模型压缩

模型压缩
网络剪枝 Netwrok pruning
剪掉网络中无用的参数。
有意思的图,连接先增加后减少。
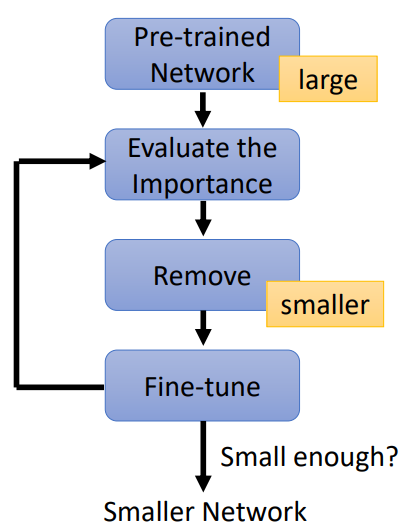
- train large model
- 评估重要性
- 参数重要性(以参数为剪枝单位)
- 比如根据权重的绝对值
- 神经元重要性(以神经元为剪枝单位)
- 比如 神经元是否为0
- 参数重要性(以参数为剪枝单位)
- 剪掉不重要的
- 微调小模型,重复执行
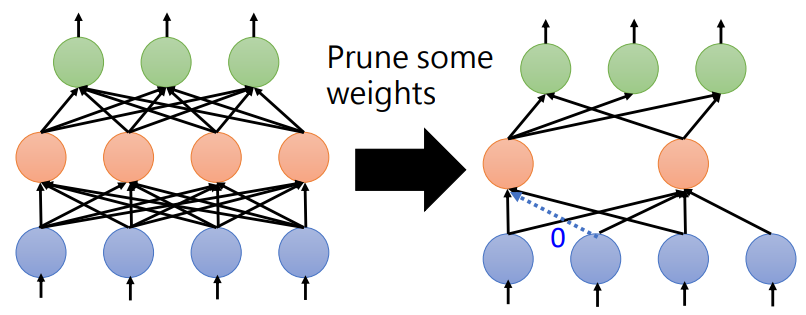
weights pruning
网络的形状会变得不规则,难以构造模型,GPU加速;虽然可以充0,但是实际网络并没有变小。
neuron pruning
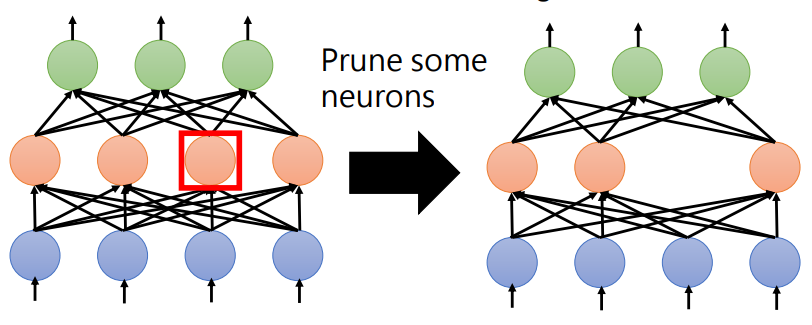
