【数据结构与算法】非比较排序(计数排序、桶排序、基数排序)
计数排序
概念
一句话︰用辅助数组对数组中出现的数字计数,元素转下标,下标转元素
假设元素均大于等于0,依次扫描原数组,将元素值k记录在辅助数组的k位上
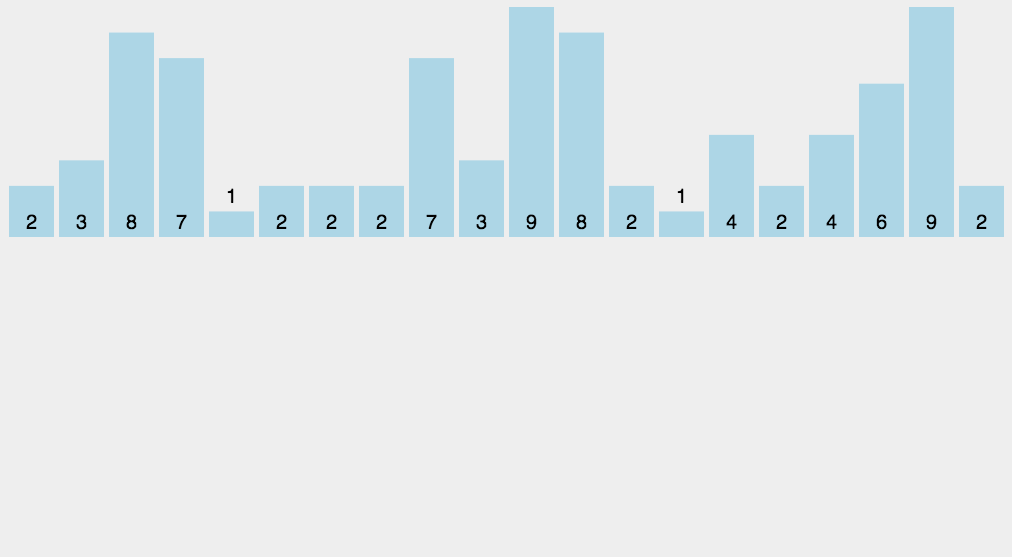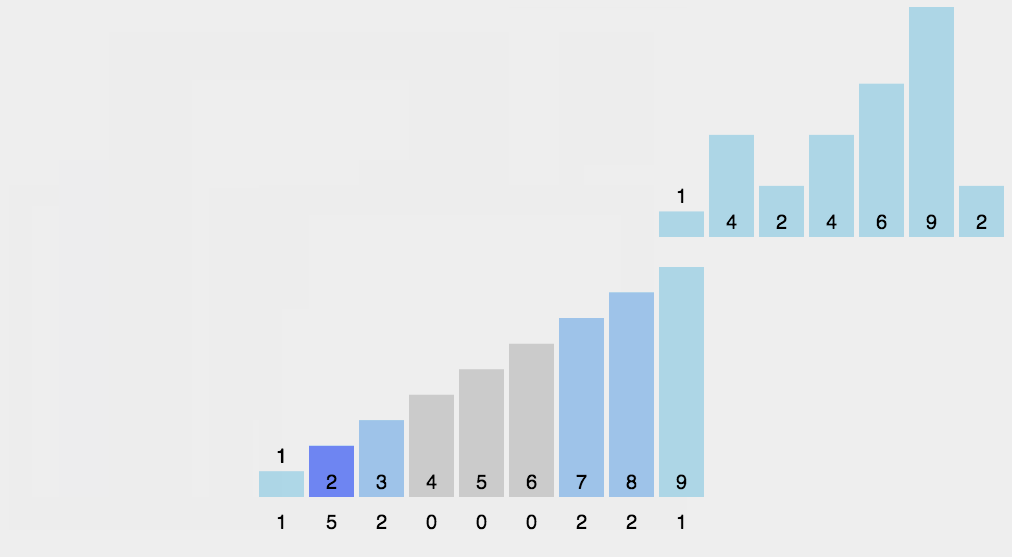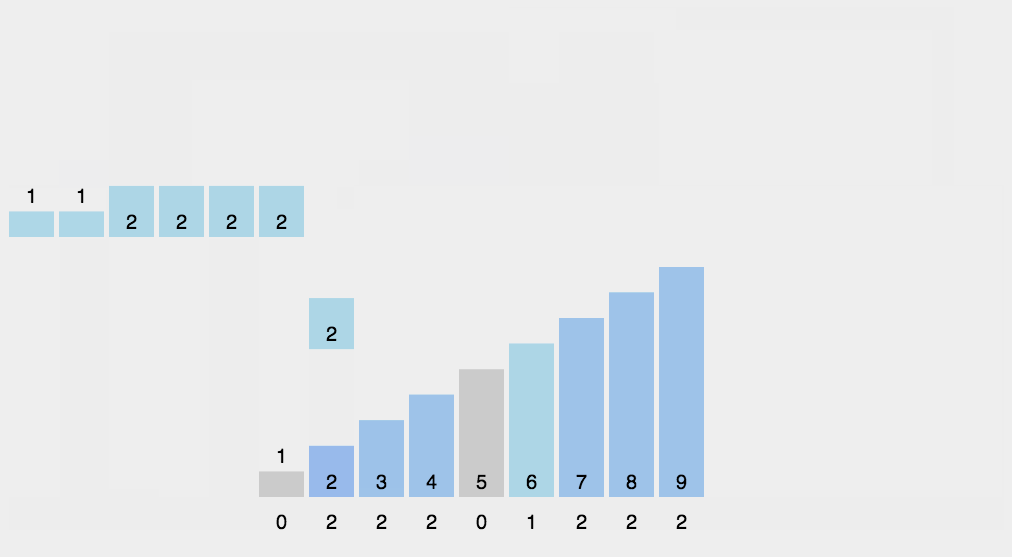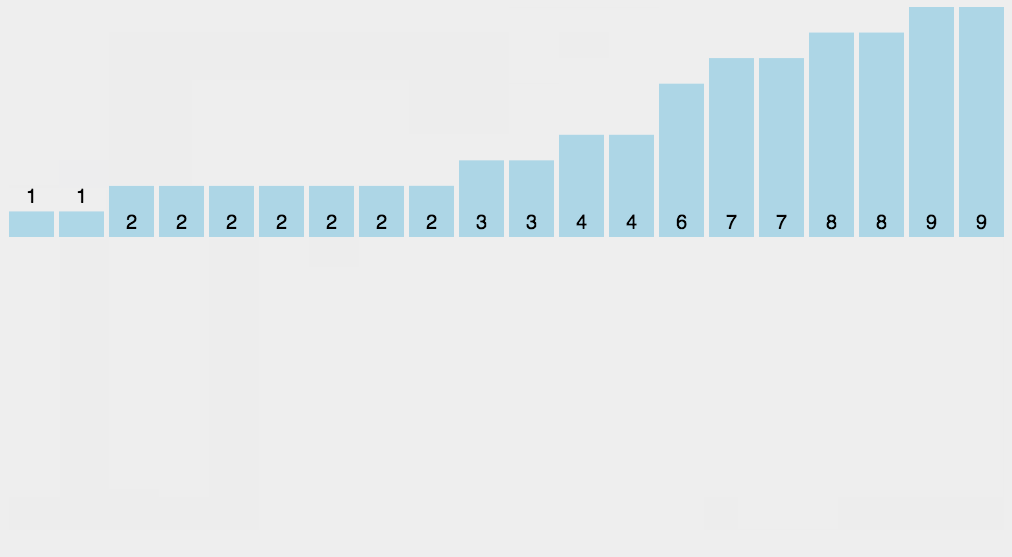
思路:开辟新的空间,空间大小为max(source)扫描source,将value作为辅助空间的下标,用辅助空间的改位置元素记录value的个数。如:9 7 5 3 1 ,helper=arr(10)。一次扫描,value为9,将helper[9]++,value为7,将helper[7]++……
