https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzIxOTczOTM4NA==&mid=2247486858&idx=1&sn=ce458d5eb6b1ad11b065d71899e31a04&chksm=97d7e81da0a0610b1e3e12415b6de1501329920c3074ab5b48e759edbb33d264a73f1a9f9faf&scene=21#wechat_redirect
简要流程
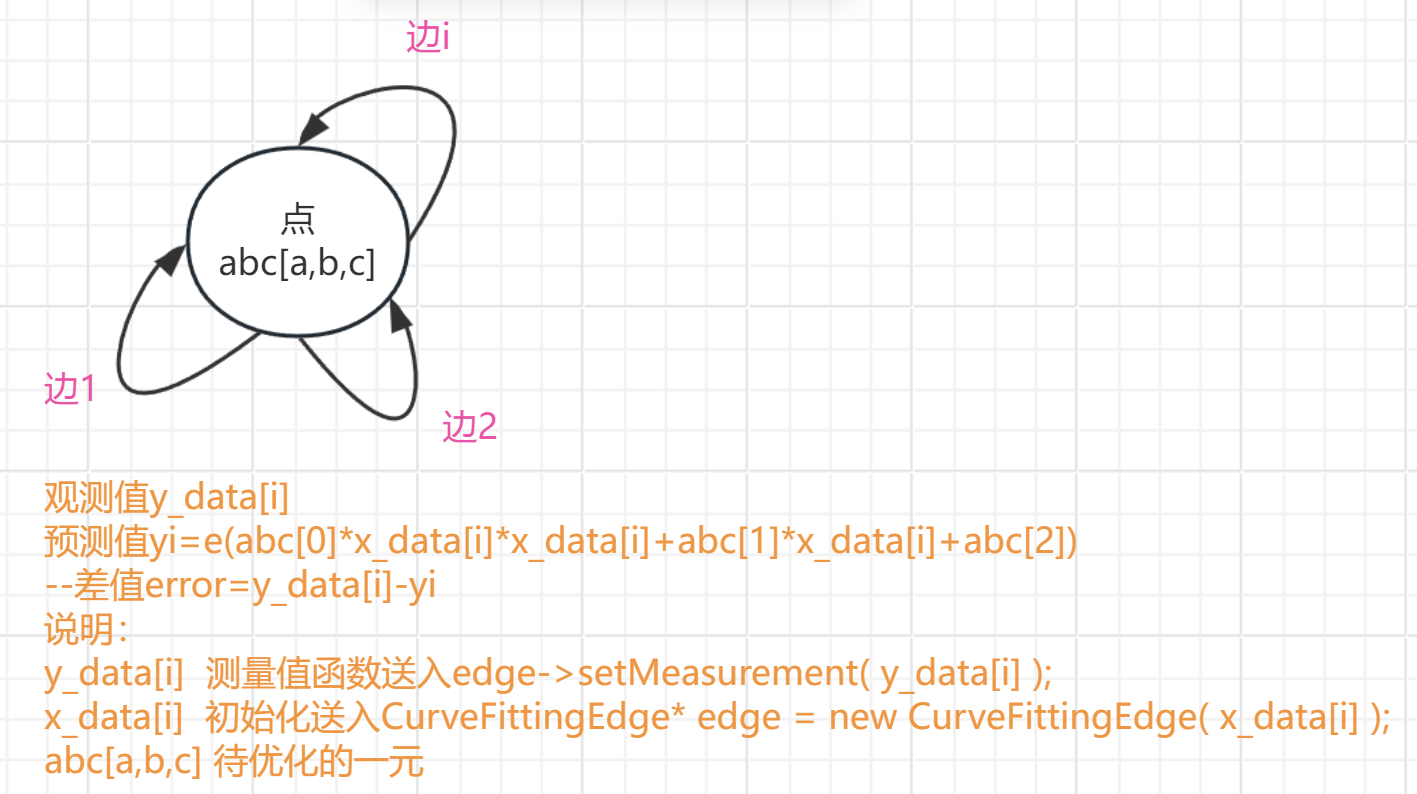
0-0获取数据 x 和 y
0-1确定要优化的量a ,b, c
1-1 获取理论模型 y=ax^2+bx+c
1-2 确定误差方程e =min||f(x+Δx)-f(x)||
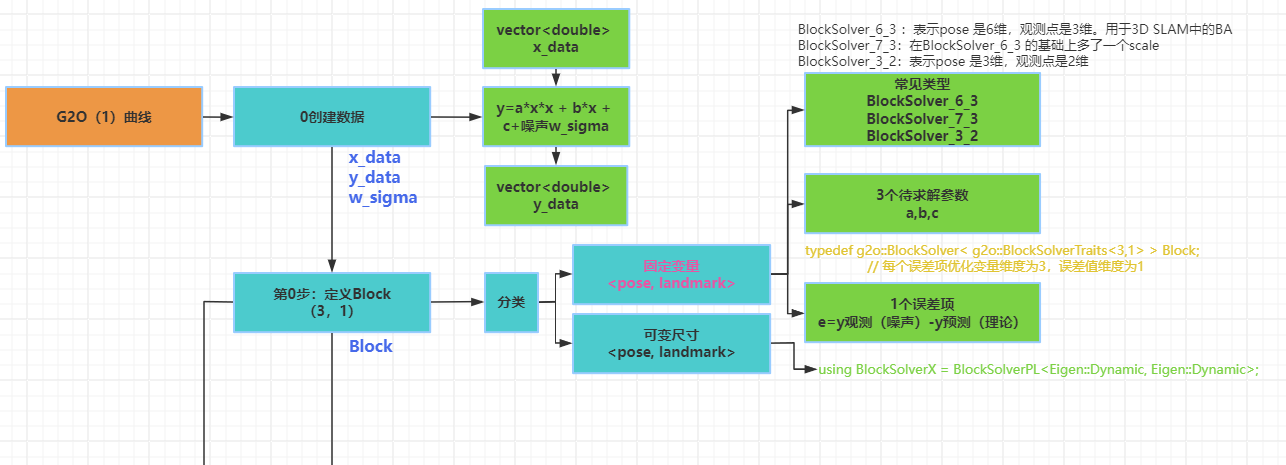
2 根据误差方程e确定一阶导J=2ax+b和二阶导H=2a 矩阵,信息矩阵
3 根据误差方程e , 求解模型(例如高斯牛顿)确定 H和g表达形式
构造 H *Δx= g最小二乘
J(x)*J(x)*Δx=-J(x) f(x)
H* Δx = g
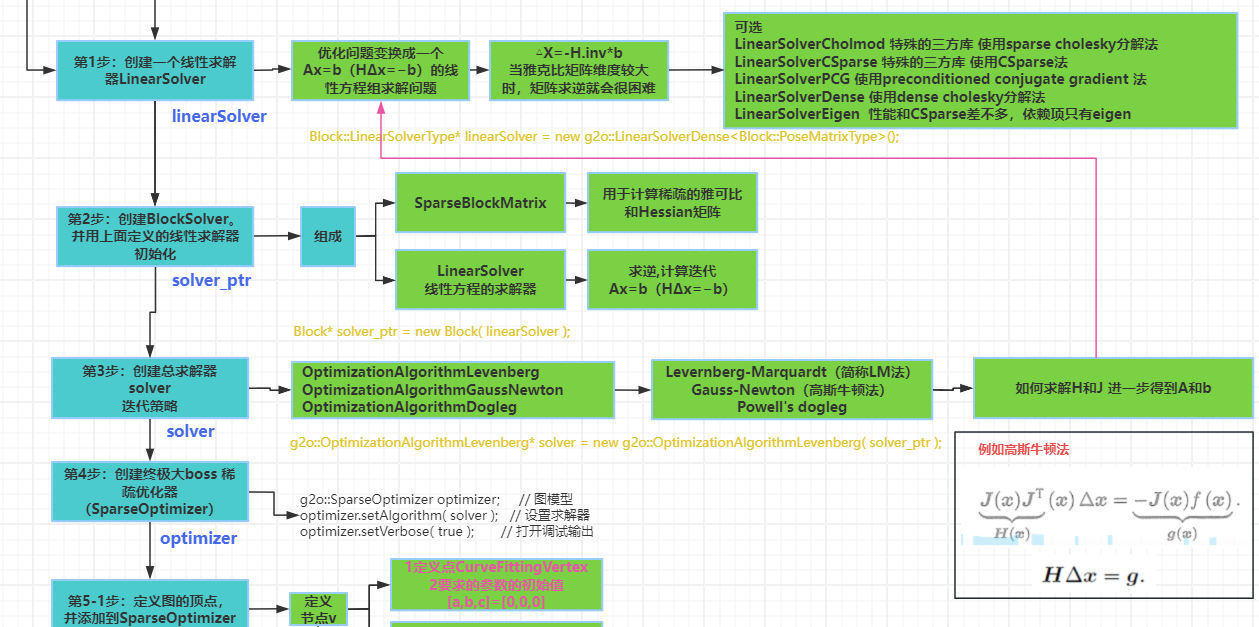
4 求解 Δx=H.inv*g 确定求解H逆的方法
5 跟新 x=x+Δx
6 求解 e =f(x+Δx)-f(x)误差
7 迭代直到小于阈值或者总次数


源码地址
G2O代码
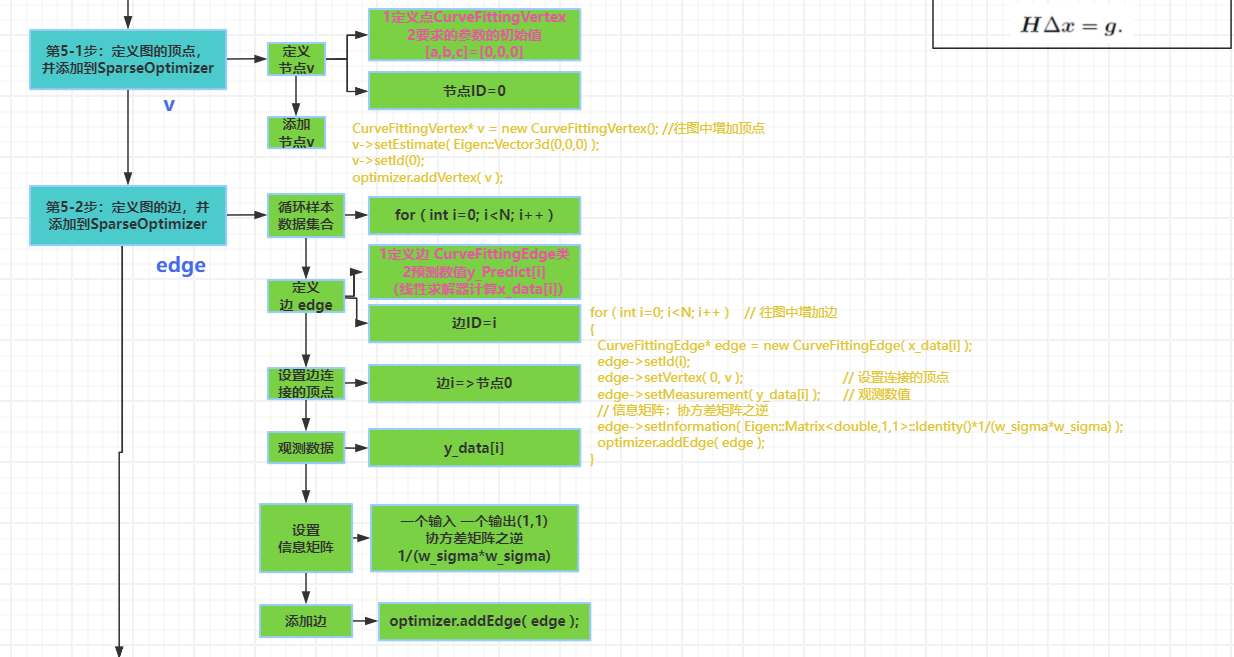
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | cmake_minimum_required( VERSION 2.8 )project( g2o_curve_fitting )set( CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release" )set( CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -O3" )# 添加cmake模块以使用ceres库list( APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake_modules )# 寻找G2Ofind_package( G2O REQUIRED )include_directories( ${G2O_INCLUDE_DIRS} "/usr/include/eigen3")# OpenCVfind_package( OpenCV REQUIRED )include_directories( ${OpenCV_DIRS} )add_executable( curve_fitting main.cpp )# 与G2O和OpenCV链接target_link_libraries( curve_fitting ${OpenCV_LIBS} g2o_core g2o_stuff) |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 | #include <iostream>#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>#include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h>#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_gauss_newton.h>#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_dogleg.h>#include <g2o/solvers/dense/linear_solver_dense.h>#include <Eigen/Core>#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>#include <cmath>#include <chrono>using namespace std; // 曲线模型的顶点,模板参数:优化变量维度和数据类型class CurveFittingVertex: public g2o::BaseVertex<3, Eigen::Vector3d>{public: EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW virtual void setToOriginImpl() // 重置 { _estimate << 0,0,0; } virtual void oplusImpl( const double* update ) // 更新 {<br> _estimate += Eigen::Vector3d(update); } // 存盘和读盘:留空 virtual bool read( istream& in ) {} virtual bool write( ostream& out ) const {}};// 误差模型 模板参数:观测值维度,类型,连接顶点类型class CurveFittingEdge: public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<1,double,CurveFittingVertex>{public: EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW CurveFittingEdge( double x ): BaseUnaryEdge(), _x(x) {} // 计算曲线模型误差 void computeError() { const CurveFittingVertex* v = static_cast<const CurveFittingVertex*> (_vertices[0]); const Eigen::Vector3d abc = v->estimate(); _error(0,0) = _measurement - std::exp( abc(0,0)*_x*_x + abc(1,0)*_x + abc(2,0) ) ; } virtual bool read( istream& in ) {} virtual bool write( ostream& out ) const {}public: double _x; // x 值, y 值为 _measurement};int main( int argc, char** argv ){ double a=1.0, b=2.0, c=1.0; // 真实参数值 int N=100; // 数据点 double w_sigma=1.0; // 噪声Sigma值 cv::RNG rng; // OpenCV随机数产生器 double abc[3] = {0,0,0}; // abc参数的估计值 vector<double> x_data, y_data; // 数据 cout<<"generating data: "<<endl; for ( int i=0; i<N; i++ ) { double x = i/100.0; x_data.push_back ( x ); y_data.push_back ( exp ( a*x*x + b*x + c ) + rng.gaussian ( w_sigma ) ); cout<<x_data[i]<<" "<<y_data[i]<<endl; } // 构建图优化,先设定g2o typedef g2o::BlockSolver< g2o::BlockSolverTraits<3,1> > Block; // 每个误差项优化变量维度为3,误差值维度为1 Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverDense<Block::PoseMatrixType>(); // 线性方程求解器 Block* solver_ptr = new Block( linearSolver ); // 矩阵块求解器 // 梯度下降方法,从GN, LM, DogLeg 中选 g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg( solver_ptr ); // g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton( solver_ptr ); // g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmDogleg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmDogleg( solver_ptr ); g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型 optimizer.setAlgorithm( solver ); // 设置求解器 optimizer.setVerbose( true ); // 打开调试输出 // 往图中增加顶点 CurveFittingVertex* v = new CurveFittingVertex(); v->setEstimate( Eigen::Vector3d(0,0,0) ); v->setId(0); optimizer.addVertex( v ); // 往图中增加边 for ( int i=0; i<N; i++ ) { CurveFittingEdge* edge = new CurveFittingEdge( x_data[i] ); edge->setId(i); edge->setVertex( 0, v ); // 设置连接的顶点 edge->setMeasurement( y_data[i] ); // 观测数值 edge->setInformation( Eigen::Matrix<double,1,1>::Identity()*1/(w_sigma*w_sigma) ); // 信息矩阵:协方差矩阵之逆 optimizer.addEdge( edge ); } // 执行优化 cout<<"start optimization"<<endl; chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); optimizer.initializeOptimization(); optimizer.optimize(100); chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>( t2-t1 ); cout<<"solve time cost = "<<time_used.count()<<" seconds. "<<endl; // 输出优化值 Eigen::Vector3d abc_estimate = v->estimate(); cout<<"estimated model: "<<abc_estimate.transpose()<<endl; return 0;} |
ceres代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | cmake_minimum_required( VERSION 2.8 )project( ceres_curve_fitting )set( CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release" )set( CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -O3" )# 添加cmake模块以使用ceres库list( APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake_modules )# 寻找Ceres库并添加它的头文件find_package( Ceres REQUIRED )include_directories( ${CERES_INCLUDE_DIRS} )# OpenCVfind_package( OpenCV REQUIRED )include_directories( ${OpenCV_DIRS} )add_executable( curve_fitting main.cpp )# 与Ceres和OpenCV链接target_link_libraries( curve_fitting ${CERES_LIBRARIES} ${OpenCV_LIBS} ) |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 | #include <iostream>#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>#include <ceres/ceres.h>#include <chrono>using namespace std;// 代价函数的计算模型struct CURVE_FITTING_COST{ CURVE_FITTING_COST ( double x, double y ) : _x ( x ), _y ( y ) {} // 残差的计算 template <typename T> bool operator() ( const T* const abc, // 模型参数,有3维 T* residual ) const // 残差 { residual[0] = T ( _y ) - ceres::exp ( abc[0]*T ( _x ) *T ( _x ) + abc[1]*T ( _x ) + abc[2] ); // y-exp(ax^2+bx+c) return true; } const double _x, _y; // x,y数据};int main ( int argc, char** argv ){ double a=1.0, b=2.0, c=1.0; // 真实参数值 int N=100; // 数据点 double w_sigma=1.0; // 噪声Sigma值 cv::RNG rng; // OpenCV随机数产生器 double abc[3] = {0,0,0}; // abc参数的估计值 vector<double> x_data, y_data; // 数据 cout<<"generating data: "<<endl; for ( int i=0; i<N; i++ ) { double x = i/100.0; x_data.push_back ( x ); y_data.push_back ( exp ( a*x*x + b*x + c ) + rng.gaussian ( w_sigma ) ); cout<<x_data[i]<<" "<<y_data[i]<<endl; } // 构建最小二乘问题 ceres::Problem problem; for ( int i=0; i<N; i++ ) { problem.AddResidualBlock ( // 向问题中添加误差项 // 使用自动求导,模板参数:误差类型,输出维度,输入维度,维数要与前面struct中一致 new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<CURVE_FITTING_COST, 1, 3> ( new CURVE_FITTING_COST ( x_data[i], y_data[i] ) ), nullptr, // 核函数,这里不使用,为空 abc // 待估计参数 ); } // 配置求解器 ceres::Solver::Options options; // 这里有很多配置项可以填 options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_QR; // 增量方程如何求解 options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true; // 输出到cout ceres::Solver::Summary summary; // 优化信息 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); ceres::Solve ( options, &problem, &summary ); // 开始优化 chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>( t2-t1 ); cout<<"solve time cost = "<<time_used.count()<<" seconds. "<<endl; // 输出结果 cout<<summary.BriefReport() <<endl; cout<<"estimated a,b,c = "; for ( auto a:abc ) cout<<a<<" "; cout<<endl; return 0;} |
手撕代码
https://liuxiaofei.com.cn/blog/g2o%E4%BC%98%E5%8C%96%E8%A7%A3%E6%9E%90-%E6%89%8B%E5%8A%A8%E5%BE%AE%E5%88%86/
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 | #include <iostream>#include <g2o/core/g2o_core_api.h>#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>#include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h>#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_gauss_newton.h>#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_dogleg.h>#include <g2o/solvers/dense/linear_solver_dense.h>#include <g2o/stuff/sampler.h>#include <Eigen/Core>#include <cmath>#include <chrono> using namespace std; // 曲线模型的顶点,模板参数:优化变量维度和数据类型class CurveFittingVertex : public g2o::BaseVertex<3, Eigen::Vector3d> {public: EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW // 重置 virtual void setToOriginImpl() override { _estimate << 0, 0, 0; } // 更新,每一轮迭代后更新参数的值Δx。 virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override { _estimate += Eigen::Vector3d(update); } // 存盘和读盘:留空 virtual bool read(istream &in) {} virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}}; // 误差模型 模板参数:观测值维度,类型,连接顶点类型class CurveFittingEdge : public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<1, double, CurveFittingVertex> {public: EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW CurveFittingEdge(double x) : BaseUnaryEdge(), _x(x) {} // 计算曲线模型误差,测量值减去估计值得到误差。 virtual void computeError() override { const CurveFittingVertex *v = static_cast<const CurveFittingVertex *> (_vertices[0]); const Eigen::Vector3d abc = v->estimate(); _error(0, 0) = _measurement - std::exp(abc(0, 0) * _x * _x + abc(1, 0) * _x + abc(2, 0)); } // 计算雅可比矩阵,和上一篇高斯牛顿法里面的求解方式是一样的。 virtual void linearizeOplus() override { const CurveFittingVertex *v = static_cast<const CurveFittingVertex *> (_vertices[0]); const Eigen::Vector3d abc = v->estimate(); double y = exp(abc[0] * _x * _x + abc[1] * _x + abc[2]); _jacobianOplusXi[0] = -_x * _x * y; _jacobianOplusXi[1] = -_x * y; _jacobianOplusXi[2] = -y; } virtual bool read(istream &in) {} virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {} public: double _x; // x 值, y 值为 _measurement}; int main(int argc, char **argv) { double ar = 1.0, br = 2.0, cr = 1.0; // 真实参数值 double ae = 2.0, be = -1.0, ce = 5.0; // 估计参数值 int N = 100; // 数据点 double w_sigma = 1.0; // 噪声Sigma值 double inv_sigma = 1.0 / w_sigma; g2o::Sampler::seedRand(); vector<double> x_data, y_data; // 数据 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { double x = i / 100.0; x_data.push_back(x); y_data.push_back(exp(ar * x * x + br * x + cr) + g2o::Sampler::gaussRand(0, 0.02));//加上一个高斯误差,来表示测量是不准确的。 } // 构建图优化,先设定g2o typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<3, 1>> BlockSolverType; // 每个误差项优化变量维度为3,误差值维度为1 typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType; // 线性求解器类型 // 梯度下降方法,可以从GN, LM, DogLeg 中选 auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton( g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>())); g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型 optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 设置求解器 optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打开调试输出 // 往图中增加顶点:待优化的参数。 //图优化的原理就是:不停的调整顶点位姿(参数)来使连接到顶点的边(误差函数)最优。 CurveFittingVertex *v = new CurveFittingVertex(); v->setEstimate(Eigen::Vector3d(ae, be, ce)); v->setId(0); optimizer.addVertex(v); // 往图中增加边:每个误差函数 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { CurveFittingEdge *edge = new CurveFittingEdge(x_data[i]); edge->setId(i); edge->setVertex(0, v); // 设置连接的顶点 edge->setMeasurement(y_data[i]); // 观测数值// 信息矩阵:协方差矩阵之逆,乘上一阶导数值用来决定当前梯度对全局梯度的贡献度。信息越清晰表明当前梯度越重要。// 即人为的根据先验概率控制误差函数的权重。 edge->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1>::Identity() * 1 / (w_sigma * w_sigma)); optimizer.addEdge(edge); } // 执行优化 cout << "start optimization" << endl; chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); optimizer.initializeOptimization(); optimizer.optimize(10); chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1); cout << "solve time cost = " << time_used.count() << " seconds. " << endl; // 输出优化值 Eigen::Vector3d abc_estimate = v->estimate(); cout << "estimated model: " << abc_estimate.transpose() << endl; return 0;} |





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
2021-11-15 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/88675419
2021-11-15 鱼眼相机矫正
2021-11-15 双一流博士整理的计算机视觉学习路线(深度学习+传统图像处理)
2020-11-15 python WGS84和ECEF坐标的转换
2017-11-15 为什么样本方差(sample variance)的分母是 n-1?