AOE网与关键路径
声明:图片及内容基于https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1BZ4y1T7Yx?from=articleDetail
原理
AOE网

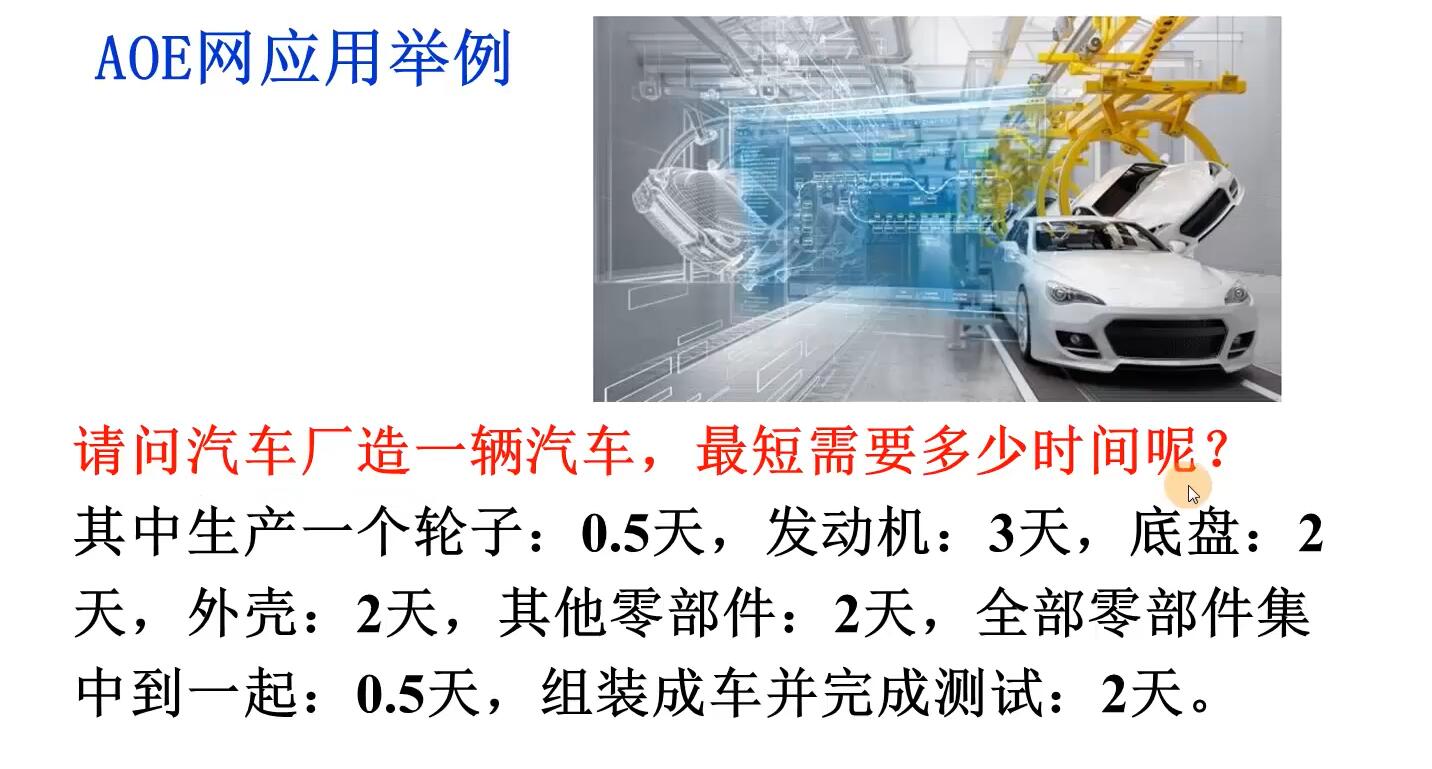
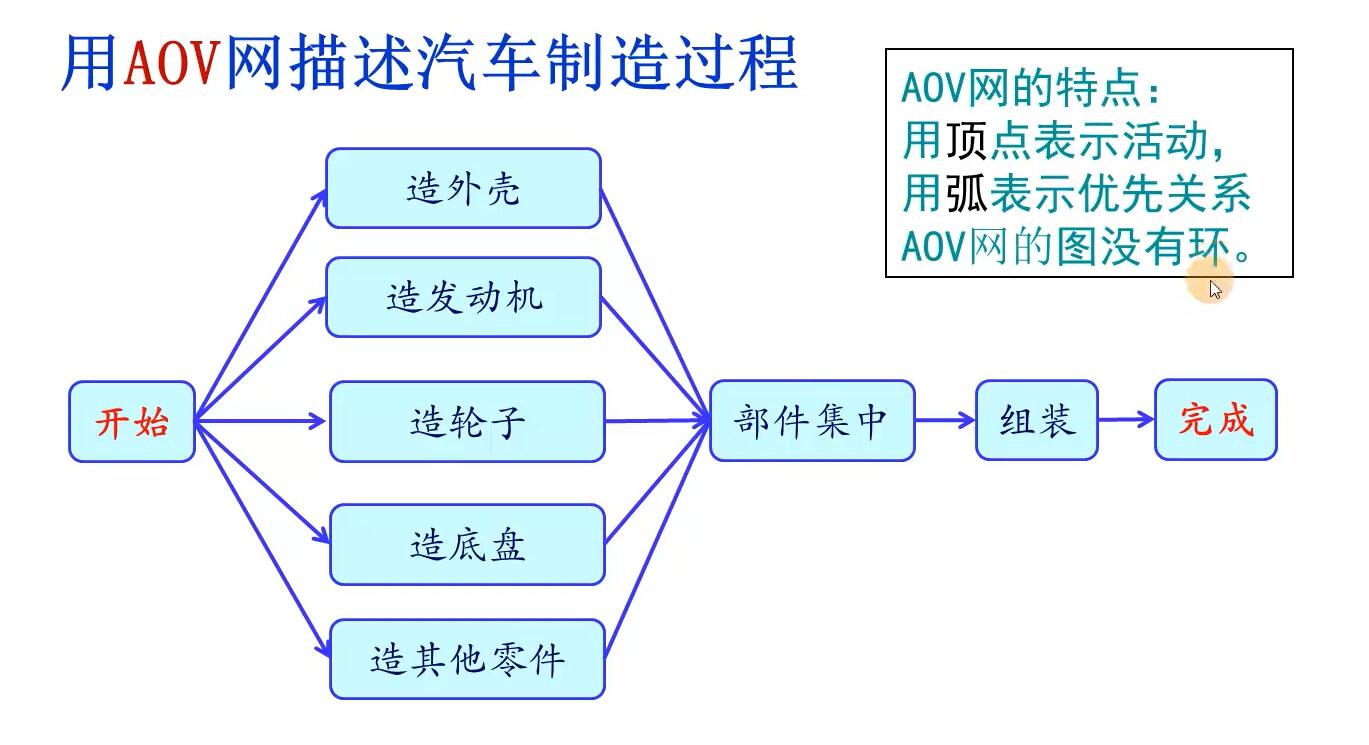

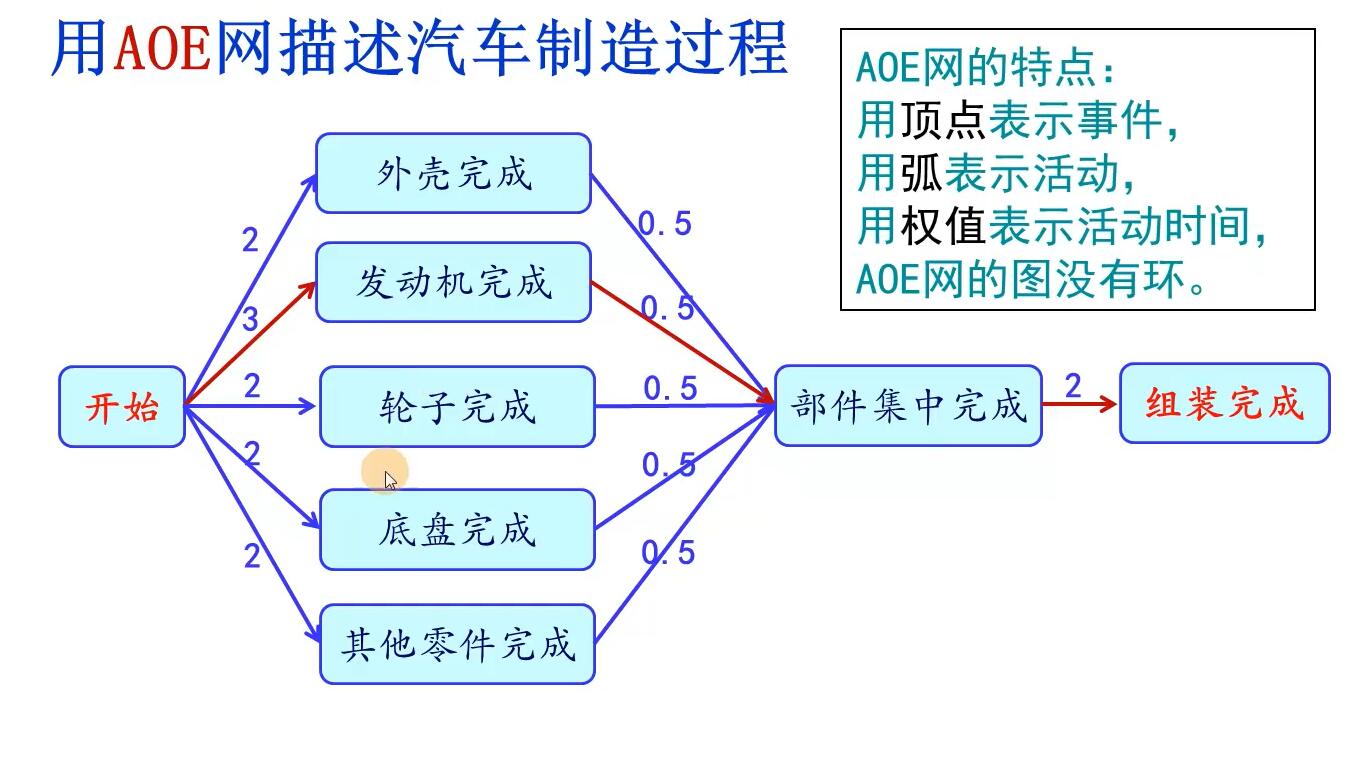
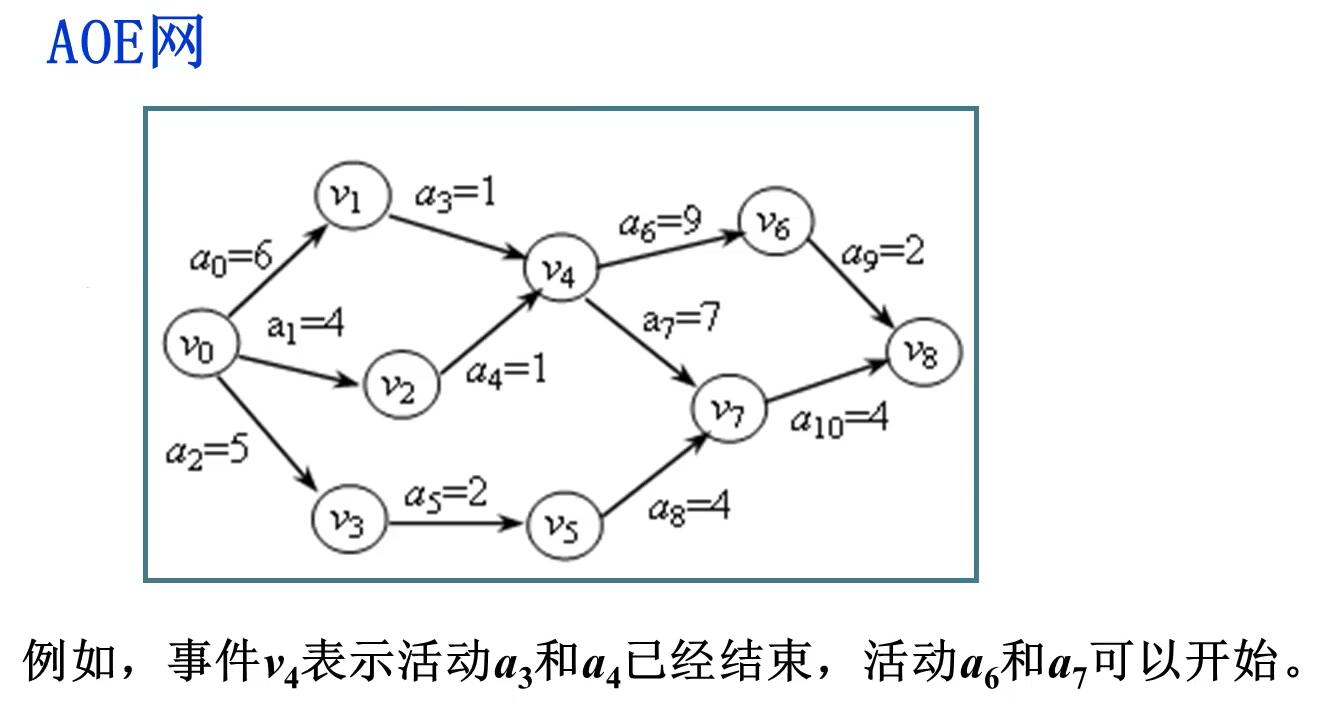
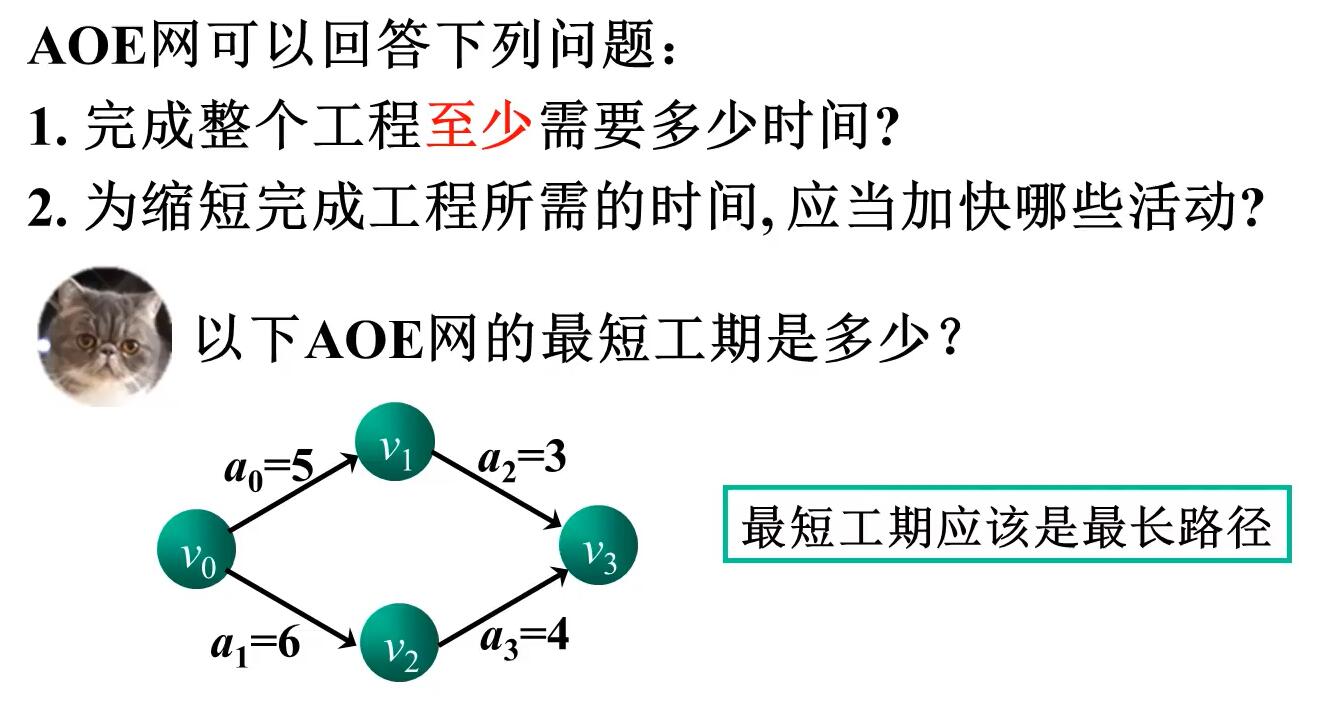
关键路径


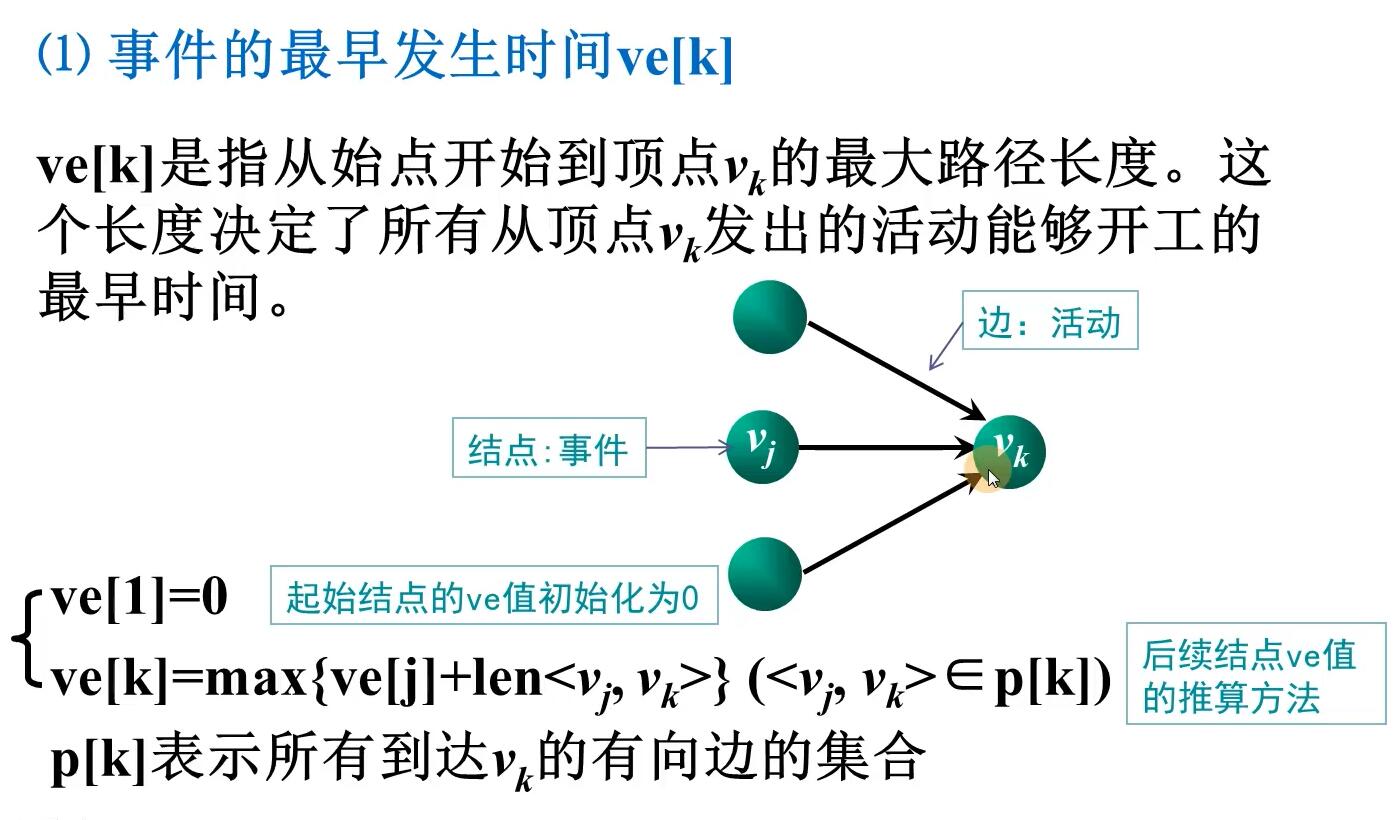
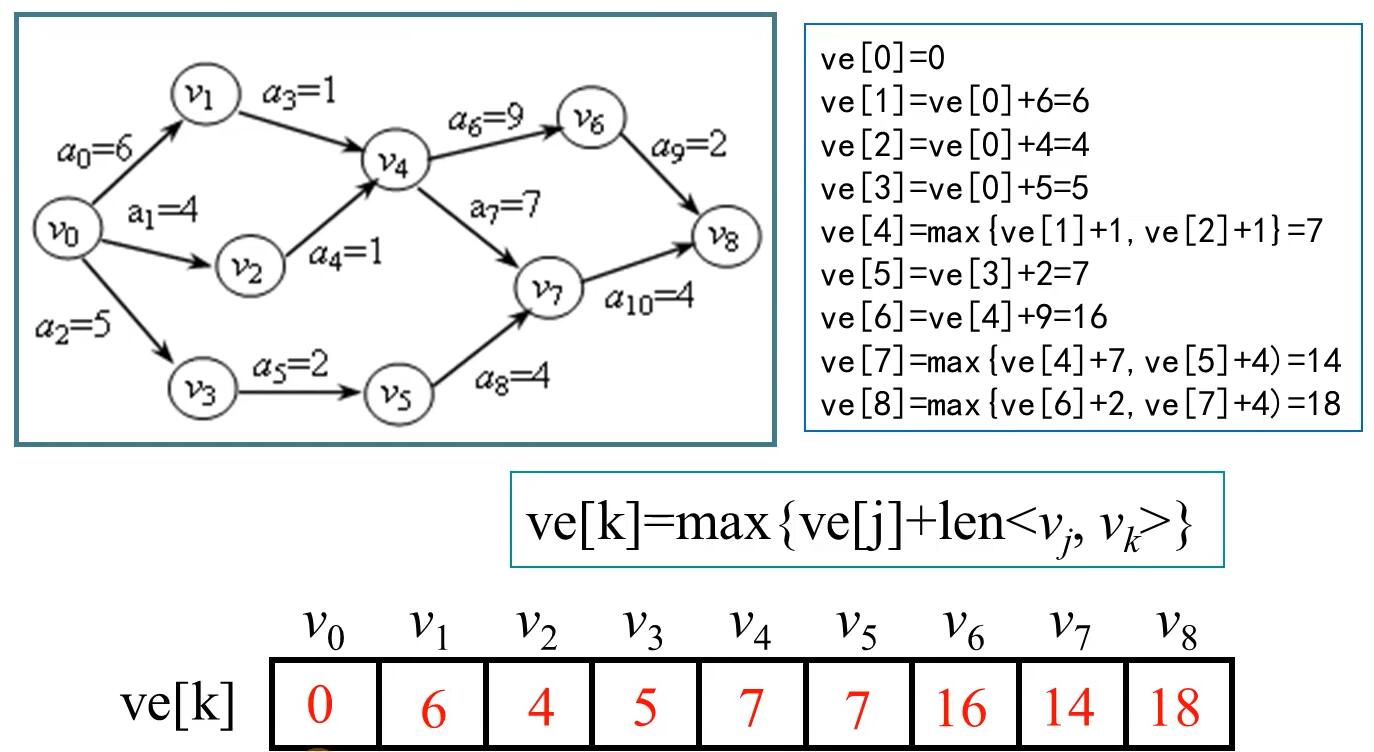
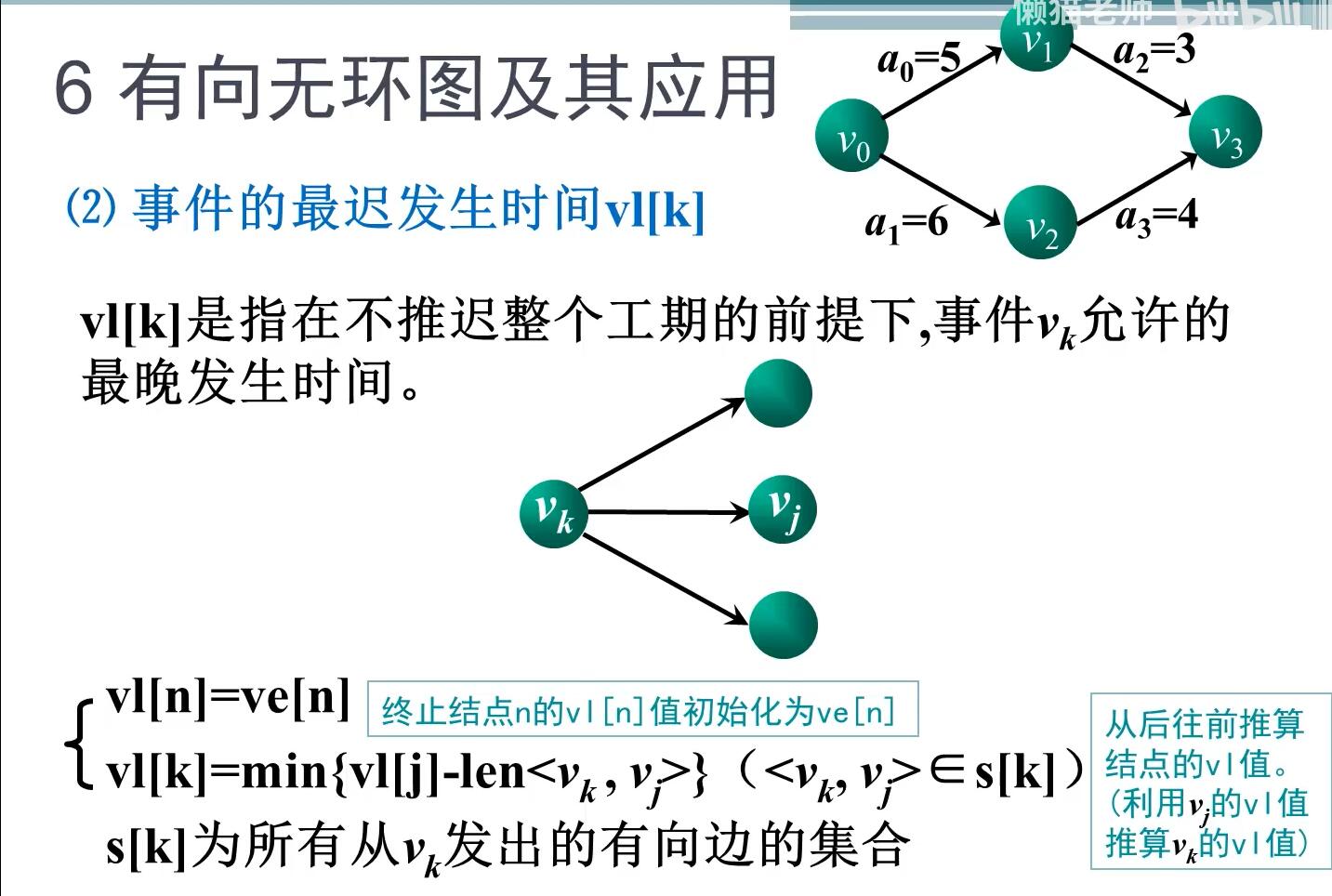

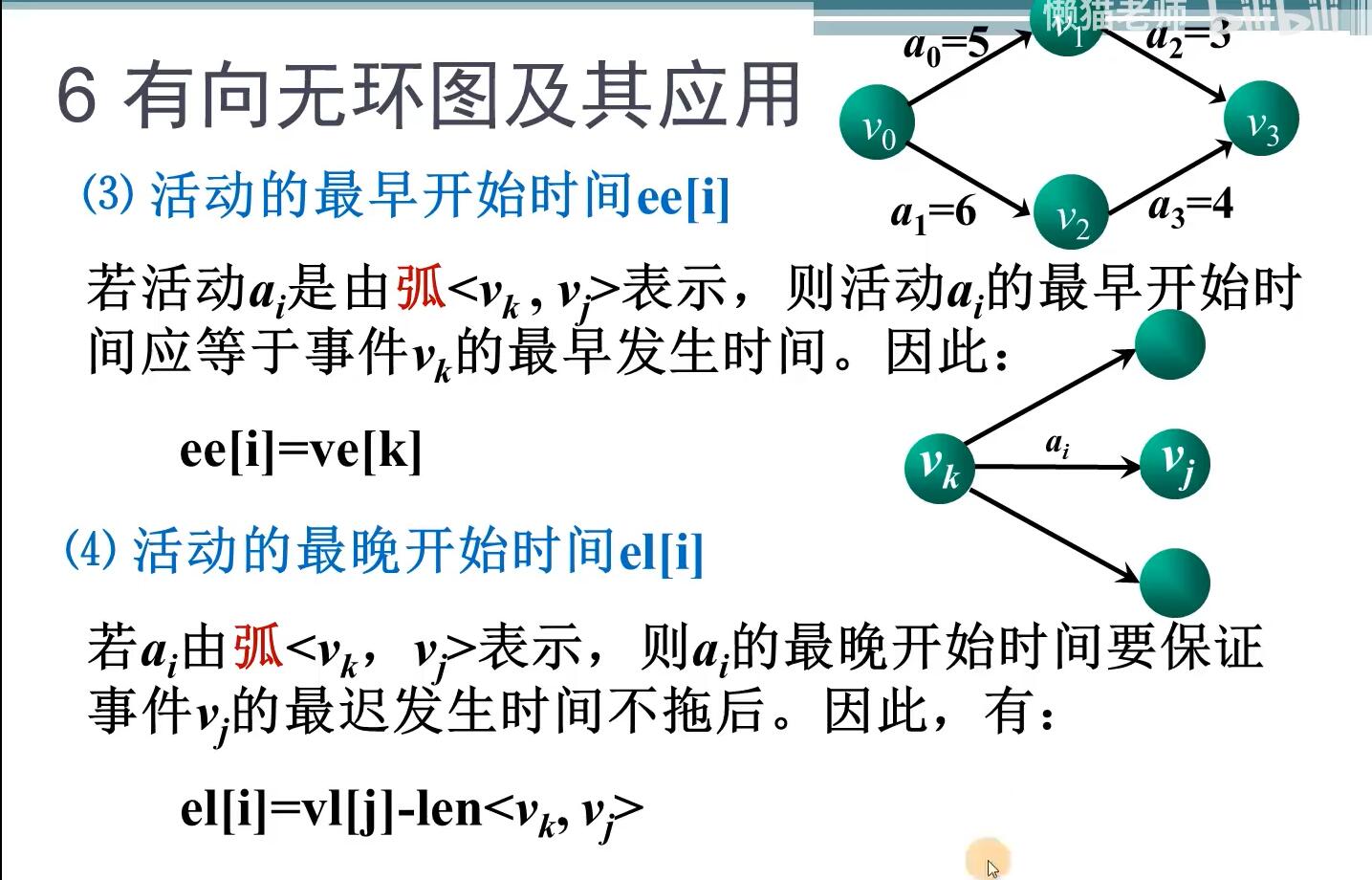
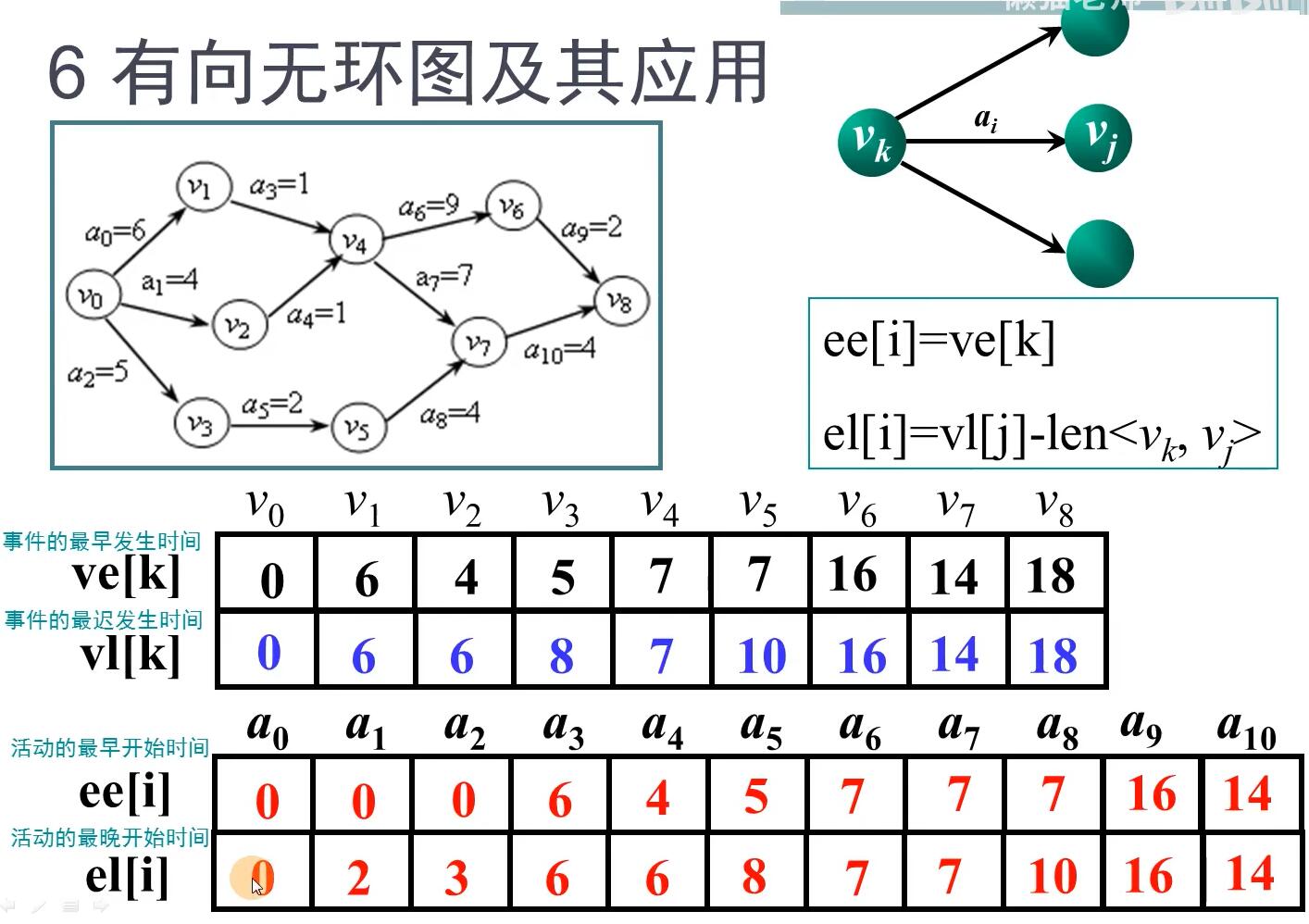
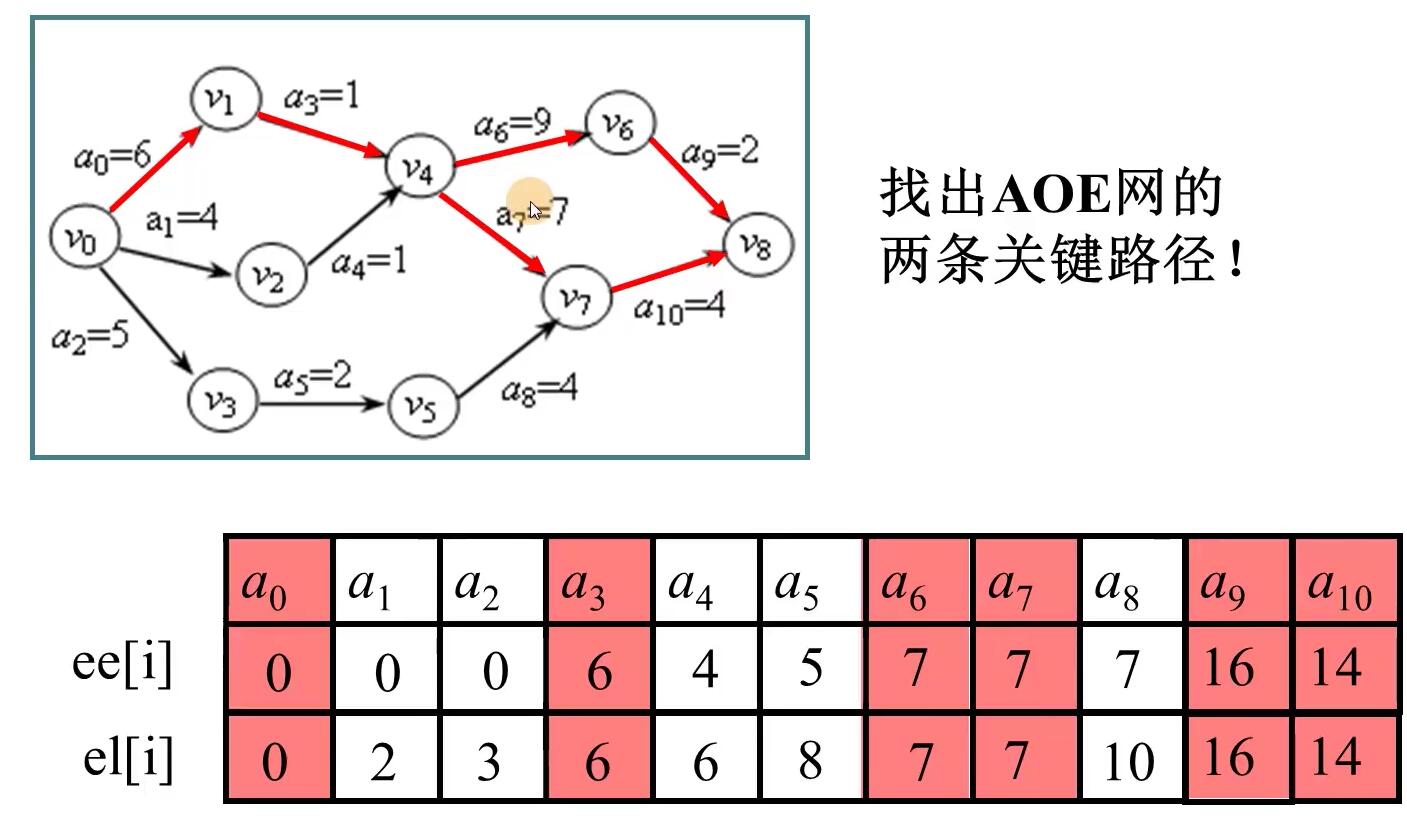

数据结构

核心代码
TopologicalSort
/*
TopologicalSort用于实现拓扑排序
参数:result用来保存处理过的拓扑排序顶点;count用来保存处理过的拓扑排序顶点的个数
功能:进行拓扑排序,将找到的拓扑顶点序号存入result数组(result可以看成一个栈,count可以看成是栈顶指针)
增加的功能:用注释=====标识,在拓扑排序的同时计算ve数组的值[事件最早发生时间]
*/
bool ALGraph ::TopologicalSort(int result[], int &count){
int stack[MAX_VERTEX]; //把顶点对应的下标压入堆栈
int top = -1;
int inVex; //用来保存从堆栈中弹出的顶点(下标)[书上的j,代表一个边的起始顶点]
