Zookeeper源码阅读(十七) 选举之队列机制与网络IO
前言
前一篇已经大概讲了基本Zookeeper选举时的选票和关于集群校验的一些概念,这一篇讲一下为了达到Zookeeper选举所设计的队列机制和实现队列机制所做的网络IO类。这部分对于zookeeper选举算法来说是基础,也是非常重要的组成部分。
队列机制概述
在 Zk思考中提到过,在zookeeper的快速选举算法真实实现中,server会为每一个peer维护一个队列来接收和发送选票。而真实的代码结构中,为了实现异步发送、接收消息的目标,zookeeper除了维护了消费队列和发送队列外,还为每一个发送队列都维护了一个发送器。值得一提的是,除了消费(接收)队列外,对于每一个发送队列和每一个发送器都是按照peer的sid分组的。
网络IO与QuorumCnxManager类
首先看下QuorumCnxManager类的结构:
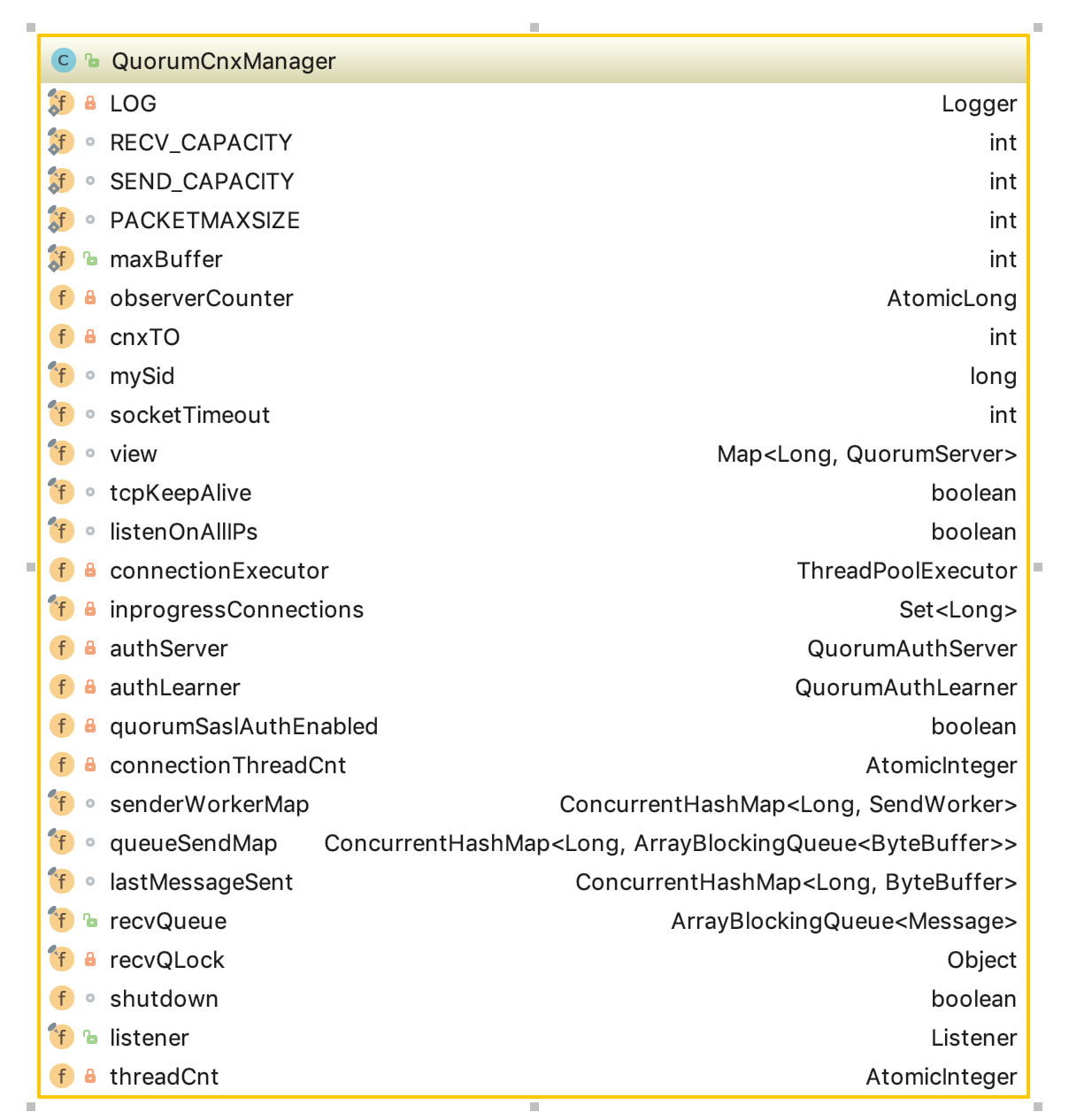
队列相关
RECV_CAPACITY 最大能接受的消息数,默认是100;
SEND_CAPACITY 发送队列最大容量,默认为1。这里这样设置是因为如果选票还没有投出去就有新的选票产生,那么代表原有的选票应该被抛弃;
recvQueue 消息接收队列,用于存放那些从其他服务器接收到的消息。
queueSendMap:消息发送队列,每个sid都会有一个队列。
senderWorkerMap:发送器集合,每个sid都会有一个发送器,用来发送对应sid的消息发送队列的消息。
lastMessageSent:保存每个sid发送的最后一条消息。
工具类介绍
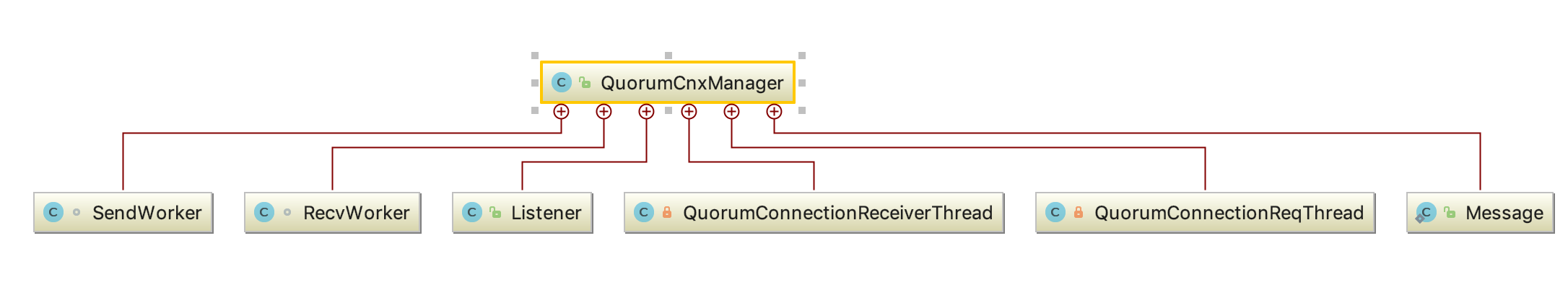
可以见到,QuorumCnxManager共有6个内部类,而它们都是为了实现选举投票传输的网络IO的内部功能类,这也是内部类设计的目的之一。我们先大致看下这些功能类的作用。
SendWorker
SendWorker就如先前所说,就是为了从发送队列中取出消息发送。sendworker类继承了ZookeeperThread类,其run方法主要就是从队列中取出相应的消息,并发送。
Long sid; //对应的发送消息队列的sid
Socket sock;
RecvWorker recvWorker; //每个接收队列对应的接收器
volatile boolean running = true;
DataOutputStream dout;
@Override
public void run() {
threadCnt.incrementAndGet();//记录当前工作线程数
try {
/**
* If there is nothing in the queue to send, then we
* send the lastMessage to ensure that the last message
* was received by the peer. The message could be dropped
* in case self or the peer shutdown their connection
* (and exit the thread) prior to reading/processing
* the last message. Duplicate messages are handled correctly
* by the peer.
*
* If the send queue is non-empty, then we have a recent
* message than that stored in lastMessage. To avoid sending
* stale message, we should send the message in the send queue.
