https://blog.csdn.net/qq_60320488/article/details/132084670
一、map2dfusion所采用的数据集如下
npupilab/npu-dronemap-dataset: NPU Drone-Map Dataset (github.com)
其中map2dfusion的数据集中包含一组图片和两个配置文件
1.config.cfg
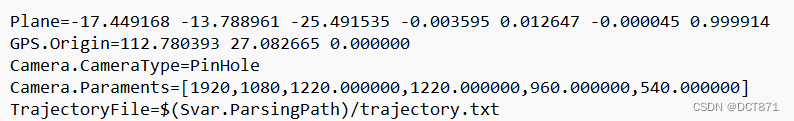
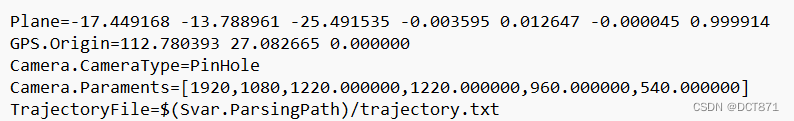
其中包含的内容:
plane为地面位姿
GPS.Origine为给定的初始GPS坐标
Camera.CameraType为采用的摄像头成像原理
Camera.Paraments为摄像头参数,前两个为图像的分辨率,后面四个分别为摄像机内参
TrajectoryFile为所存图像及其位姿的配置文件
2.trajectory.txt
其中包含8个数据:
第1位为图片的时间戳,也是图片名称,
第2~4位是摄像头的translation
第5~8位是摄像头的rotation,采用的四元数的格式
所以要使用orb-slam生成该格式的位姿数据,此处为了提高建图融合的效果,选取将所有帧及其位姿用于建图
二、在orb-slam的System.cc中添加如下函数,保存所有的轨迹。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 | void System::SaveTrajectoryTUM(const string &filename){ cout << endl << "Saving camera trajectory to " << filename << " ..." << endl; vector<KeyFrame*> vpKFs = mpMap->GetAllKeyFrames(); sort(vpKFs.begin(),vpKFs.end(),KeyFrame::lId); // Transform all keyframes so that the first keyframe is at the origin. // After a loop closure the first keyframe might not be at the origin. cv::Mat Two = vpKFs[0]->GetPoseInverse(); ofstream f; f.open(filename.c_str()); f << fixed; // Frame pose is stored relative to its reference keyframe (which is optimized by BA and pose graph). // We need to get first the keyframe pose and then concatenate the relative transformation. // Frames not localized (tracking failure) are not saved. // For each frame we have a reference keyframe (lRit), the timestamp (lT) and a flag // which is true when tracking failed (lbL). list<ORB_SLAM2::KeyFrame*>::iterator lRit = mpTracker->mlpReferences.begin(); list<double>::iterator lT = mpTracker->mlFrameTimes.begin(); list<bool>::iterator lbL = mpTracker->mlbLost.begin(); for(list<cv::Mat>::iterator lit=mpTracker->mlRelativeFramePoses.begin(), lend=mpTracker->mlRelativeFramePoses.end();lit!=lend;lit++, lRit++, lT++, lbL++) { if(*lbL) continue; KeyFrame* pKF = *lRit; cv::Mat Trw = cv::Mat::eye(4,4,CV_32F); // If the reference keyframe was culled, traverse the spanning tree to get a suitable keyframe. while(pKF->isBad()) { Trw = Trw*pKF->mTcp; pKF = pKF->GetParent(); } Trw = Trw*pKF->GetPose()*Two; cv::Mat Tcw = (*lit)*Trw; cv::Mat Rwc = Tcw.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3).t(); cv::Mat twc = -Rwc*Tcw.rowRange(0,3).col(3); vector<float> q = Converter::toQuaternion(Rwc); f << setprecision(6) << *lT << " " << setprecision(9) << 100*twc.at<float>(0) << " " << -1*100*twc.at<float>(1) << " " << 100*twc.at<float>(2) << " " << q[0] << " " << q[1] << " " << q[2] << " " << q[3] << endl; } f.close(); cout << endl << "trajectory saved!" << endl;} |
在Examples\Monocular\的mono_tum.cc中将SaveKeyFrameTrajectoryTUM改为SaveTrajectoryTUM,重新编译即可。
三、重新配置orbslam中的yaml配置文件
新建一个TUMX.yaml文件,

fx,fy,cx,cy是摄像头内参,改为config.cfg中Camera.Paraments的后四位
k1,k2,k3,p1,p2为摄像头的畸变参数,这里全部设置为0
由于数据集的分辨率较高,考虑到性能限制,将fps设置为5

将nFeatures设置为2000
iniThFAST设置为10
minThFAST设置为3
四、在数据集中运行如下代码生成一个rgb文件用于slam