为什么舍本逐末?不直接train小模型
小网络难以训练,为什么?
-
根据大乐透假说 Lottery Ticket Hypothesis
可以理解为增加试验次数,样本量等,海选总会有好的;大模型包含了很多小的子模型
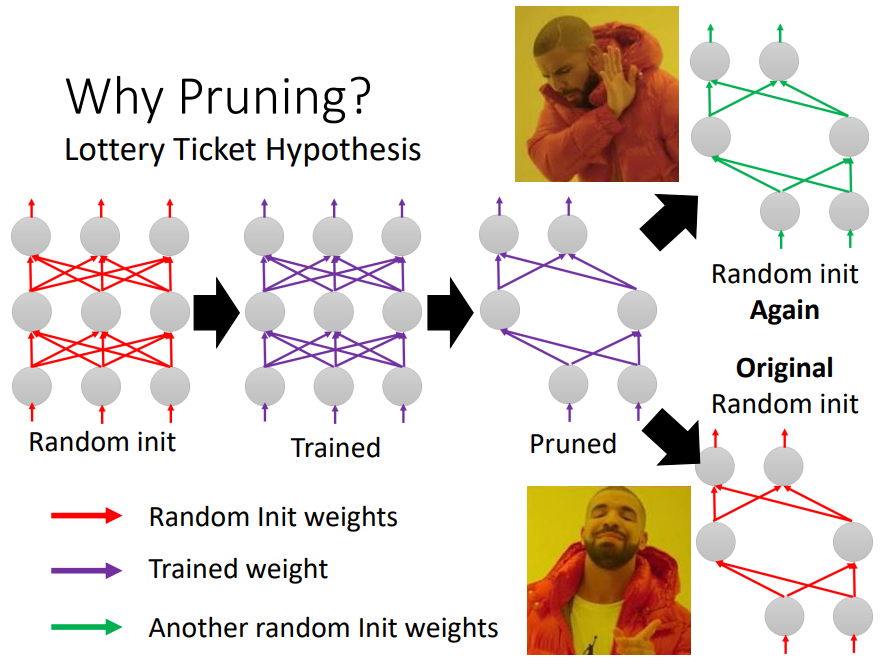
调大学习率,也许会得到和大乐透假说不一样的结果。
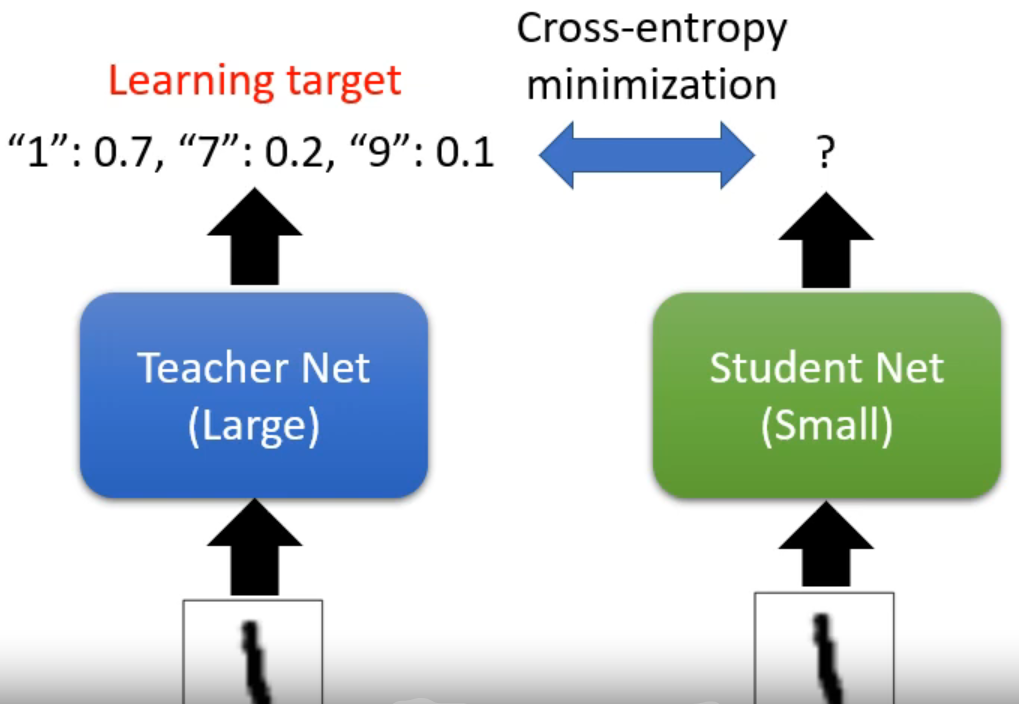
知识蒸馏 knowledge Distillation
Student Net 拟合Teacher Net 的输出
temperature softmax
使用了平滑的思想
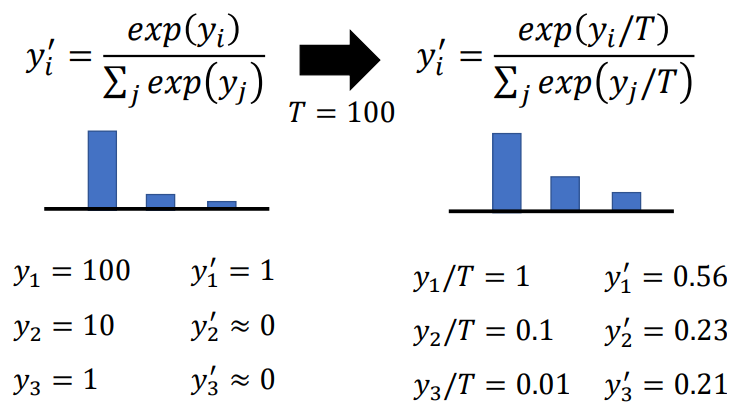
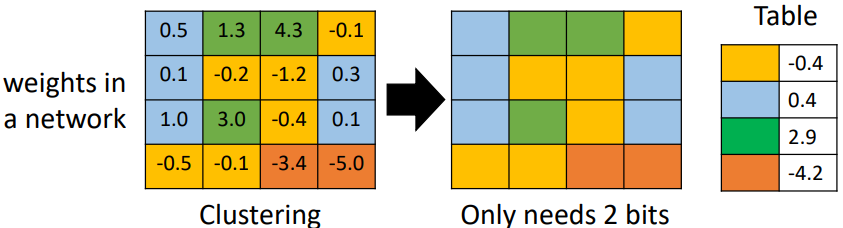
Parameter Quantization