*/
ArrayBlockingQueue<ByteBuffer> bq = queueSendMap.get(sid);//从对应的sid的发送队列中取出发送的消息
if (bq == null || isSendQueueEmpty(bq)) {
ByteBuffer b = lastMessageSent.get(sid);//如果没有消息了,那么取出上次发送的最后一条消息
if (b != null) {
LOG.debug("Attempting to send lastMessage to sid=" + sid);
send(b);//发送上次的最后一条消息
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.error("Failed to send last message. Shutting down thread.", e);
this.finish();
}
try {
while (running && !shutdown && sock != null) {
ByteBuffer b = null;
try {
ArrayBlockingQueue<ByteBuffer> bq = queueSendMap
.get(sid); //从对应的sid的发送队列中取出发送的消息
if (bq != null) {
b = pollSendQueue(bq, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);取出并发送
} else {//没有记录
LOG.error("No queue of incoming messages for " +
"server " + sid);
break;
}
if(b != null){//更新最后一条消息,并发送
lastMessageSent.put(sid, b);
send(b);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.warn("Interrupted while waiting for message on queue",
e);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.warn("Exception when using channel: for id " + sid
+ " my id = " + QuorumCnxManager.this.mySid
+ " error = " + e);
}
this.finish();
LOG.warn("Send worker leaving thread");
}
可以看到在run方法中,主要的逻辑是比较清晰的,但是要注意注释中提到的,最后一条消息会发送两次的这个特点。这是为了防止如果接收方在接收消息前挂了消息没有被正确处理,算是一种重试的措施吧。而且在接收方对于受到重复消息有处理措施。但是如果丢失了超过一条怎么办呢。。。
另外,send方法中主要处理了一些序列化相关的操作,比较清晰,而finish方法主要对socket连接及接收器等进行了清理操作,并设置了运行的状态等相关参数。
synchronized void send(ByteBuffer b) throws IOException {
byte[] msgBytes = new byte[b.capacity()];
try {
b.position(0);
b.get(msgBytes);
} catch (BufferUnderflowException be) {
LOG.error("BufferUnderflowException ", be);
return;
}
dout.writeInt(b.capacity());
dout.write(b.array());//写消息
dout.flush();
}
synchronized boolean finish() {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Calling finish for " + sid);
}
if(!running){//如果已经关闭,不再重复清理
/*
* Avoids running finish() twice.
*/
return running;
}
running = false;//设置running状态
closeSocket(sock);//关闭socket连接
// channel = null;
this.interrupt();//设置线程中断
if (recvWorker != null) {
recvWorker.finish();//关闭接收器
}
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Removing entry from senderWorkerMap sid=" + sid);
}
senderWorkerMap.remove(sid, this);//删除接收器
threadCnt.decrementAndGet();//计算工作线程,-1
return running;
}
Message
Message类是server(peer)间相互传输的数据结构,简单清晰。
static public class Message {
Message(ByteBuffer buffer, long sid) {
this.buffer = buffer;
this.sid = sid;
}
ByteBuffer buffer; //消息体
long sid; // peer的sid
}
Listener
Listener类也是一个线程,一直在监听electionPort,然后接受外部连接。
if (listenOnAllIPs) {
int port = view.get(QuorumCnxManager.this.mySid)
.electionAddr.getPort();
addr = new InetSocketAddress(port);//获取peer的连接信息,是从配置中读到,然后存在QuorumPeer.QuorumServer内部类中
} else {
addr = view.get(QuorumCnxManager.this.mySid)
.electionAddr;//
}
LOG.info("My election bind port: " + addr.toString());
setName(view.get(QuorumCnxManager.this.mySid)
.electionAddr.toString());
ss.bind(addr);//绑定连接地址
while (!shutdown) {
Socket client = ss.accept();
setSockOpts(client);//建立连接
LOG.info("Received connection request "
+ client.getRemoteSocketAddress());
// Receive and handle the connection request
// asynchronously if the quorum sasl authentication is
// enabled. This is required because sasl server
// authentication process may take few seconds to finish,
// this may delay next peer connection requests.
