浅析Array.from()的语法及常见使用:将类数组转为数组、浅拷贝普通数组/深拷贝嵌套数组、使用默认值填充数组、序列生成器、数组去重合并
一、Array.from()
Array.from() 方法从一个类似数组或可迭代对象创建一个新的,浅拷贝的数组实例。
1、语法:Array.from(arrayLike[, mapFn[, thisArg]])
arrayLike:必传参数,想要转换成数组的伪数组对象或可迭代对象。
mapFn:可选参数,是在集合中的每个项目上调用的函数。返回的值将插入到新集合中。mapFn(item,index){...}
thisArg:可选参数,执行回调函数mapFn时 this 对象。这个参数很少使用。
返回值是一个新的数组实例。
// 例如,让我们将类数组的每一项乘以2:
const someNumbers = { '0': 10, '1': 15, length: 2 };
Array.from(someNumbers, value => value * 2); // => [20, 30]
2、Array.from() 可以通过以下方式来创建数组对象:
(1)伪数组对象(拥有一个 length 属性和若干索引属性的任意对象)
(2)可迭代对象(可以获取对象中的元素,如 Map和 Set 等)
Array.from() 方法有一个可选参数 mapFn,让你可以在最后生成的数组上再执行一次 map 方法后再返回。也就是说 Array.from(obj, mapFn, thisArg) 就相当于 Array.from(obj).map(mapFn, thisArg), 除非创建的不是可用的中间数组。
from() 的 length 属性为 1 ,即 Array.from.length === 1。
3、代码使用示例:
// 从 String 生成数组
Array.from('foo'); // [ "f", "o", "o" ]
// 从 Set 生成数组 - 去重
const set = new Set(['foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'foo']);
Array.from(set); // [ "foo", "bar", "baz" ]
// 从 Map 生成数组
const map = new Map([[1, 2], [2, 4], [4, 8]]);
Array.from(map); // [[1, 2], [2, 4], [4, 8]]
const mapper = new Map([['1', 'a'], ['2', 'b']]);
Array.from(mapper.values()); // ['a', 'b'];
Array.from(mapper.keys()); // ['1', '2'];
// 从类数组对象(arguments)生成数组
function f() {
return Array.from(arguments);
}
f(1, 2, 3); // [ 1, 2, 3 ]
// 在 Array.from 中使用箭头函数
// Using an arrow function as the map function to
// manipulate the elements
Array.from([1, 2, 3], x => x + x); // [2, 4, 6]
// Generate a sequence of numbers
// Since the array is initialized with `undefined` on each position,
// the value of `v` below will be `undefined`
Array.from({length: 5}, (v, i) => i); // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
Array.from({length: 5}, (v, i) => v); // [undefined, undefined, undefined, undefined, undefined]
// 序列生成器(指定范围)
const range = (start, stop, step) => Array.from({ length: (stop - start) / step + 1}, (_, i) => start + (i * step));
range(0, 4, 1); // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
// Generate numbers range 1..10 with step of 2
range(1, 10, 2); // [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
// Generate the alphabet using Array.from making use of it being ordered as a sequence
range('A'.charCodeAt(0), 'Z'.charCodeAt(0), 1).map(x => String.fromCharCode(x));
// ["A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "I", "J", "K", "L", "M"
, "N", "O", "P", "Q", "R", "S", "T", "U", "V", "W", "X", "Y", "Z"]
// 数组去重合并
function combine(){
let arr = [].concat.apply([], arguments); //没有去重复的新数组
return Array.from(new Set(arr));
}
var m = [1, 2, 2], n = [2,3,3];
console.log(combine(m,n)); // [1, 2, 3]
二、Array.from() 常用5个用途
Array.from() 允许在 JavaScript 集合(如: 数组、类数组对象、或者是字符串、map 、set 等可迭代对象) 上进行有用的转换。
1、将类数组转换成数组 —— Array.from() 第一个用途:将类数组对象转换成数组。
通常,你会碰到的类数组对象有:函数中的 arguments 关键字,或者是一个 DOM 集合。在下面的示例中,让我们对函数的参数求和:
function sumArguments() {
return Array.from(arguments).reduce((sum, num) => sum + num);
}
sumArguments(1, 2, 3); // => 6
Array.from(arguments) 将类数组对象 arguments 转换成一个数组,然后使用数组的 reduce 方法求和。
此外,Array.from() 的第一个参数可以是任意一个可迭代对象,我们继续看一些例子:
Array.from('Hey'); // => ['H', 'e', 'y']
Array.from(new Set(['one', 'two'])); // => ['one', 'two']
const map = new Map();
map.set('one', 1)
map.set('two', 2);
Array.from(map); // => [['one', 1], ['two', 2]]
2、克隆一个数组
在 JavaScript 中有很多克隆数组的方法。正如你所想,Array.from() 可以很容易的实现数组的浅拷贝。
const numbers = [3, 6, 9];
const numbersCopy = Array.from(numbers);
numbers === numbersCopy; // => false
numbersCopy.push(7);
numbers // [3, 6, 9]
numbersCopy // [3, 6, 9, 7]
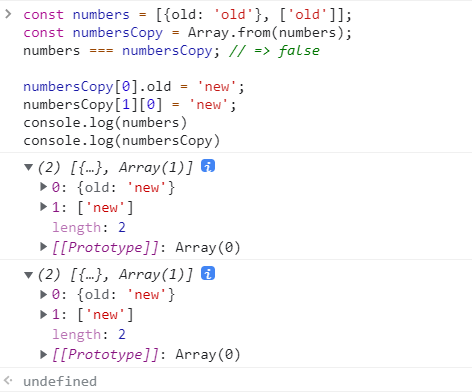
(这里我们需要注意一下:浅拷贝与深拷贝的含义,起初第一个没有嵌套数组的例子,我看未改变原数组,还以为这是深拷贝了,其实也是浅拷贝;只有试了第2个例子有嵌套数组之后,才发现原数组也改变了,所以这就是一个浅拷贝。深拷贝和浅拷贝的含义还是要搞清楚哦)
Array.from(numbers) 创建了对 numbers 数组的浅拷贝,numbers === numbersCopy 的结果是 false,意味着虽然 numbers 和 numbersCopy 有着相同的项,但是它们是不同的数组对象。
是否可以使用 Array.from() 创建数组的克隆,包括所有嵌套的?挑战一下!
