如果想深入了解IMU和GPS融合原理,可以看看这篇文章: 重读经典《Quaternion kinematics for the error-state Kalman filter》,这也是Coursera课程关于这一项目的参考文献。
(124条消息) 动手学无人驾驶(6):基于IMU和GPS数据融合的自车定位_自动驾驶小学生的博客-CSDN博客_基于imu和gps数据融合的自车定位

大家可以先看看下面这个视频,对本项目要介绍的内容有个初步了解,视频链接为:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1cE411D7Y9?p=18
Coursera 自动驾驶教程:Part2 - State Estimation and Localization for Self-Driving Cars
文章目录






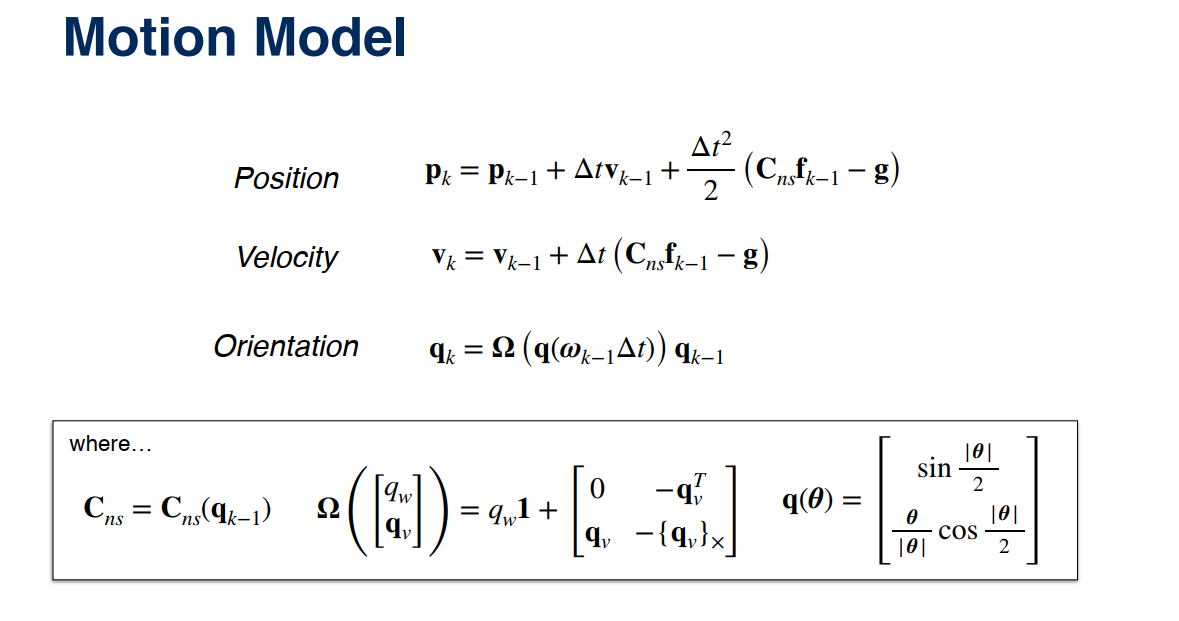



3.4 Sensor Fusion
介绍完理论部分,下面我们开始一步步实现代码部分。
(1)使用IMU数据进行更新,需要注意旋转矩阵的计算。

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | # 1. Update state with IMU inputsC_ns = Quaternion(*q_est[k-1]).to_mat() #rotational matrixC_ns_dot_f_km = np.dot(C_ns, imu_f.data[k-1])# 1.1 Linearize the motion model and compute Jacobiansp_est[k] = p_est[k-1] + delta_t * v_est[k-1] + (delta_t**2)/2.0 * (C_ns.dot(imu_f.data[k-1]) + g)v_est[k] = v_est[k-1] + delta_t*(C_ns.dot(imu_f.data[k-1]) + g)# Instead of using Omega, we use quaternion multiplication q_est[k] = Quaternion(axis_angle = imu_w.data[k-1] * delta_t).quat_mult_right(q_est[k-1]) |
(2)状态协方差矩阵的更新

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | # 2. Propagate uncertainty# Global orientation error, over local orientation error# See Sola technical reportF = np.identity(9)F[:3, 3:6] = delta_t * np.identity(3)#F[3:6, 6:] = -(C_ns.dot(skew_symmetric(imu_f.data[k-1].reshape((3,1)))))F[3:6,6:9] = -skew_symmetric(C_ns_dot_f_km) *delta_tQ = np.identity(6)Q[:, :3] *= delta_t**2 * var_imu_fQ[:, -3:] *= delta_t**2 * var_imu_wp_cov[k] = F.dot(p_cov[k-1]).dot(F.T) + l_jac.dot(Q).dot(l_jac.T) #uncertainty |
(3)计算kalman增益

1 2 | # 3.1 Compute Kalman GainK_k = p_cov_check.dot(h_jac.T).dot(np.linalg.inv(h_jac.dot(p_cov_check).dot(h_jac.T)+np.identity(3)*sensor_var)) |
(4)计算误差状态
1 2 | # 3.2 Compute error stateerrorState = K_k.dot(y_k - p_check) |
5)误差状态修正
1 2 3 4 5 6 | # 3.3 Correct predicted statep_hat = p_check + errorState[:3]v_hat = v_check + errorState[3:6]q_hat = Quaternion(euler=errorState[6:]).quat_mult_left(\ q_check) # left or right |
(6)修正状态协方差矩阵
1 2 | # 3.4 Compute corrected covariancep_cov_hat = (np.identity(9) - K_k.dot(h_jac)).dot(p_cov_check) |
到这一步,就完成了整个处理过程,可以看看最终的结果,途中橙色为轨迹真值位置,蓝色为估计的轨迹位置。

也可以绘制误差分布图,如下图所示,这里使用的3 σ 3\sigma3σ标准。
至此,本文要介绍的内容就结束了。基于IMU和GPS的位置定位,关键点在于IMU的运动模型,特别是四元数更新部分,里面牵涉到的变化比较多,需要留心。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
2019-11-08 触发信号装置