if (quorumSaslAuthEnabled) {
receiveConnectionAsync(client);//接受新的连接,之所以要分异步和同步是因为sasl校验比较耗时,所以采用异步的方式,在后面会详细解释
} else {
receiveConnection(client);
}
numRetries = 0;
}
异步接收peer的connection连接这部分在3.4.12之后的版本里都是有的,但是不确定3.4.10-11这几个版本是否有。这部分主要是
RecvWorker
RecvWorker和SendWorker类似,区别是sendworker是从队列中取出消息发出,而且发送队列的长度为1,而接收队列的默认长度为100。
@Override
public void run() {
threadCnt.incrementAndGet();//活跃线程计数
try {
while (running && !shutdown && sock != null) {
/**
* Reads the first int to determine the length of the
* message
*/
int length = din.readInt();
if (length <= 0 || length > PACKETMAXSIZE) {
throw new IOException(
"Received packet with invalid packet: "
+ length);
}
/**
* Allocates a new ByteBuffer to receive the message
*/
//为新来的消息分配内存
byte[] msgArray = new byte[length];
din.readFully(msgArray, 0, length);
ByteBuffer message = ByteBuffer.wrap(msgArray);
addToRecvQueue(new Message(message.duplicate(), sid));//把消息加入接收队列
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.warn("Connection broken for id " + sid + ", my id = "
+ QuorumCnxManager.this.mySid + ", error = " , e);
} finally {
LOG.warn("Interrupting SendWorker");
sw.finish();
if (sock != null) {
closeSocket(sock);
}
}
}
这里加入接收队列有一点特别:
public void addToRecvQueue(Message msg) {
synchronized(recvQLock) {
if (recvQueue.remainingCapacity() == 0) {//如果没有空余空间
try {
recvQueue.remove();//会强制把第一条消息删掉
} catch (NoSuchElementException ne) {
// element could be removed by poll()
LOG.debug("Trying to remove from an empty " +
"recvQueue. Ignoring exception " + ne);
}
}
try {
recvQueue.add(msg);
} catch (IllegalStateException ie) {
// This should never happen
LOG.error("Unable to insert element in the recvQueue " + ie);
}
}
}
可以看到,如果接收队列满了,接收队列的第一条消息会被强制删除。
QuorumConnectionReceiverThread
/**
* Thread to receive connection request from peer server.
*/
private class QuorumConnectionReceiverThread extends ZooKeeperThread {
private final Socket sock;
QuorumConnectionReceiverThread(final Socket sock) {
super("QuorumConnectionReceiverThread-" + sock.getRemoteSocketAddress());
this.sock = sock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
receiveConnection(sock);
}
}
可以看到,QuorumConnectionReceiverThread目的就是为了接收新的socket连接。在listener部分提到,在侦听electionPort时发现新的连接可能会有异步的处理,实现代码如下:
/**
* Server receives a connection request and handles it asynchronously via
* separate thread.
*/
public void receiveConnectionAsync(final Socket sock) {
try {
connectionExecutor.execute(
new QuorumConnectionReceiverThread(sock));//把QuorumConnectionReceiverThread放入线程池中并执行
connectionThreadCnt.incrementAndGet();
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOG.error("Exception handling connection, addr: {}, closing server connection",
sock.getRemoteSocketAddress());
closeSocket(sock);
}
}
可以看到,这里利用了线程池来管理QuorumConnectionReceiverThread线程,并利用线程池的线程和队列实现异步处理的目的。
QuorumConnectionReqThread
QuorumConnectionReqThread和QuorumConnectionReceiverThread非常类似,只是QuorumConnectionReqThread是负责向peer建立连接的线程。
/**
* Thread to send connection request to peer server.