-
混合精度
-
Weight clustering
-
常出现的参数使用更少的bits
- 如 Huffman encoding
架构设计 architecture design
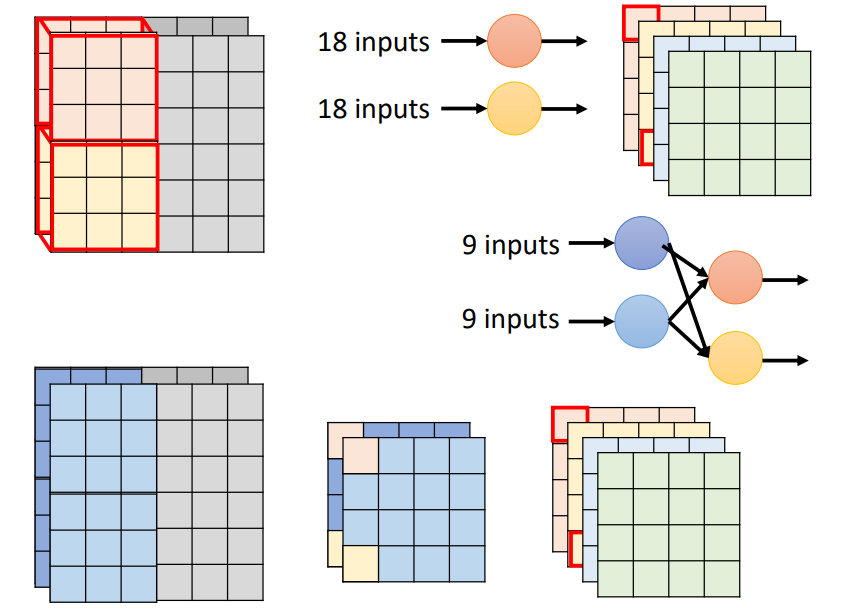
Depthwise Separable Convolution
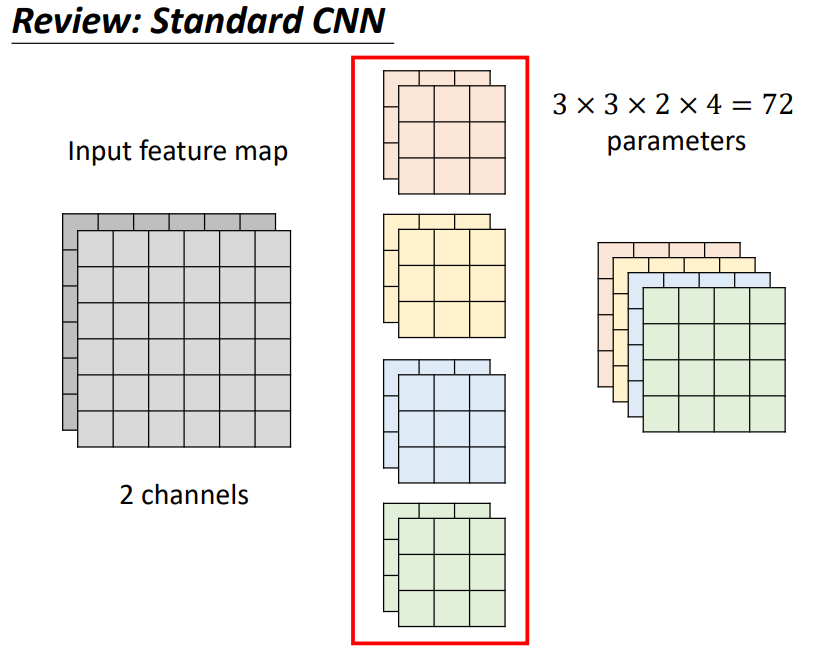
1 Depthwise Convolution
- Filter number = Input channel number
- Each filter only considers one channel.
- The filters are 𝑘 × 𝑘 matrices
- There is no interaction between channels.