int outVex;//遍历一个顶点的所有邻接边结点时,用outVex暂存当前处理的顶点[书上的k,代表一个边的终止顶点]
ArcNode *p;
//初始化事件最早发生时间ve数组=====
for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
ve[i]=0;
}
//遍历顶点表,把入度为0的压栈
for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
if(adjList[i].in==0){
stack[++top]=i;
}
}
//完成拓扑排序
count=0;
while(top!=-1){
inVex=stack[top--];
result[count]=inVex;
count++;
p=adjList[inVex].firstEdge;
while(p){
outVex=p->adjvex;
adjList[outVex].in--;
if(adjList[outVex].in==0)
stack[++top]=outVex;
if(ve[inVex]+p->weight>ve[outVex])
ve[outVex]=ve[inVex]+p->weight;
p=p->next;
}
}
//判断拓扑排序是否正确
if(count==vertexNum)
return true;
return false;
}
CriticalPath
/*
CriticalPath用于求关键路径
首先调用TopologicalSort函数检查是否是一个没有环的图
*/
bool ALGraph::CriticalPath(){
int resultStack[MAX_VERTEX]; //存储拓扑排序结果序列(存储下标)
int resultTop; //拓扑排序有效顶点个数(栈顶指针)
ArcNode *p;
int i,count;
int inVex,outVex; //inVex,outVex,分别代表一条边的起点顶点号和终点顶点号
if(!TopologicalSort(resultStack,count)) {
return false;
}
//输出拓扑排序的顶点处理顺序
