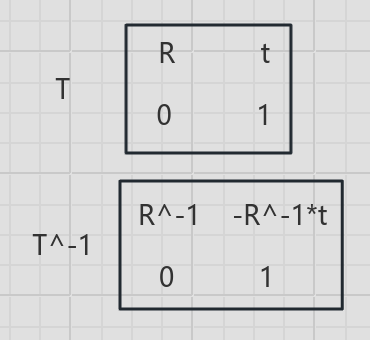
1-1 位姿矩阵 T和 Rt 变换 无尺度
Matrix3d RelativeR;
Vector3d Relativet;
Relativet<<0,0,10;
double currentScale=2;
//RelativeR<<1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1;// 单位阵
//RelativeR<<0,-1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1; // 旋转90度
double yaw = 0; // 绕Z轴的角度
double pitch = 0; // 绕Y轴的角度
double roll = 0; // 绕X轴的角度
RelativeR = Eigen::AngleAxisd(yaw, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ())
* Eigen::AngleAxisd(pitch, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY())
* Eigen::AngleAxisd(roll, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
cout<< "RelativeR "<<RelativeR <<endl;
// 假设位姿矩阵 T Eigen::Matrix4d T_vo_to_GNSS_ENU = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity(); T.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity(); // 设置旋转部分为单位矩阵 T.block<3, 1>(0, 3) << 0, 0, 0; // 设置平移部分为 (0, 0, 0) // 设置旋转部分 //T.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = currentR; //Matrix3d currentR // 设置平移部分 //T.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = currentT; // Vector3d currentT // Eigen::Matrix3d R_v_to_g = T.block<3, 3>(0, 0); // Eigen::Vector3d t_v_to_g = T.block<3, 1>(0, 3);
1-2 位姿矩阵 T和 sRt 变换 s尺度作用在T的R上 ( svd分解 t=质心1-sR质心2)
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Core>
int main()
{
// 假设给定的尺度因子、旋转矩阵和平移向量
double s = 2.0;
Eigen::Matrix3d R = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity(); // 假设为单位矩阵
Eigen::Vector3d t(1.0, 2.0, 3.0); // 假设平移向量为 (1, 2, 3)
// 初始化位姿矩阵 T
Eigen::Matrix4d T = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity();
// 设置旋转矩阵 R(乘以尺度因子 s)
T.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = s * R;
// 设置平移向量 t
T.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = t;
// 输出位姿矩阵 T
std::cout << "Pose Matrix T:\n" << T << std::endl;
return 0;
}
1-3 位姿矩阵 T和 sRt 变换 s尺度作用在整个T (不用 svd分解 s应该乘上R)
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Core>
int main()
{
// 假设给定的尺度因子、旋转矩阵和平移向量
double s = 2.0;
Eigen::Matrix3d R = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity(); // 假设为单位矩阵
Eigen::Vector3d t(1.0, 2.0, 3.0); // 假设平移向量为 (1, 2, 3)
// 初始化位姿矩阵 T
Eigen::Matrix4d T = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity();
// 设置旋转矩阵 R
T.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = R;
// 设置平移向量 t
T.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = t;
// 设置尺度因子 s
T *= s;
// 输出位姿矩阵 T
std::cout << "Pose Matrix T:\n" << T << std::endl;
return 0;
}


1安装sophus
2 使用代码
2-1 R,t矩阵 q四元数转换so3和se3

CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0)
project(useSophus)
# 为使用 sophus,需要使用find_package命令找到它
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
# Eigen
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
add_executable(useSophus useSophus.cpp)
target_link_libraries(useSophus Sophus::Sophus)
add_subdirectory(example)
useSophus.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include "sophus/se3.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
/// 本程序演示sophus的基本用法
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
// 沿Z轴转90度的旋转矩阵
Matrix3d R = AngleAxisd(M_PI / 2, Vector3d(0, 0, 1)).toRotationMatrix();
// 或者四元数
Quaterniond q(R);
Sophus::SO3d SO3_R(R); // Sophus::SO3d可以直接从旋转矩阵构造
Sophus::SO3d SO3_q(q); // 也可以通过四元数构造
// 二者是等价的
cout << "SO(3) from matrix:\n" << SO3_R.matrix() << endl;
cout << "SO(3) from quaternion:\n" << SO3_q.matrix() << endl;
cout << "they are equal" << endl;
// 使用对数映射获得它的李代数
Vector3d so3 = SO3_R.log();
cout << "so3 = " << so3.transpose() << endl;
// hat 为向量到反对称矩阵
cout << "so3 hat=\n" << Sophus::SO3d::hat(so3) << endl;
// 相对的,vee为反对称到向量
cout << "so3 hat vee= " << Sophus::SO3d::vee(Sophus::SO3d::hat(so3)).transpose() << endl;
// 增量扰动模型的更新
Vector3d update_so3(1e-4, 0, 0); //假设更新量为这么多
Sophus::SO3d SO3_updated = Sophus::SO3d::exp(update_so3) * SO3_R;
cout << "SO3 updated = \n" << SO3_updated.matrix() << endl;
cout << "*******************************" << endl;
// 对SE(3)操作大同小异
Vector3d t(1, 0, 0); // 沿X轴平移1
Sophus::SE3d SE3_Rt(R, t); // 从R,t构造SE(3)
Sophus::SE3d SE3_qt(q, t); // 从q,t构造SE(3)
cout << "SE3 from R,t= \n" << SE3_Rt.matrix() << endl;
cout << "SE3 from q,t= \n" << SE3_qt.matrix() << endl;
// 李代数se(3) 是一个六维向量,方便起见先typedef一下 typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d; Vector6d se3 = SE3_Rt.log(); cout << "se3 = " << se3.transpose() << endl; // 观察输出,会发现在Sophus中,se(3)的平移在前,旋转在后. // 同样的,有hat和vee两个算符 cout << "se3 hat = \n" << Sophus::SE3d::hat(se3) << endl; cout << "se3 hat vee = " << Sophus::SE3d::vee(Sophus::SE3d::hat(se3)).transpose() << endl; // 最后,演示一下更新 Vector6d update_se3; //更新量 update_se3.setZero(); update_se3(0, 0) = 1e-4; Sophus::SE3d SE3_updated = Sophus::SE3d::exp(update_se3) * SE3_Rt; cout << "SE3 updated = " << endl << SE3_updated.matrix() << endl; return 0; }
// 提取平移和旋转部分
Eigen::Vector3d t_ij = T_ij.translation(); // j在 i坐标系下的位姿
Eigen::Matrix3d R_ij = T_ij.rotationMatrix(); // j在 i坐标系下的位姿
例子2 真值和测量值计算平均方误差