如此这般之后,我们遍历helper,如果该位(index)的值为0,说明index不曾在source中出现
如果该位(index)的值为1,说明index在source中出现了1次,为2自然是出现了2次
遍历helper就能将source修复为升序排列
- 时间复杂度: 扫描一次source,扫描一次helper,复杂度为O(N+k)
- 空间复杂度:辅助空间k,k=maxOf(source)
- 非原址排序
- 稳定性:相同元素不会出现交叉,非原址都是拷来拷去
- 如果要优化一下空间,可以求minOf(source),helper的长度位max-min+1,这样能短点
- 计数有缺陷,数据较为密集或范围较小时,适用。
代码实现
public static void countSort(int[] source) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < source.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, source[i]);
}
int[] helper = new int[max + 1];
for (int e : source) {
helper[e]++;
}
int current = 0; //数据回填的下标
for (int i = 1; i < helper.length; i++) {
while (helper[i] > 0) {
source[current++] = i;
helper[i]--;
}
}
}
桶排序
概念

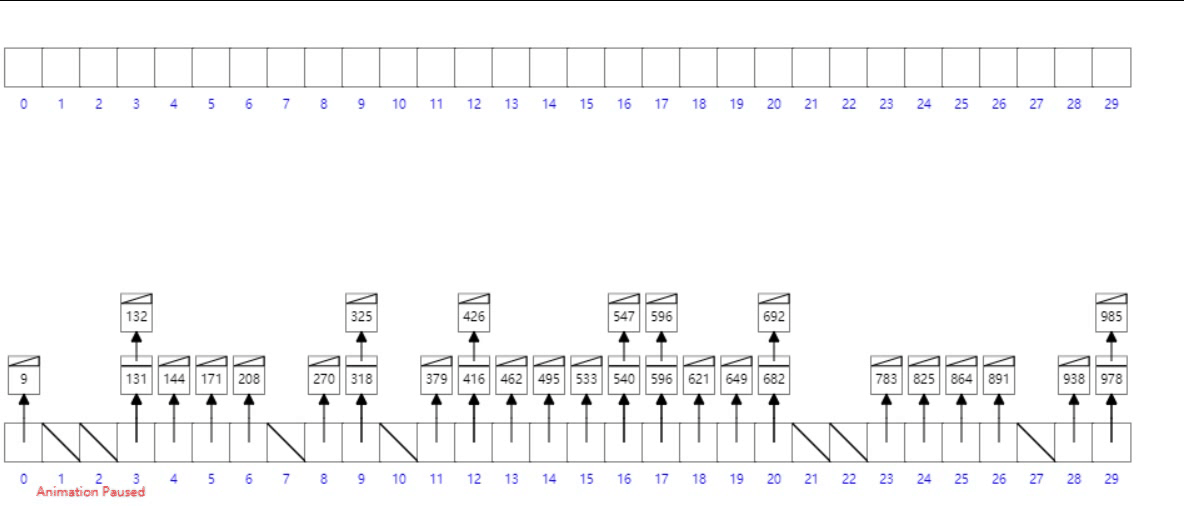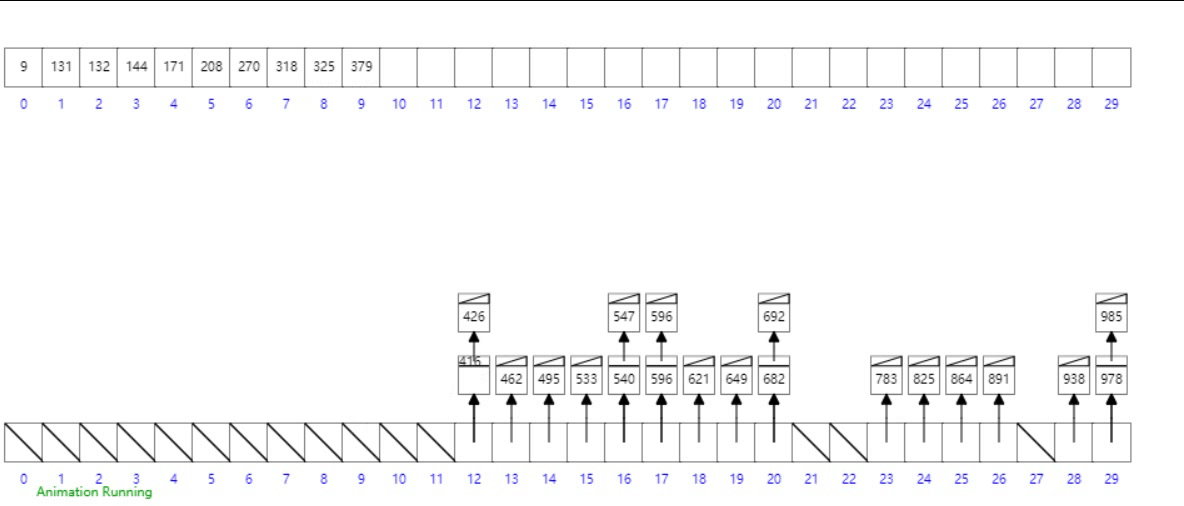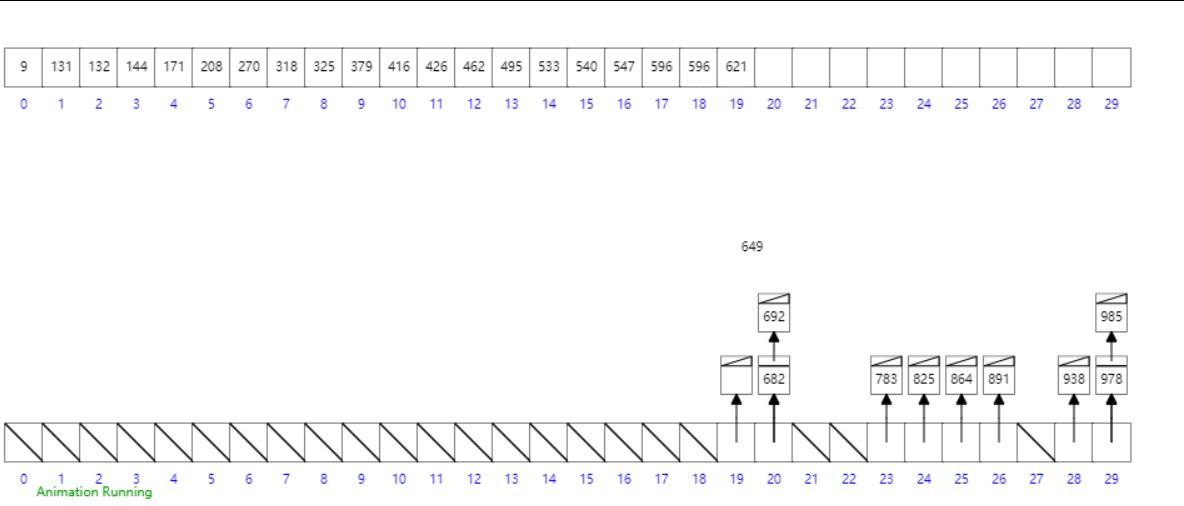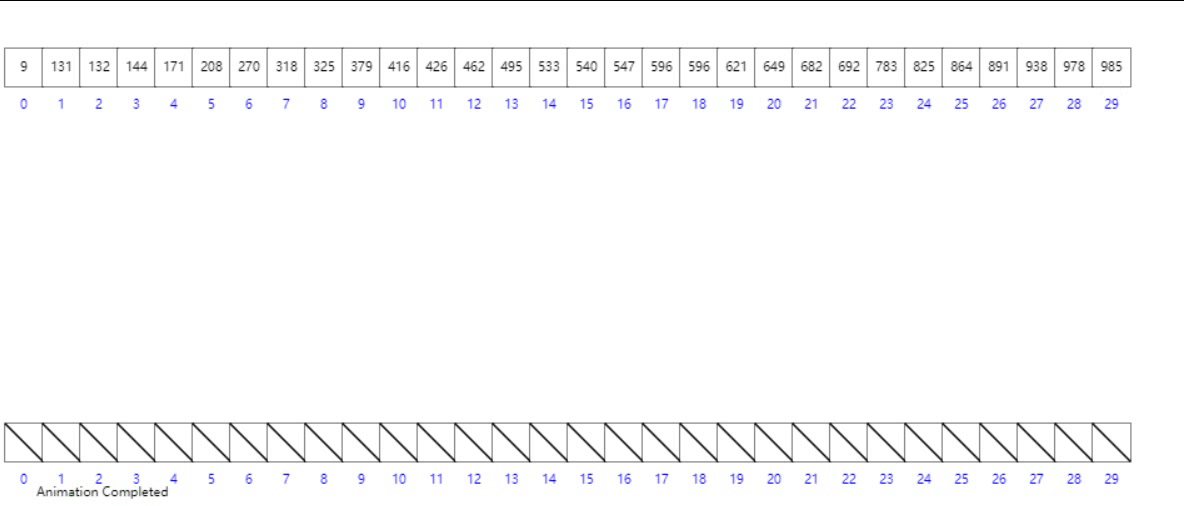
工作的原理是将数组分到有限数量的桶子里。每个桶子再个别排序(有可能再使用别的排序算法或是以递归方式继续使用桶排序进行排序)。
- 设置一个定量的数组当作空桶;
- 遍历输入数据,并且把数据一个一个放到对应的桶里去;
- 对每个不是空的桶进行排序;
- 从不是空的桶里把排好序的数据拼接起来。
- 最后按照数组下标遍历链表即可
桶排序是鸽巢排序的一种归纳结果。当要被排序的数组内的数值是均匀分配的时候,桶排序使用线性时间(Θ(n))。
但桶排序并不是 比较排序,他不受到 O(n log n) 下限的影响。
- 时间复杂度: O(N+C),其中C=N*(logN-logM)
- 空间复杂度:N+M,M为桶的个数
- 非原址排序
- 稳定性:稳定
桶排序假设数据会均匀入桶,在这个前提下,桶排序很快!