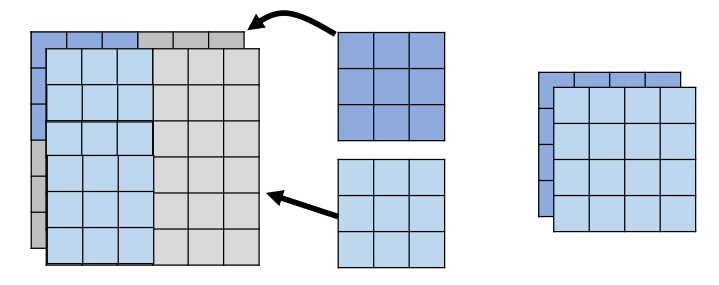
2 Pointwise Convolution
专门用来跨 channel
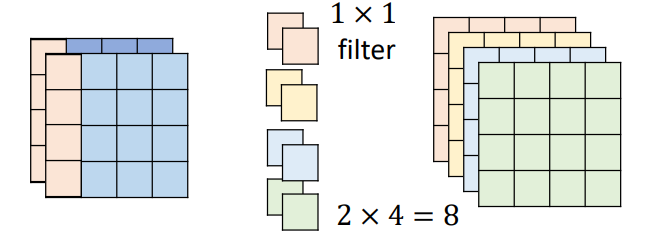
- must filter
参数变化:
I: input channel
O: output channel
原理(为什么有效)
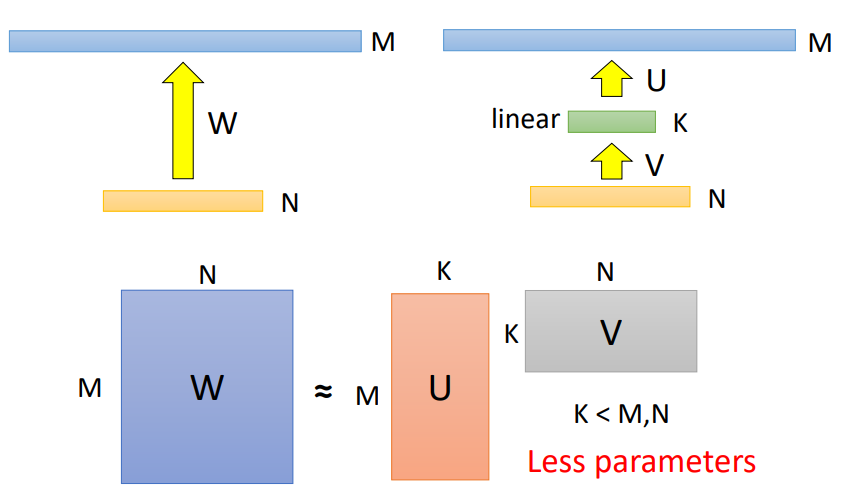
Low rank approximation
Dynamic Computation
按照资源分配
方法:
-
模型的每一层接出来训练,使用选不同的层
-
Multi-Scale Dense Network (MSDNet)
-
Dynamic width
-
Computation based on Sample Difficulty
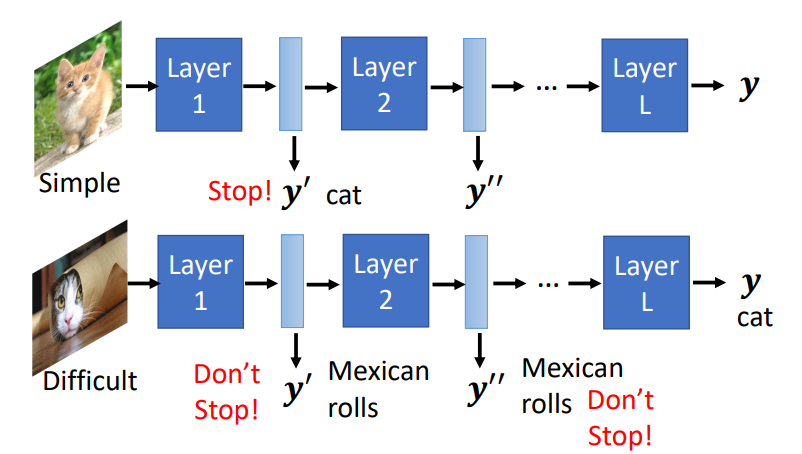
- SkipNet: Learning Dynamic Routing in Convolutional Networks
- Runtime Neural Pruning
- BlockDrop: Dynamic Inference Paths in Residual Networks
code
knowledge Distillation
来自 https://keras.io/examples/vision/knowledge_distillation/
class Distiller(keras.Model):
def __init__(self, student, teacher):
super(Distiller, self).__init__()
self.teacher = teacher
self.student = student
def compile(
self,
optimizer,
metrics,
student_loss_fn,
distillation_loss_fn,
alpha=0.1,
temperature=3,
):
""" Configure the distiller.