CMakeLists.txt
option(USE_UBUNTU_20 "Set to ON if you are using Ubuntu 20.04" OFF)
find_package(Pangolin REQUIRED)
if(USE_UBUNTU_20)
message("You are using Ubuntu 20.04, fmt::fmt will be linked")
find_package(fmt REQUIRED)
set(FMT_LIBRARIES fmt::fmt)
endif()
include_directories(${Pangolin_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_executable(trajectoryError trajectoryError.cpp)
target_link_libraries(trajectoryError ${Pangolin_LIBRARIES} ${FMT_LIBRARIES})
trajectoryError.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pangolin/pangolin.h>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>
using namespace Sophus;
using namespace std;
string groundtruth_file = "./example/groundtruth.txt";
string estimated_file = "./example/estimated.txt";
typedef vector<Sophus::SE3d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Sophus::SE3d>> TrajectoryType;
void DrawTrajectory(const TrajectoryType >, const TrajectoryType &esti);
TrajectoryType ReadTrajectory(const string &path);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
TrajectoryType groundtruth = ReadTrajectory(groundtruth_file);
TrajectoryType estimated = ReadTrajectory(estimated_file);
assert(!groundtruth.empty() && !estimated.empty());
assert(groundtruth.size() == estimated.size());
// compute rmse
double rmse = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < estimated.size(); i++) {
Sophus::SE3d p1 = estimated[i], p2 = groundtruth[i];
double error = (p2.inverse() * p1).log().norm();
rmse += error * error;
}
rmse = rmse / double(estimated.size());
rmse = sqrt(rmse);
cout << "RMSE = " << rmse << endl;
DrawTrajectory(groundtruth, estimated);
return 0;
}
TrajectoryType ReadTrajectory(const string &path) {
ifstream fin(path);
TrajectoryType trajectory;
if (!fin) {
cerr << "trajectory " << path << " not found." << endl;
return trajectory;
}
while (!fin.eof()) {
double time, tx, ty, tz, qx, qy, qz, qw;
fin >> time >> tx >> ty >> tz >> qx >> qy >> qz >> qw;
Sophus::SE3d p1(Eigen::Quaterniond(qw, qx, qy, qz), Eigen::Vector3d(tx, ty, tz));
trajectory.push_back(p1);
}
return trajectory;
}
void DrawTrajectory(const TrajectoryType >, const TrajectoryType &esti) {
// create pangolin window and plot the trajectory
pangolin::CreateWindowAndBind("Trajectory Viewer", 1024, 768);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
pangolin::OpenGlRenderState s_cam(
pangolin::ProjectionMatrix(1024, 768, 500, 500, 512, 389, 0.1, 1000),
pangolin::ModelViewLookAt(0, -0.1, -1.8, 0, 0, 0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0)
);
pangolin::View &d_cam = pangolin::CreateDisplay()
.SetBounds(0.0, 1.0, pangolin::Attach::Pix(175), 1.0, -1024.0f / 768.0f)
.SetHandler(new pangolin::Handler3D(s_cam));
while (pangolin::ShouldQuit() == false) {
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
d_cam.Activate(s_cam);
glClearColor(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
glLineWidth(2);
for (size_t i = 0; i < gt.size() - 1; i++) {
glColor3f(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f); // blue for ground truth
glBegin(GL_LINES);
auto p1 = gt[i], p2 = gt[i + 1];
glVertex3d(p1.translation()[0], p1.translation()[1], p1.translation()[2]);
glVertex3d(p2.translation()[0], p2.translation()[1], p2.translation()[2]);
glEnd();
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < esti.size() - 1; i++) {
glColor3f(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); // red for estimated
glBegin(GL_LINES);
auto p1 = esti[i], p2 = esti[i + 1];
glVertex3d(p1.translation()[0], p1.translation()[1], p1.translation()[2]);
glVertex3d(p2.translation()[0], p2.translation()[1], p2.translation()[2]);
glEnd();
}
pangolin::FinishFrame();
usleep(5000); // sleep 5 ms
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号