代码实现
链表定义
class LinkedNode{
LinkedNode next;
int value;
LinkedNode(int value){
this.value = value;
}
}
桶排序
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2,3,6,5,2,4,8,6};
sort(arr);
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
// 根据桶的个数来确定hash函数,这份代码适合桶的个数等于数组长度
private static int hash(int element, int max, int length) { //哈希规则
return (element * length) / (max + 1);
}
private static void sort(int[] arr) {
int length = arr.length;
LinkedNode[] bucket = new LinkedNode[length]; // 桶的个数=length
int max = maxOf(arr);// 求max
// 入桶
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int value = arr[i];//扫描每个元素
int hash = hash( arr[i], max, length ); // 桶的下标
if (bucket[hash] == null) {
bucket[hash] = new LinkedNode( value ); // 初始化链表表头
} else {
insertInto( value, bucket[hash], bucket, hash ); // 插入链表
}
}
int k = 0; // 记录数组下标
//出桶,回填arr
for (LinkedNode node : bucket) {
if (node != null) {
while (node != null) {
arr[k++] = node.value;
node = node.next;
}
}
}
}
private static int maxOf(int[] arr) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int num: arr){
max = Math.max(max,num);
}
return max;
}
private static void insertInto(int value, LinkedNode head, LinkedNode[] bucket, int hash) {
LinkedNode newNode = new LinkedNode( value );