Args:
optimizer: Keras optimizer for the student weights
metrics: Keras metrics for evaluation
student_loss_fn: Loss function of difference between student
predictions and ground-truth
distillation_loss_fn: Loss function of difference between soft
student predictions and soft teacher predictions
alpha: weight to student_loss_fn and 1-alpha to distillation_loss_fn
temperature: Temperature for softening probability distributions.
Larger temperature gives softer distributions.
"""
super(Distiller, self).compile(optimizer=optimizer, metrics=metrics)
self.student_loss_fn = student_loss_fn
self.distillation_loss_fn = distillation_loss_fn
self.alpha = alpha
self.temperature = temperature
def train_step(self, data):
# Unpack data
x, y = data
# Forward pass of teacher
teacher_predictions = self.teacher(x, training=False)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# Forward pass of student
student_predictions = self.student(x, training=True)
# Compute losses
student_loss = self.student_loss_fn(y, student_predictions)
distillation_loss = self.distillation_loss_fn(
tf.nn.softmax(teacher_predictions / self.temperature, axis=1),
tf.nn.softmax(student_predictions / self.temperature, axis=1),
)
loss = self.alpha * student_loss + (1 - self.alpha) * distillation_loss
# Compute gradients
trainable_vars = self.student.trainable_variables
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, trainable_vars)
# Update weights
self.optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, trainable_vars))
# Update the metrics configured in `compile()`.
self.compiled_metrics.update_state(y, student_predictions)
# Return a dict of performance
results = {m.name: m.result() for m in self.metrics}
results.update(
{"student_loss": student_loss, "distillation_loss": distillation_loss}
)
return results
def test_step(self, data):
# Unpack the data
x, y = data
# Compute predictions
y_prediction = self.student(x, training=False)
# Calculate the loss
student_loss = self.student_loss_fn(y, y_prediction)
# Update the metrics.
self.compiled_metrics.update_state(y, y_prediction)
# Return a dict of performance
results = {m.name: m.result() for m in self.metrics}
results.update({"student_loss": student_loss})
return results
distiller = Distiller(student=student, teacher=teacher)
distiller.compile(
optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(),
metrics=[keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy()],
student_loss_fn=keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
distillation_loss_fn=keras.losses.KLDivergence(),
alpha=0.1,
temperature=10,
)
Quantization
quantize model
来自 https://www.tensorflow.org/model_optimization/guide/quantization/training_example?hl=zh-cn
import tensorflow_model_optimization as tfmot
quantize_model = tfmot.quantization.keras.quantize_model
# q_aware stands for for quantization aware.
q_aware_model = quantize_model(model)
# `quantize_model` requires a recompile.
q_aware_model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])
q_aware_model.summary()
quantize layer
# Create a base model
base_model = setup_model()
base_model.load_weights(pretrained_weights) # optional but recommended for model accuracy
# Helper function uses `quantize_annotate_layer` to annotate that only the
# Dense layers should be quantized.
def apply_quantization_to_dense(layer):
if isinstance(layer, tf.keras.layers.Dense):
return tfmot.quantization.keras.quantize_annotate_layer(layer)
return layer
# Use `tf.keras.models.clone_model` to apply `apply_quantization_to_dense`
# to the layers of the model.
annotated_model = tf.keras.models.clone_model(
base_model,
clone_function=apply_quantization_to_dense,
)
# Now that the Dense layers are annotated,
# `quantize_apply` actually makes the model quantization aware.
quant_aware_model = tfmot.quantization.keras.quantize_apply(annotated_model)
quant_aware_model.summary()
references
【1】https://speech.ee.ntu.edu.tw/~hylee/ml/ml2021-course-data/tiny_v7.pdf
【2】https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1lJS0ApIyi7eZ2b3GMyGxjPShI8jXM2UC
【3】https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1iuEkPP-SvCopHEN9X6xiPA8E6eACbL5u
【4】https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1CIn-Qqn9LBz-0f71Skm4vmdTDnE17uwy
【5】https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1G1_I5xoxnX4xfLUmQjxCZKw40rRjjZMQ
【6】https://colab.research.google.com/github/ga642381/ML2021-Spring/blob/main/HW13/HW13.ipynb
【7】https://github.com/nlp-with-transformers/notebooks/blob/main/08_model-compression.ipynb
【8】DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!