HDUOJ-----1541 Stars
Stars
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submission(s): 3680 Accepted Submission(s): 1449
Problem Description
Astronomers often examine star maps where stars are represented by points on a plane and each star has Cartesian coordinates. Let the level of a star be an amount of the stars that are not higher and not to the right of the given star. Astronomers want to know the distribution of the levels of the stars.
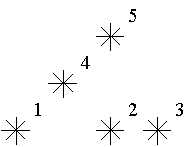
For example, look at the map shown on the figure above. Level of the star number 5 is equal to 3 (it's formed by three stars with a numbers 1, 2 and 4). And the levels of the stars numbered by 2 and 4 are 1. At this map there are only one star of the level 0, two stars of the level 1, one star of the level 2, and one star of the level 3.
You are to write a program that will count the amounts of the stars of each level on a given map.
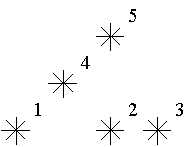
For example, look at the map shown on the figure above. Level of the star number 5 is equal to 3 (it's formed by three stars with a numbers 1, 2 and 4). And the levels of the stars numbered by 2 and 4 are 1. At this map there are only one star of the level 0, two stars of the level 1, one star of the level 2, and one star of the level 3.
You are to write a program that will count the amounts of the stars of each level on a given map.
Input
The first line of the input file contains a number of stars N (1<=N<=15000). The following N lines describe coordinates of stars (two integers X and Y per line separated by a space, 0<=X,Y<=32000). There can be only one star at one point of the plane. Stars are listed in ascending order of Y coordinate. Stars with equal Y coordinates are listed in ascending order of X coordinate.
Output
The output should contain N lines, one number per line. The first line contains amount of stars of the level 0, the second does amount of stars of the level 1 and so on, the last line contains amount of stars of the level N-1.
Sample Input
5
1 1
5 1
7 1
3 3
5 5
Sample Output
1
2
1
1
0
Source
Recommend
LL
树状数组:
对于这样的数据结构,有特定的函数,可用.....至于其中的具体原因,也非三言两语能见真相于天下....,推荐去看数据结构相关书籍...
树状数组开始有lowbit()-----》这个函数与数字的字节有关,.....,看书
代码模式很简单为:

int lowbit(int x) { return x&(-x) //-x其实是~X+1的结果.... }
然后就是一个add()
代码模式为:
1 void add(int pos , int d ) 2 { 3 while(pos<maxn) //为po【】数组的边界 4 { 5 po[pos]+=d; //d为所要加的数值 6 pos+=lowbit(pos); //pos 为数组指针.... 7 } 8 }
最后为求和:
sum();
代码模式:
int sum(int x) { int ans ; while(x>0) { ans+=po[x]; x-=lowbit(x); } }
树状数组的最普遍的用途是用来快速求解一条线段a___b的和.....
所以面对问题,就要想尽办法将他转化到这种模式上来...这样就可以用这种方法来求解了啊...
代码如下::
1 /*作者 : 龚细军,树状数组*/ 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #define maxn 35000 6 #include<cstdlib> 7 using namespace std; 8 9 int po[maxn+4],leve[maxn+4]; 10 11 int lowbit(int x) 12 { 13 return x&(-x); 14 } 15 16 void add(int x) 17 { 18 while(x<maxn) 19 { 20 po[x]++; 21 x+=lowbit(x); 22 } 23 } 24 25 int sum(int pos) 26 { 27 int ans=0; 28 while(pos>0) 29 { 30 ans+=po[pos]; 31 pos-=lowbit(pos); 32 } 33 return ans; 34 } 35 36 int main() 37 { 38 int n,y,i,x; 39 while(cin>>n) 40 { 41 memset(po,0,sizeof(po)); 42 memset(leve,0,sizeof(int)*n); 43 for(i=1;i<=n;i++) 44 { 45 /*y轴是升序的...所以不要予以考虑....*/ 46 scanf("%d %d",&x,&y); 47 x++; /*右移一位,搓掉o,那样的话,就要经历无数次的lowbit(),调用,会超时*/ 48 leve[sum(x)]++; /*放大避免x,轴有相同的数字*/ 49 add(x); 50 } 51 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 52 { 53 printf("%d\n",leve[i]); 54 } 55 } 56 return 0; 57 }
编程是一种快乐,享受代码带给我的乐趣!!!