//小于头节点,放在头上
if (value <= head.value) {
newNode.next = head;
// 替换头节点
bucket[hash] = newNode;
return;
}
/*往后找第一个比当前值大的节点,放在这个节点的前面*/
LinkedNode p = head;
LinkedNode pre = p;
while (p != null && value > p.value) {
pre = p;
p = p.next;
}
if (p == null) { // 跑到末尾了
pre.next = newNode;
} else { // 插入pre和p之间
pre.next = newNode;
newNode.next = p;
}
}
基数排序
概念

思路:是一种特殊的桶排序
初始化0-9号十个桶,
按个位数字,将关键字入桶,入完后,依次遍历10个桶,按检出顺序回填到数组中,如
321 322 331 500 423 476 926
0:500
1:321 331
2:322
3:423
4:无
5:无
6:476 926
检出后数组序列为: 500 321 331 423 476 926,然后取十位数字重复过程一,得到
0:500
1:无
2:321 423 926
3:331
4:无
5:无
7:476
检出后数组序列为: 500 321 423 926 331 476,然后取百位数字重复过程一,得到
0:无
1:无
2:无
3:321 331
4:423 476
5:500
9:926
检出后数组序列为: 321 331 423 476 500 926,已然有序
但是我们应该继续入桶,不过因为再高位全部是0了,这些元素会按顺序全部进入0号桶,这时0号桶的size==数组的size,这时结束标志
最后再回填到数组,数组就是升序排列的了
代码实现
法一:ArrayList实现二维数组(形象表示桶)
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2, 6, 3, 2, 5, 32, 42, 2, 5, 4, 7, 9, 3};
radixSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
// 10个桶,每个桶装的数个数不定,适合用数组加ArrayList
private static ArrayList[] bucket = new ArrayList[10];
// 初始化桶
static {
for (int i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
bucket[i] = new ArrayList();
}
}
public static void radixSort(int[] arr, int begin, int end) {