cout<<"拓扑排序的顶点处理顺序是:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
cout<<resultStack[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
//输出ve数组的值
cout<<"ve数组的值为:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
cout<<"ve["<<i<<"]="<<ve[i]<<endl;
}
//完成关键路径的求解
resultTop=count-1;
inVex=resultStack[resultTop--];
for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
vl[i]=ve[inVex];
}
while(resultTop!=-1){
inVex=resultStack[resultTop--];
p=adjList[inVex].firstEdge;
while(p){
outVex=p->adjvex;
if(vl[inVex]>vl[outVex]-p->weight)
vl[inVex]=vl[outVex]-p->weight;
p=p->next;
}
}
cout<<"vl数组的值为:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
cout<<"vl["<<i<<"]="<<vl[i]<<endl;
}
return true;
}
完整代码
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_VERTEX = 30; //图的最大顶点数
struct ArcNode /*边表*/
{
int weight; //增加权值分量,代表活动时间=====
int adjvex;
ArcNode *next;
};
struct VertexNode /*顶点表*/
{
int in; //增加入度字段-----
char vertex;
ArcNode *firstEdge;
};
class ALGraph {
private:
VertexNode *adjList; //邻接表
int vertexNum, arcNum;
int *ve, *vl; //ve数组是事件最早发生时间,vl事件最迟发生时间(数组长度跟顶点数相等)=====
public:
ALGraph(char v[], int n, int e);
~ALGraph();
void inputEdges();
bool setEdge(int vi,int vj,int weight);
void displayData();
bool TopologicalSort(int result[], int &count); //拓扑排序
bool CriticalPath(); //求关键路径
};
ALGraph:: ALGraph(char v[], int n, int e){
vertexNum = n;
arcNum = e;
adjList = new VertexNode[vertexNum];
for (int i=0; i<vertexNum; i++) {
//输入顶点信息,初始化顶点表
adjList[i].in = 0; //增加in的初始化-----
adjList[i].vertex = v[i];
adjList[i].firstEdge = NULL;
}
ve = new int[vertexNum];
vl = new int[vertexNum];
}
ALGraph ::~ALGraph(){
ArcNode *p,*pre;
//遍历顶点表数组,把顶点表指向的所有边结点删除
for(int i=0; i<vertexNum; i++){
p = adjList[i].firstEdge;
adjList[i].firstEdge = NULL;
while(p){
pre = p;
p = p-> next;
delete pre;
}
}
delete [] adjList;
delete [] ve;
delete [] vl;
}
void ALGraph ::inputEdges(){ //=====
cout << "请输入两个事件顶点编号(范围0-"<< vertexNum-1 << ")和活动时间:"<<endl;
