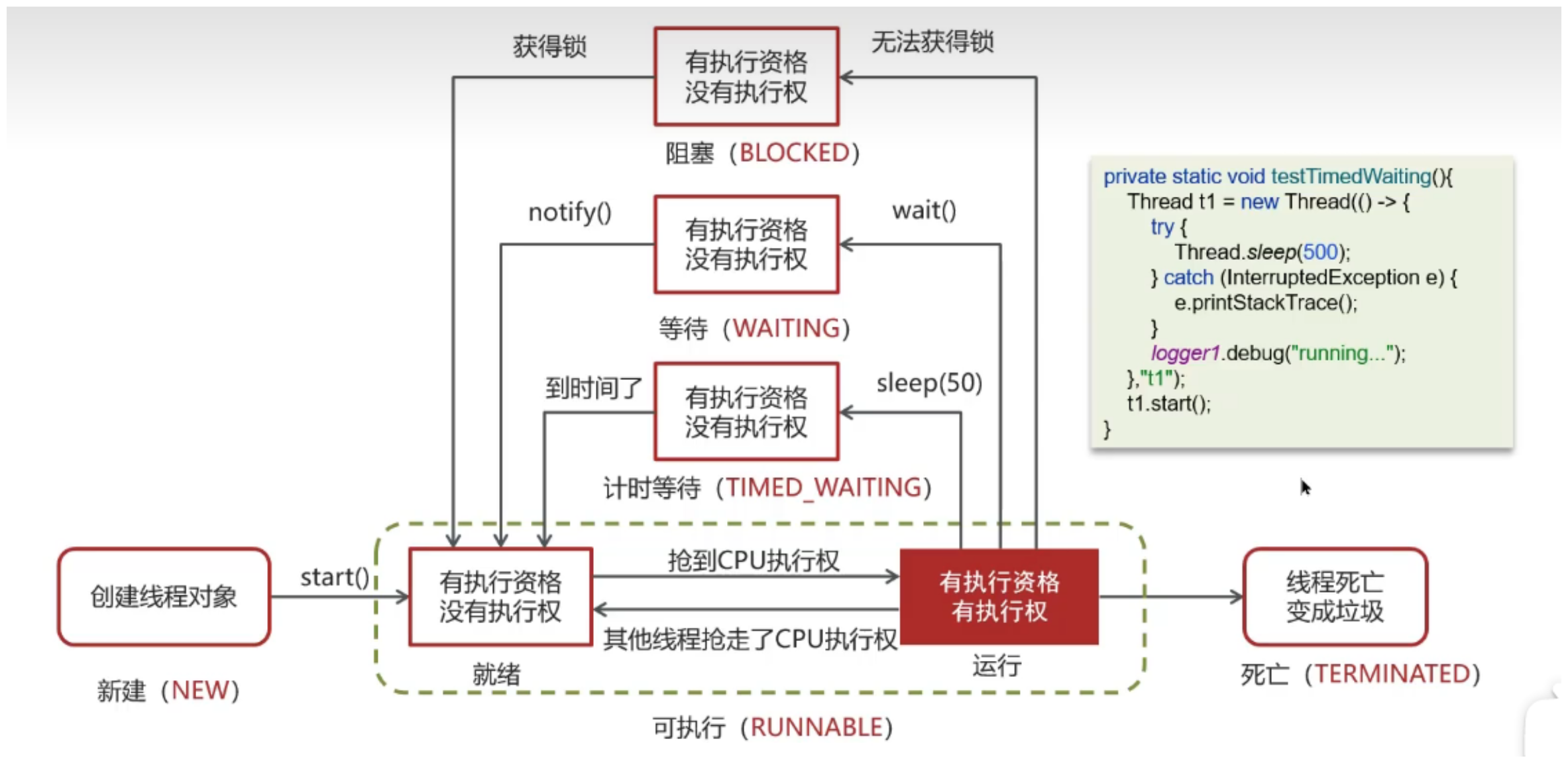
阻塞状态
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class T {
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (T.class) {
try {
Thread.sleep(6000);
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy:MM:dd hh:mm:ss sss")
.format(System.currentTimeMillis()) + ":"
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Locked");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "线程1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (T.class) {/*new Object(),不同锁,不阻塞线程2争抢时间片*/
try {
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy:MM:dd hh:mm:ss sss")
.format(System.currentTimeMillis()) + ":"
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Locked");
} catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
}, "线程2").start();
}
}
等待
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class T {
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o = new Object();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (o) {
try {
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy:MM:dd hh:mm:ss sss")
.format(System.currentTimeMillis()) + ":"
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=》5s后才能继续执行");
o.wait();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "线程1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (o) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy:MM:dd hh:mm:ss sss")
.format(System.currentTimeMillis()) + ":"
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + "唤醒");
o.notify();//注释此行,永久Waiting
} catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
}, "线程2").start();
}
}