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 | import numpy as npimport os# 图片文件夹,后面的/不能省from PIL import Image img_path = 'D:/slam/phantom3-village-kfs-master/phantom3-village-kfs-master/' # print(files) # 当前路径下所有非目录子文件# with open(img_path+"\opt_poses.txt") as f:# read_data = f.readlines()# # print(read_data)count = 0for root, dirs, files in os.walk(img_path, topdown=False): print(root) # 当前目录路径 print(dirs) # 当前目录下所有子目录 with open("D:/slam/phantom3-village-kfs-master/phantom3-village-kfs-master"+"/rgb.txt", 'w') as g: # count = 0 for i in files: # count = count +0.1 # print(i[-3:-1]+i[-1]) # if(i[-3:-1]+i[-1] == "jpg"): # #print(count) # #I = Image.open('./cadastre_gray/'+i) # count = int(i[6:-1].split('.')[0]) # print(count) # # print(read_data[count][0:7] +' '+ i) # write_date[count] = time_list[count] +' '+ time_list[count]+'.jpg' +"\n" # print(write_date[count]) # # print(read_data[count][0:7]) # #I.save('./picture/'+time_list[count]+'.jpg') # print(count) # print(i[0:9] + '.'+i[9] +i[11:17]) #for i in range(10): #name = str(count)+".jpg" #g.writelines(str(count) + ' ' + name + '\n') print(i[0:-4]) g.writelines(i[0:-4] + ' ' + i + '\n') # g.writelines(i[0:9] + '.'+i[9] +i[11:17]+ ' '+ i[0:9] + '.'+i[9] +i[11:17]+".jpg\n") #out.save('D:/slam/phantom3-village-kfs-master/phantom3-npu-master/phantom3-npu-master/npu/'+i) count = count + 0.01 # for i in range(len(files)): # print(write_date[i]) # # g.writelines(write_date[i]) # count=count+1 # print(count)# I = Image.open('./image.png')# print(type(I)) #---><class 'PIL.JpegImagePlugin.JpegImageFile'># print(I.size) #--->(1280, 720)# I.show()# I.save('./save.png') |
随后将生成的KeyFrameTrajectory作为trajectory.txt运行map2dfusion的进程即可
其中将产生的点云文件用于ransac平面拟合,得到的结果用于config的plane中,即可得到相对优秀的融合结果。
ransac平面拟合如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 | import randomimport numpy as npfrom math import acos, sin, cos, fabs, sqrt, logfrom matplotlib import pyplot as pltfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3Dimport csvdef new_csv(): with open("pcltest.csv", "w") as csvfile: writer = csv.writer(csvfile) # 先写入columns_name # writer.writerow(["a", "b", "c", "d", "message"]) writer.writerows([[1, 2, 3, 4, ',']]) def getData(filepath, row_need=1000): """ 加载数据并且取其中的部分行 """ data = np.loadtxt(filepath, delimiter=",") row_total = data.shape[0] print(row_total) row_sequence = np.arange(row_total) np.random.shuffle(row_sequence) return data[row_sequence[0:row_need], :] def solve_plane(A, B, C): """ 求解平面方程 :param A: 点A :param B: 点B :param C: 点C :return: Point(平面上一点),Quaternion(平面四元数),Nx(平面的法向量) """ # 两个常量 N = np.array([0, 0, 1]) Pi = 3.1415926535 # 计算平面的单位法向量,即BC 与 BA的叉积 Nx = np.cross(B - C, B - A) Nx = Nx / np.linalg.norm(Nx) # 计算单位旋转向量与旋转角(范围为0到Pi) Nv = np.cross(Nx, N) angle = acos(np.dot(Nx, N)) # 考虑到两个向量夹角不大于Pi/2,这里需要处理一下 if angle > Pi / 2.0: angle = Pi - angle Nv = -Nv # FIXME: 此处如何确定平面上的一个点??? # Point = (A + B + C) / 3.0 Point = B # 计算单位四元数 Quaternion = np.append(Nv * sin(angle / 2), cos(angle / 2)) # print("旋转向量:\t", Nv) # print("旋转角度:\t", angle) # print("对应四元数:\t", Quaternion) return