int d = 1; //入桶依据的位初始化为1
int dNum = maxbits(arr, begin, end); //获取最大数字的位数
while (d <= dNum) { //做dNum次入桶出桶操作
radixSort(arr, begin, end, d++); //依据第二个参数d入桶和出桶
}
}
private static void radixSort(int[] arr, int begin, int end, int d) {
//全部入桶
for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
putInBucket(arr[i], getDigitOn(arr[i], d)); //把每个数字的第d位入桶
}
//每个桶中的元素依次压入原数组
int k = 0; //k是原数组下标
for (int j = 0; j < bucket.length; j++) {// 每个桶
for (Object m : bucket[j]) {
arr[k++] = (Integer) m;
}
}
clearAll(); // 记得清空桶
}
private static int getDigitOn(int num, int d) { //获取num的第d位的数字
return ((num / ((int) Math.pow(10, d - 1))) % 10);
}
private static void putInBucket(int data, int digitOn) { //入桶
bucket[digitOn].add(data);
}
private static void clearAll() { //对每个桶调用clear方法进行清空
for (ArrayList b : bucket) {
b.clear();
}
}
private static int maxbits(int[] arr, int begin, int end) { //获取数组中的最大元素的位数
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, arr[i]);
}
int dNum = 0;
while (max != 0) { //获取最大值的位数
dNum++;
max /= 10;
}
return dNum;
}
法二:前缀和数组模拟
- 首先按照数组元素的个位数组将其入桶
- 其次构造前缀和数组
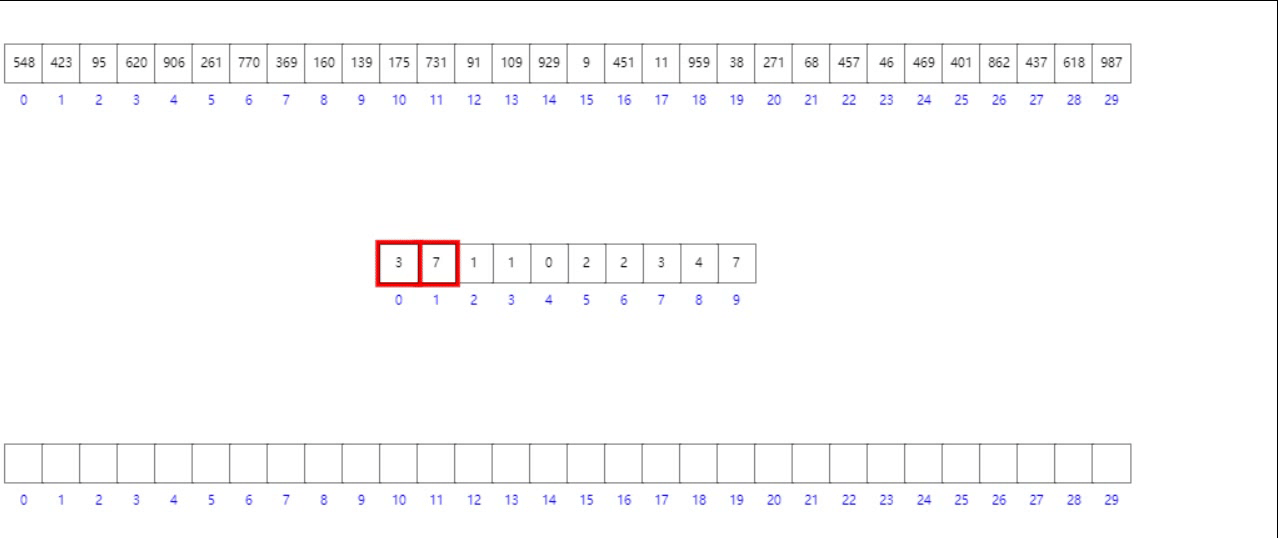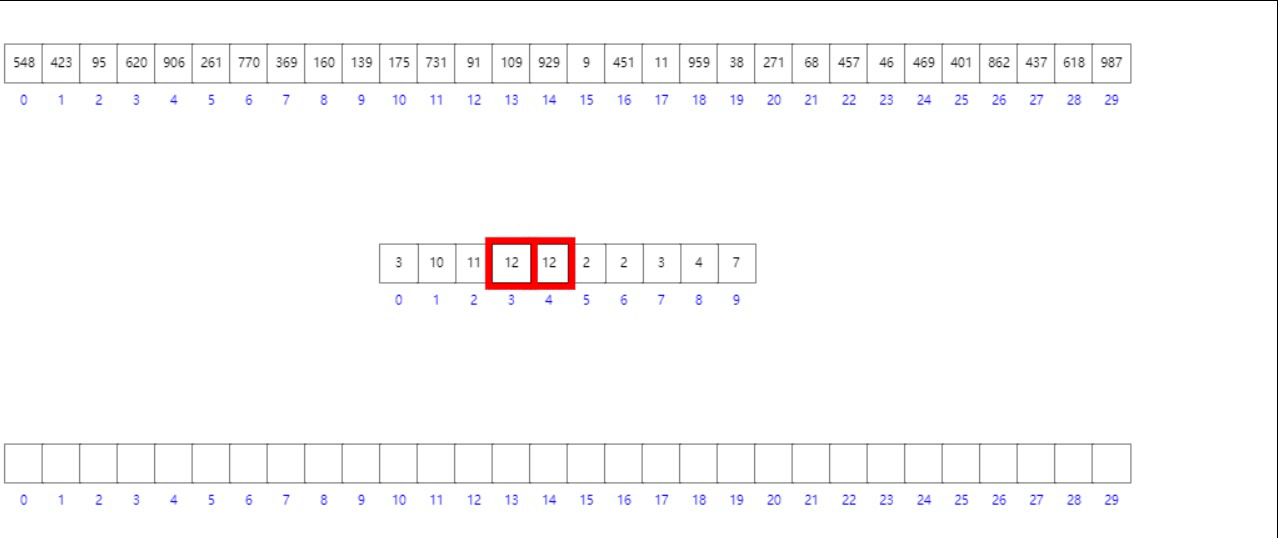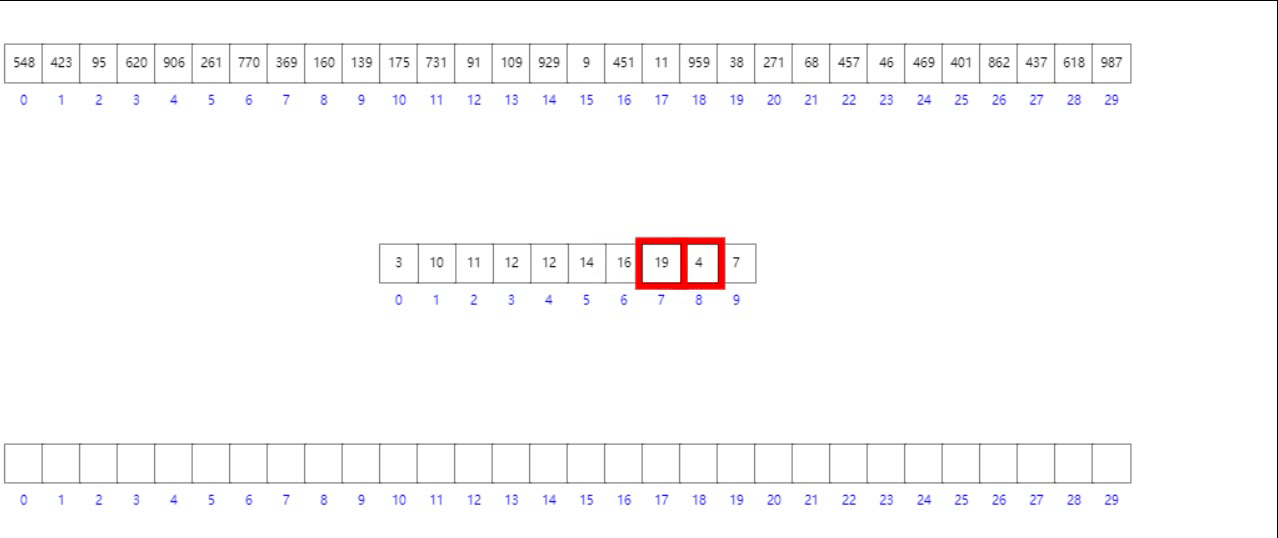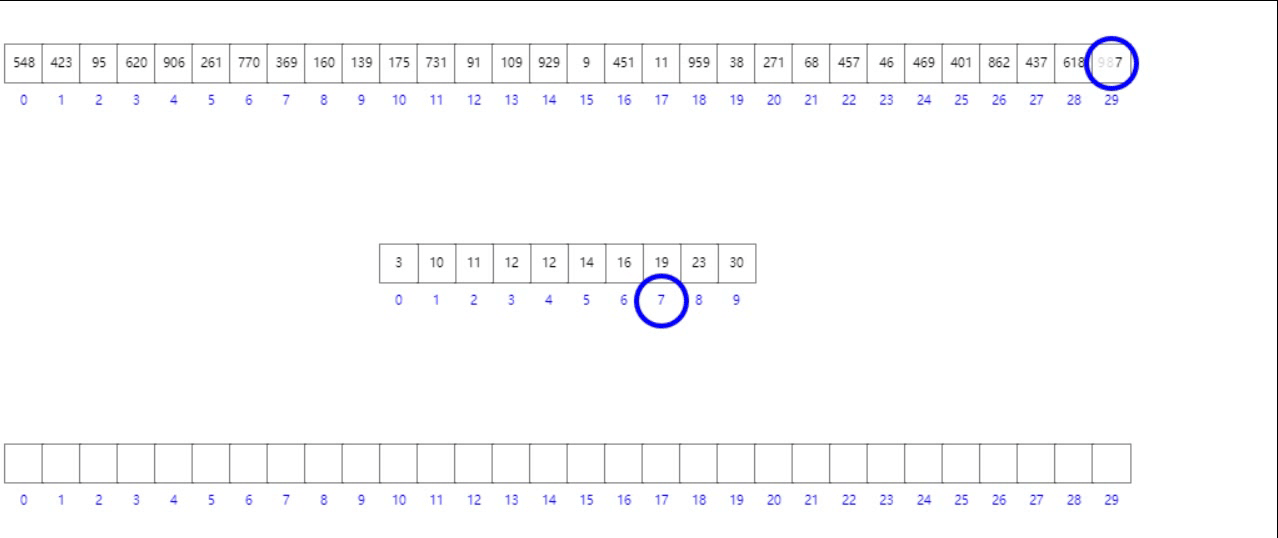