function recursiveClone(val) {
return Array.isArray(val) ? Array.from(val, recursiveClone) : val;
}
const numbers = [[0, 1, 2], ['one', 'two', 'three']];
const numbersClone = recursiveClone(numbers);
numbersClone; // => [[0, 1, 2], ['one', 'two', 'three']]
numbers[0] === numbersClone[0] // => false
recursiveClone() 能够对数组的深拷贝,通过判断 数组的 item 是否是一个数组,如果是数组,就继续调用 recursiveClone() 来实现了对数组的深拷贝。
3、使用值填充数组
如果你需要使用相同的值来初始化数组,那么 Array.from() 将是不错的选择。我们来定义一个函数,创建一个填充相同默认值的数组:
const length = 3;
const init = 0;
const result = Array.from({ length }, () => init);
result; // => [0, 0, 0]
result 是一个新的数组,它的长度为3,数组的每一项都是0。调用 Array.from() 方法,传入一个类数组对象 { length } 和 返回初始化值的 mapFunction 函数。
但是,有一个替代方法 array.fill() 可以实现同样的功能。
const length = 3;
const init = 0;
const result = Array(length).fill(init);
fillArray2(0, 3); // => [0, 0, 0]
fill() 使用初始值正确填充数组。
(1)使用对象填充数组:当初始化数组的每个项都应该是一个新对象时,Array.from() 是一个更好的解决方案:
const length = 3;
const resultA = Array.from({ length }, () => ({}));
const resultB = Array(length).fill({});
resultA; // => [{}, {}, {}]
resultB; // => [{}, {}, {}]
resultA[0] === resultA[1]; // => false
resultB[0] === resultB[1]; // => true
由 Array.from 返回的 resultA 使用不同空对象实例进行初始化。之所以发生这种情况是因为每次调用时,mapFunction,即此处的 () => ({}) 都会返回一个新的对象。然后,fill() 方法创建的 resultB 使用相同的空对象实例进行初始化,不会跳过空项。
(2)使用 array.map 怎么样?是不是可以使用 array.map() 方法来实现?我们来试一下:
const length = 3;
const init = 0;
const result = Array(length).map(() => init);
result; // => [undefined, undefined, undefined] [empty × 3]
map() 方法似乎不正常,创建出来的数组不是预期的 [0, 0, 0],而是一个有3个空项的数组。这是因为 Array(length) 创建了一个有3个空项的数组(也称为稀疏数组),但是 map() 方法会跳过空项。
4、生成数字范围
你可以使用 Array.from() 生成值范围。例如,下面的 range 函数生成一个数组,从0开始到 end - 1。
function range(end) {
return Array.from({ length: end }, (_, index) => index);
}
range(4); // => [0, 1, 2, 3]
在 range() 函数中,Array.from() 提供了类似数组的 {length:end} ,以及一个简单地返回当前索引的 map 函数 。这样你就可以生成值范围。
5、数组去重
由于 Array.from() 的入参是可迭代对象,因而我们可以利用其与 Set 结合来实现快速从数组中删除重复项。
function unique(array) {
return Array.from(new Set(array));
}
unique([1, 1, 2, 3, 3]); // => [1, 2, 3]
Array.from() 方法接受类数组对象以及可迭代对象,它可以接受一个 map 函数,并且,这个 map 函数不会跳过值为 undefined 的数值项。这些特性给 Array.from() 提供了很多可能。如上所述,你可以轻松的:将类数组对象转换为数组,克隆一个数组,使用初始化填充数组,生成一个范围,实现数组去重。实际上,Array.from() 是非常好的设计,灵活的配置,允许很多集合转换。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
2017-09-15 项目笔记:测试类的编写
2017-09-15 unexpected token: * 和 java.lang.ClassCastException: [Ljava.lang.Object; cannot be cast to 解决办法