for (int i=0; i<arcNum; i++) {
//输入边的信息存储在边表中
int vi,vj, weight;
cin >> vi >> vj >> weight; //输入边依附的两个顶点的编号
if(!setEdge(vi,vj,weight)){
cout << "输入的顶点编号超过范围或者相等,需要重新输入" << endl;
i--;
}
}
}
bool ALGraph::setEdge(int vi,int vj, int weight){ //=====
//修改setEdge函数,把vj顶点表中的入度+1 -----
ArcNode *s;
if (vi>=0 && vi<vertexNum && vj>=0 && vj<vertexNum && vi!=vj){
//创建一个边结点vj
s = new ArcNode;
s->adjvex = vj;
s->weight = weight; //=====
//把边结点vj插入到顶点表vi项的邻接表中,成为第一个结点
s->next = adjList[vi].firstEdge;
adjList[vi].firstEdge = s;
//vj顶点表中的入度+1 -----
adjList[vj].in++;
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
void ALGraph ::displayData(){
ArcNode *p;
cout << "输出图的存储情况:"<<endl;
for(int i=0; i<vertexNum; i++){
cout << "顶点" << adjList[i].vertex << "的入度为:" << adjList[i].in <<",从这个顶点发出的的边为:" << endl;//-----
p = adjList[i].firstEdge;
if (!p)
cout << "没有。"<< endl;
while(p){
cout <<"<" << i <<"," << p->adjvex<< ">" << p->weight <<endl;
p = p->next;
}
}
}
/*
TopologicalSort用于实现拓扑排序