- 逆向遍历原数组,根据个位数字找到其在目标有序数组中的位置
- 循环最大数的位数次,模拟了入桶出桶过程
public static void radixSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
radixSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, maxbits(arr));
}
public static int maxbits(int[] arr) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, arr[i]);
}
int res = 0;
while (max != 0) {
res++;
max /= 10;
}
return res;
}
public static void radixSort(int[] arr, int begin, int end, int digit) {
final int radix = 10;
int i = 0, j = 0;
int[] bucket = new int[end - begin + 1];
for (int d = 1; d <= digit; d++) {
int[] count = new int[radix];
for (i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
j = getDigit(arr[i], d);
count[j]++;
}
for (i = 1; i < radix; i++) { //获得前缀和数组
count[i] = count[i] + count[i - 1];
}
for (i = end; i >= begin; i--) { //倒叙遍历原数组
j = getDigit(arr[i], d);
bucket[count[j] - 1] = arr[i];
count[j]--;
}
for (i = begin, j = 0; i <= end; i++, j++) { //辅助数组拷贝回原数组
arr[i] = bucket[j];
}
}
}
public static int getDigit(int x, int d) { //获取数字x的第d位数字
return ((x / ((int) Math.pow(10, d - 1))) % 10);
}
-
时间复杂度O(kN)
假设最大的数有k位,就要进行k次入桶和回填,每次入桶和回填是线性的,所以整体复杂度为kN,
其中k为最大数的10进制位数 -
空间复杂度O(N+k)
桶是10个,10个桶里面存n个元素,这些空间都是额外开辟的,所以额外的空间是N+k,k是进制 -
非原址排序
-
稳定性:稳定
假设有相等的元素,它们会次第入桶,次第回数组,不会交叉,所以是稳定的