Point, Quaternion, Nx def solve_distance(M, P, N): """ 求解点M到平面(P,Q)的距离 :param M: 点M :param P: 平面上一点 :param N: 平面的法向量 :return: 点到平面的距离 """ # 从四元数到法向量 # A = 2 * Q[0] * Q[2] + 2 * Q[1] * Q[3] # B = 2 * Q[1] * Q[2] - 2 * Q[0] * Q[3] # C = -Q[0] ** 2 - Q[1] ** 2 + Q[2] ** 2 + Q[3] ** 2 # D = -A * P[0] - B * P[1] - C * P[2] # 为了计算简便,直接使用求解出的法向量 A = N[0] B = N[1] C = N[2] D = -A * P[0] - B * P[1] - C * P[2] return fabs(A * M[0] + B * M[1] + C * M[2] + D) / sqrt(A ** 2 + B ** 2 + C ** 2) def RANSAC(data): """ 使用RANSAC算法估算模型 """ # 数据规模 SIZE = data.shape[0] # 迭代最大次数,每次得到更好的估计会优化iters的数值,默认10000 iters = 10000 # 数据和模型之间可接受的差值,默认0.25 sigma = 0.15 # 内点数目 pretotal = 0 # 希望的得到正确模型的概率,默认0.99 Per = 0.999 # 初始化一下 P = np.array([]) Q = np.array([]) N = np.array([]) for i in range(iters): # 随机在数据中选出三个点去求解模型 sample_index = random.sample(range(SIZE), 3) P, Q, N = solve_plane(data[sample_index[0]], data[sample_index[1]], data[sample_index[2]]) # 算出内点数目 total_inlier = 0 for index in range(SIZE): if solve_distance(data[index], P, N) < sigma: total_inlier = total_inlier + 1 # 判断当前的模型是否比之前估算的模型好 if total_inlier > pretotal: print(total_inlier / SIZE) iters = log(1 - Per) / log(1 - pow(abs(total_inlier / SIZE), 2)) pretotal = total_inlier # 判断是否当前模型已经符合超过一半的点 if total_inlier > SIZE / 2: break return P, Q, N def draw(data, P, N): """ 画出散点图和平面 :param data: 三维点 :param N: 平面法向量 """ # 创建一个画布figure,然后在这个画布上加各种元素。 fig = plt.figure() # 将画布作用于 Axes3D 对象上。 ax = Axes3D(fig) # 画出散点图 ax.scatter(data[0], data[1], data[2], c="gold") # 画出平面 x = np.linspace(-30, 30, 10) y = np.linspace(-30, 30, 10) X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y) Z = -(N[0] * X + N[1] * Y - (N[0] * P[0] + N[1] * P[1] + N[2] * P[2])) / N[2] ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z) # 画出坐标轴 ax.set_xlabel('X label') ax.set_ylabel('Y label') ax.set_zlabel('Z label') plt.show() def test(): A = np.random.randn(3) B = np.random.randn(3) C = np.random.randn(3) P, Q, N = solve_plane(A, B, C) print("Plane:\t", P, Q) D = np.random.randn(3) print("Point:\t", D) d = solve_distance(D, P, N) print("Distance:\t", d) if __name__ == '__main__': data = getData("pcltest.csv") P, Q, N = RANSAC(data) print("Plane:\t", np.append(P, Q)) draw(data.T, P, N) |
其他
1 平面参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | bool Map2DPrepare::prepare(const pi::SE3d& plane,const PinHoleParameters& camera, const std::deque<std::pair<cv::Mat,pi::SE3d> >& frames){ if(frames.size()==0||camera.w<=0||camera.h<=0||camera.fx==0||camera.fy==0) { cerr<<"Map2D::prepare:Not valid prepare!\n"; return false; } _camera=camera;_fxinv=1./camera.fx;_fyinv=1./camera.fy; _plane =plane; _frames=frames; for(std::deque<std::pair<cv::Mat,pi::SE3d> >::iterator it=_frames.begin();it!=_frames.end();it++) { pi::SE3d& pose=it->second; pose=plane.inverse()*pose;//plane coordinate } return true;} |





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!
2022-01-09 c++学习例程(2)类的使用
2020-01-09 50 python使用进程