参数:result用来保存处理过的拓扑排序顶点;count用来保存处理过的拓扑排序顶点的个数
功能:进行拓扑排序,将找到的拓扑顶点序号存入result数组(result可以看成一个栈,count可以看成是栈顶指针)
增加的功能:用注释=====标识,在拓扑排序的同时计算ve数组的值[事件最早发生时间]
*/
bool ALGraph ::TopologicalSort(int result[], int &count){
int stack[MAX_VERTEX]; //把顶点对应的下标压入堆栈
int top = -1;
int inVex; //用来保存从堆栈中弹出的顶点(下标)[书上的j,代表一个边的起始顶点]
int outVex;//遍历一个顶点的所有邻接边结点时,用outVex暂存当前处理的顶点[书上的k,代表一个边的终止顶点]
ArcNode *p;
//初始化事件最早发生时间ve数组=====
for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
ve[i]=0;
}
//遍历顶点表,把入度为0的压栈
for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
if(adjList[i].in==0){
stack[++top]=i;
}
}
//完成拓扑排序
count=0;
while(top!=-1){
inVex=stack[top--];
result[count]=inVex;
count++;
p=adjList[inVex].firstEdge;
while(p){
outVex=p->adjvex;
adjList[outVex].in--;
if(adjList[outVex].in==0)
stack[++top]=outVex;
if(ve[inVex]+p->weight>ve[outVex])
ve[outVex]=ve[inVex]+p->weight;
p=p->next;
}
}
//判断拓扑排序是否正确
if(count==vertexNum)
return true;
return false;
}
/*