*/
private class QuorumConnectionReqThread extends ZooKeeperThread {
final Socket sock;
final Long sid;
QuorumConnectionReqThread(final Socket sock, final Long sid) {
super("QuorumConnectionReqThread-" + sid);
this.sock = sock;
this.sid = sid;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try{
initiateConnection(sock, sid);//和sid的peer建立连接
} finally {
inprogressConnections.remove(sid);//把connection删掉
}
}
}
QuorumCnxManager类的功能方法
初始化连接:initiateConnection与startConnection。前者主要就是调用后者,进行了一些异常的处理,主要的功能部分在startConnection。
private boolean startConnection(Socket sock, Long sid)
throws IOException {
DataOutputStream dout = null;
DataInputStream din = null;
try {
// Sending id and challenge
dout = new DataOutputStream(sock.getOutputStream());
dout.writeLong(this.mySid);//把自己的sid写入
dout.flush();
din = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(sock.getInputStream()));
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.warn("Ignoring exception reading or writing challenge: ", e);
closeSocket(sock);
return false;
}
// authenticate learner
authLearner.authenticate(sock, view.get(sid).hostname);//加入了sasl的认证
// If lost the challenge, then drop the new connection
if (sid > this.mySid) {//如果自己的sid小于连接的sid,直接关闭
LOG.info("Have smaller server identifier, so dropping the " +
"connection: (" + sid + ", " + this.mySid + ")");
closeSocket(sock);
// Otherwise proceed with the connection
} else {//如果自己的sid大于连接的sid,初始化sendworker和recvworker
SendWorker sw = new SendWorker(sock, sid);
RecvWorker rw = new RecvWorker(sock, din, sid, sw);
sw.setRecv(rw);//sengworker记录recvworker
SendWorker vsw = senderWorkerMap.get(sid);//校验原有的senderWorkerMap里是否有sendworker
if(vsw != null)
vsw.finish();//如果有,直接关闭
senderWorkerMap.put(sid, sw);//加入新建的sendworker
queueSendMap.putIfAbsent(sid, new ArrayBlockingQueue<ByteBuffer>(SEND_CAPACITY));//新建发送队列
sw.start();//启动sendworker和recvworker
rw.start();
return true;
}
return false;
}
开始连接peer。上面初始化连接主要初始化了sendworker,recvworker和相关队列,但是对于实际的网络连接来说,这些都是底层的相关逻辑,对于一个进程来说,连接到一台peer才是真正比较完整的业务功能,而这部分业务逻辑是在connectOne里实现的。
/**
* Try to establish a connection to server with id sid.
*
* @param sid server id
*/
synchronized public void connectOne(long sid){
if (!connectedToPeer(sid)){//没连接上的时候去尝试连接
InetSocketAddress electionAddr;
if (view.containsKey(sid)) {
electionAddr = view.get(sid).electionAddr;//获取对应的sid的地址
} else {
LOG.warn("Invalid server id: " + sid);
return;
}
try {
LOG.debug("Opening channel to server " + sid);
Socket sock = new Socket();
setSockOpts(sock);
sock.connect(view.get(sid).electionAddr, cnxTO);//socket连接信息
LOG.debug("Connected to server " + sid);
// Sends connection request asynchronously if the quorum
// sasl authentication is enabled. This is required because
// sasl server authentication process may take few seconds to
// finish, this may delay next peer connection requests.
if (quorumSaslAuthEnabled) {
initiateConnectionAsync(sock, sid);//这里就是用之前说的QuorumConnectionReqThread线程去连接
} else {
initiateConnection(sock, sid);
}
} catch (UnresolvedAddressException e) {
// Sun doesn't include the address that causes this
// exception to be thrown, also UAE cannot be wrapped cleanly
// so we log the exception in order to capture this critical
// detail.