CriticalPath用于求关键路径
首先调用TopologicalSort函数检查是否是一个没有环的图
*/
bool ALGraph::CriticalPath(){
int resultStack[MAX_VERTEX]; //存储拓扑排序结果序列(存储下标)
int resultTop; //拓扑排序有效顶点个数(栈顶指针)
ArcNode *p;
int i,count;
int inVex,outVex; //inVex,outVex,分别代表一条边的起点顶点号和终点顶点号
if(!TopologicalSort(resultStack,count)) {
return false;
}
//输出拓扑排序的顶点处理顺序
cout<<"拓扑排序的顶点处理顺序是:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
cout<<resultStack[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
//输出ve数组的值
cout<<"ve数组的值为:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
cout<<"ve["<<i<<"]="<<ve[i]<<endl;
}
//完成关键路径的求解
resultTop=count-1;
inVex=resultStack[resultTop--];
for(int i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
vl[i]=ve[inVex];
}
while(resultTop!=-1){
inVex=resultStack[resultTop--];
p=adjList[inVex].firstEdge;
while(p){
outVex=p->adjvex;
if(vl[inVex]>vl[outVex]-p->weight)
vl[inVex]=vl[outVex]-p->weight;
p=p->next;
}
}
cout<<"vl数组的值为:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
cout<<"vl["<<i<<"]="<<vl[i]<<endl;
}
return true;
}
int main(){
char vertex[MAX_VERTEX];
int num,edge;
cout << "请输入顶点个数和边的个数:";
cin >> num >> edge;
for(int i=0; i<num; i++)
vertex[i] = i + '0';
ALGraph graph(vertex,num,edge);
graph.inputEdges();
graph.displayData();
if(!graph.CriticalPath()){
cout << "这个图有回路,不能求关键路径。";
}
//记住,main函数调用结束后,会自动调用析构函数,对图的数据以及ve,vl数组进行释放。
return 0;
}
输入:
9 11
0 1 6
0 2 4
0 3 5
1 4 1
2 4 1
3 5 2
4 6 9
4 7 7
5 7 4
6 8 2
7 8 4
输出:
输出图的存储情况:
顶点0的入度为:0,从这个顶点发出的的边为:
<0,3>5
<0,2>4
<0,1>6
顶点1的入度为:1,从这个顶点发出的的边为:
<1,4>1
顶点2的入度为:1,从这个顶点发出的的边为:
<2,4>1
顶点3的入度为:1,从这个顶点发出的的边为:
<3,5>2
顶点4的入度为:2,从这个顶点发出的的边为:
<4,7>7
<4,6>9
顶点5的入度为:1,从这个顶点发出的的边为:
<5,7>4
顶点6的入度为:1,从这个顶点发出的的边为:
<6,8>2
顶点7的入度为:2,从这个顶点发出的的边为:
<7,8>4
顶点8的入度为:2,从这个顶点发出的的边为:
没有。
拓扑排序的顶点处理顺序是:
0 1 2 4 6 3 5 7 8
ve数组的值为:
ve[0]=0
ve[1]=6
ve[2]=4
ve[3]=5
ve[4]=7
ve[5]=7
ve[6]=16
ve[7]=14
ve[8]=18
vl数组的值为:
vl[0]=0
vl[1]=6
vl[2]=6
vl[3]=8
vl[4]=7
vl[5]=10
vl[6]=16
vl[7]=14
vl[8]=18