LOG.warn("Cannot open channel to " + sid
+ " at election address " + electionAddr, e);
// Resolve hostname for this server in case the
// underlying ip address has changed.
if (view.containsKey(sid)) {
view.get(sid).recreateSocketAddresses();//重连
}
throw e;
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.warn("Cannot open channel to " + sid
+ " at election address " + electionAddr,
e);
// We can't really tell if the server is actually down or it failed
// to connect to the server because the underlying IP address
// changed. Resolve the hostname again just in case.
if (view.containsKey(sid)) {
view.get(sid).recreateSocketAddresses();//重连
}
}
} else {
LOG.debug("There is a connection already for server " + sid);
}
}
其实逻辑上来说就是一台server要连接另一台peer,connectOne方法里通过起QuorumConnectionReqThread来initiateConnection(同步或者异步),在这一步会初始化队列和相关的发送器、接收器。
接收connection。正如初始化connection分为两个函数,接收connection也类似。接收connection分为同步和异步两种方式,receiveConnection和receiveConnectionAsync,区别在于是否用QuorumConnectionReceiverThread去做这件事。但无论哪种方式,最终都会进入handleConnection。
private void handleConnection(Socket sock, DataInputStream din)
throws IOException {
Long sid = null;
try {
// Read server id
sid = din.readLong();//读取连接的sid
if (sid < 0) { // this is not a server id but a protocol version (see ZOOKEEPER-1633)//这个可能是之前zk报文的一个bug
sid = din.readLong();//重新读
// next comes the #bytes in the remainder of the message
// note that 0 bytes is fine (old servers)
int num_remaining_bytes = din.readInt();
if (num_remaining_bytes < 0 || num_remaining_bytes > maxBuffer) {
LOG.error("Unreasonable buffer length: {}", num_remaining_bytes);
closeSocket(sock);
return;
}
byte[] b = new byte[num_remaining_bytes];
// remove the remainder of the message from din
int num_read = din.read(b);
if (num_read != num_remaining_bytes) {
LOG.error("Read only " + num_read + " bytes out of " + num_remaining_bytes + " sent by server " + sid);
}
}
if (sid == QuorumPeer.OBSERVER_ID) {//如果是observer
/*
* Choose identifier at random. We need a value to identify
* the connection.
*/
sid = observerCounter.getAndDecrement();//生成一个id
LOG.info("Setting arbitrary identifier to observer: " + sid);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
closeSocket(sock);//关闭socket
LOG.warn("Exception reading or writing challenge: " + e.toString());
return;
}
// do authenticating learner
LOG.debug("Authenticating learner server.id: {}", sid);
authServer.authenticate(sock, din);//sasl认证
//If wins the challenge, then close the new connection.
if (sid < this.mySid) {//如果大于自己sid
/*
* This replica might still believe that the connection to sid is
* up, so we have to shut down the workers before trying to open a
* new connection.
*/
SendWorker sw = senderWorkerMap.get(sid);//取出sendworker并关闭
if (sw != null) {
sw.finish();
}
/*
* Now we start a new connection
*/
LOG.debug("Create new connection to server: " + sid);
closeSocket(sock);//关闭socket
connectOne(sid);
// Otherwise start worker threads to receive data.
} else {
SendWorker sw = new SendWorker(sock, sid);//初始化
RecvWorker rw = new RecvWorker(sock, din, sid, sw);
sw.setRecv(rw);
SendWorker vsw = senderWorkerMap.get(sid);
if(vsw != null)
vsw.finish();//删除原来的worker
senderWorkerMap.put(sid, sw);//新建队列,添加worker
queueSendMap.putIfAbsent(sid, new ArrayBlockingQueue<ByteBuffer>(SEND_CAPACITY));
sw.start();
rw.start();//启动sendworker和recvworker
return;
}
}
通过初始化连接和关闭连接可以知道,在这两步zk都会根据sid来进行判断,标准就是:
发出连接时,要求自己sid大,完成SendWorker和ReceiveWorker的构造以及线程启动,否则close
接收连接时,要求自己sid小,完成SendWorker和ReceiveWorker的构造以及线程启动,否则close
生产与消费
发送队列的生产
在zk选举时,主要利用toSend方法发送消息。这里需要强调的是,这里的生产指的是发送队列的生产。
/**
* Processes invoke this message to queue a message to send. Currently,
* only leader election uses it.
*/
public void toSend(Long sid, ByteBuffer b) {
/*
* If sending message to myself, then simply enqueue it (loopback).
*/
if (this.mySid == sid) {//如果是发给自己,直接加入到recv的队列。
b.position(0);
addToRecvQueue(new Message(b.duplicate(), sid));//这里因为是特殊情况,所以这里实际上为接收队列做了生产
/*
* Otherwise send to the corresponding thread to send.
*/
} else {
/*
* Start a new connection if doesn't have one already.
*/
//发送到别的,那么把消息放到发送队列中
ArrayBlockingQueue<ByteBuffer> bq = new ArrayBlockingQueue<ByteBuffer>(SEND_CAPACITY);
ArrayBlockingQueue<ByteBuffer> bqExisting = queueSendMap.putIfAbsent(sid, bq);
if (bqExisting != null) {
addToSendQueue(bqExisting, b);//逻辑很简单,就是往发送队列里插入一条消息
} else {
addToSendQueue(bq, b);
}
connectOne(sid);
}
}
发送队列的消费
在ZK选举时,利用tosend方法实现了发送队列的生产。在之前的代码中也有看到,在QuorumCnxManager中,线程会一直从发送队列中取出消息发送,而这个消费的过程就是在pollSendQueue方法中。
/**
* Retrieves and removes buffer at the head of this queue,
* waiting up to the specified wait time if necessary for an element to
* become available.
*
* {@link ArrayBlockingQueue#poll(long, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit)}
*/
private ByteBuffer pollSendQueue(ArrayBlockingQueue<ByteBuffer> queue,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return queue.poll(timeout, unit);//从队列中取出
}
接收队列的生产
正如发送队列的生产中可以看到,在sid是自己的时候会加入接收队列中,而且在RecvWorker中,会增加持续插入接收到的消息。
public void addToRecvQueue(Message msg) {
synchronized(recvQLock) {
if (recvQueue.remainingCapacity() == 0) {//如果没有剩余容量,删除一个
try {
recvQueue.remove();
} catch (NoSuchElementException ne) {
// element could be removed by poll()
LOG.debug("Trying to remove from an empty " +
"recvQueue. Ignoring exception " + ne);
}
}
try {
recvQueue.add(msg);//把消息加入对垒
} catch (IllegalStateException ie) {
// This should never happen
LOG.error("Unable to insert element in the recvQueue " + ie);
}
}
}
接收队列的消费
public Message pollRecvQueue(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return recvQueue.poll(timeout, unit);//从接收队列取出
}
思考
QuorumCnxManager作为网络IO的管理器,我们其实需要从收发两端去理解。在zk的机制里,只有sid大的机器才能有效连接sid小的机器。QuorumCnxManager里有收发线程利用异步的方式,或者QuorumCnxManager主体本身的同步机制来管理收发Worker,一旦一个大sid的机器主动连接了另一台小sid的机器,在发送方,QuorumCnxManager就会自动创建发送队列和对应sid的收发worker(注意,虽然接收队列只有一条,但是对于每一个),在接收方也同样,每个sid对应的收发worker和发送队列也会被建立。而在选举的实现中,只需要不断从接收队列中取出消息或者往发送队列中添加消息即可。从方法的角度来说:
Server A(sid: 2)和Server B(sid: 1)相互连接,A和B都通过connectAll,实际上是connectone方法相互连接,在方法内部调用了initiateConnection和startConnection建立连接,只有A->B的连接会生效, 这时A会初始化sid为1的发送队列和收发worker。而由于Listener线程一直在监控electionPort端口,一旦有连接上来,B便会初始化自己这边的发送队列和收发worker。最终通过双方建立的队列和worker进行通信。
发送队列的生产,消费与调用顺序
生产 QuorumCnxManager#toSend QuorumCnxManager#addToSendQueue 消费 QuorumCnxManager.SendWorker#run QuorumCnxManager#pollSendQueue 发送 QuorumCnxManager.SendWorker#run SendWorker#send
对于接收队列满了时删除第一个这个不是很理解,如果集群很大,处理得比较慢,这样是不是会丢掉选票?
参考
从Paxos到zookeeper


