NMS: 非极大值抑制(Non-Maximum Suppression),
功能:从大量的预测结果中筛选出得分最高的结果。
思路:NMS的主要思路是通过计算目标框之间的重叠度(即IOU,交并比)来剔除非最佳结果。
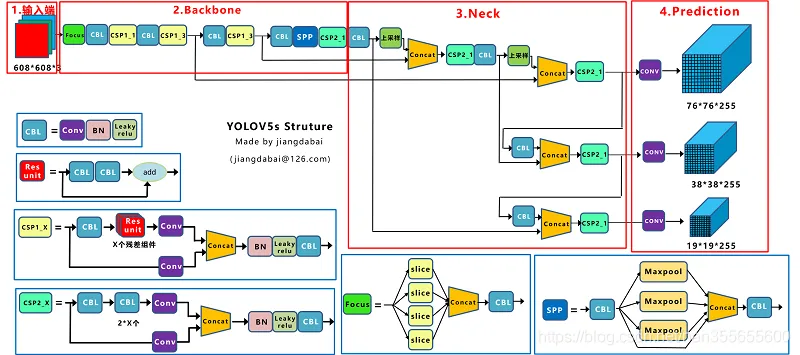
一张图片经过模型的前向推理之后,会输出非常多的检测结果,如下图Prediction所示:
以一组数据来说明,推理一张图片,模型输入大小为640*640,2个类别,推理的结果产生的预测框计算:
20 * 20 * 3
40 * 40 * 3
80 * 80 * 3
总计:25200
20、40、80 代表生成的不同预测网格尺度,yolov5会输出3种尺度的预测结果,分别大尺度20*20,中尺度40*40,小尺度80*80
3 代表每一个网格有3个预测框bounding box
所以要从这25200个数据中筛选出最好的两个结果,因为检查两个类别。筛选的过程就是NMS。
NMS: 非极大值抑制(Non-Maximum Suppression),
通过设定置信度阈值和IOU阈值,将预测框中置信度低于阈值的框过滤掉,只保留置信度高的框。
对剩下的框按照置信度进行降序排序,确保置信度高的框排在前面。
从置信度最高的框开始,计算它和剩下所有预测框的IOU。剩下的预测框中IOU低于设定的IOU阈值保留预测框。
重复上述步骤,直到遍历完所有的预测框,并得到最终筛选出来的目标框。
传入的 prediction 为预测框,形状为:[29, 27783, 7] ,代表着推理的图片一共29张,每一张图片预测结果有27783个预测框,7代表预测结果x,y,w,h,confidence, cls1, cls2。
设定一些nms中参数上线,主要用于在超过范围时限制。
max_wh: 图像最大的宽高
max_nms: 进入筛选预测框的上线
time_limit: 时间限制
multi_label: 多标签标识
merge:merge-nms标识
构建结果张量output,每一行由6个参数构成,分别是x,y,w,h,confidence,cls。这个就是模型推理的最后结果。xc[xi] 获取阈值筛选的正负结果,x[xc[xi]] 通过布尔数组获取其中为True的结果,也就是置信度大于阈值的结果。
判断结果中没有大于阈值的结果,则跳过下面的流程
置信度在模型推理的结果上还有进一步的处理,将置信度 * 类别得分才是真正的confidence。x[:, 5:] 获取所有类别得分,x[:, 4:5] 获取置信度得分。两者乘积才是最终的confidence。
获取结果中的预测框位置信息,并将位置信息从xywh转换成x1y1x2y2的格式。
在类别大于1的情况下,multi_label 为真,首先判断上一步confidence的结果中大于阈值的数据,并获取保留结果的预测框坐标轴i和j。 x为二维向量,i 代表 大于阈值的预测框所在的行,j代表所在的列。然后将位置信息、confidence、类别信息连接成新的向量。其中:
box[i]:xywh
x[i, 5 + j, None]: 获得了所有大于阈值预测框的confidence
j[:, None]: 类别ID
对置信度排序,获取从大到小的预测框的下标,并过滤超出范围的预测框。对多类别中不同类别的预测框做一个偏移操作,防止不同类别的预测框互相影响。最后得到预测框坐标 boxes 和 置信度 scores。
nms 筛选。nms筛选使用的是torchvision的工具,传入预测框位置,置信度,iou阈值,得到一个一维张量。
torchvision.ops.nms 可以用纯python的操作代替。如下代码就是完成nms筛选的过程。主要流程:
传入预测框
计算所有预测框的面积
对置信度从大到小排序
循环筛选
保存预测框第一个值,也就是最大置信度的值
计算该值和剩余所有预测框的IOU,保存小于iou_thresh的预测框,大于的丢弃
循环以上操作,直到所有的预测框都筛选完
收尾工作中获取预测值,打印处理时间等
最终的输出结果是:
输出分别代表:x1, y1, x2, y2, confidence, cls_index。
x1
y1
x2
y2
概率
类别
556
174
634
214
0.069
0
参考:yolov5 nms 源码理解_nc = prediction.shape[2] - 5 # number of classes-CSDN博客
def non_max_suppression (
prediction ,
conf_thres = 0.25 ,
iou_thres = 0.45 ,
classes = None ,
agnostic = False ,
multi_label = False ,
labels =(),
max_det = 300 ,
nm = 0 , # number of masks
):
"""Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results to reject overlapping detections
Returns:
list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls]
"""
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1 , f 'Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1 , f 'Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
if isinstance ( prediction , ( list , tuple )): # YOLOv5 model in validation model, output = (inference_out, loss_out)
prediction = prediction [ 0 ] # select only inference output
"""
Pdb) pp prediction.shape
torch.Size([29, 27783, 7])
"""
device = prediction . device
mps = 'mps' in device . type # Apple MPS
if mps : # MPS not fully supported yet, convert tensors to CPU before NMS
prediction = prediction . cpu ()
"""
(Pdb) bs
29
(Pdb) nc
2
(Pdb) xc.shape
torch.Size([29, 27783])
"""
bs = prediction . shape [ 0 ] # batch size
nc = prediction . shape [ 2 ] - nm - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction [..., 4 ] > conf_thres # candidates
breakpoint ()
# Settings
# min_wh = 2 # (pixels) minimum box width and height
max_wh = 7680 # (pixels) maximum box width and height
max_nms = 30000 # maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms()
time_limit = 0.5 + 0.05 * bs # seconds to quit after
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
merge = False # use merge-NMS
t = time . time ()
mi = 5 + nc # mask start index
output = [ torch . zeros (( 0 , 6 + nm ), device = prediction . device )] * bs
for xi , x in enumerate ( prediction ): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
"""
(Pdb) xc.shape
torch.Size([29, 27783])
(Pdb) xc[0]
tensor([False, False, False, ..., True, True, True], device='cuda:0')\
(Pdb) xc[0].shape
torch.Size([27783])
(Pdb) x.shape
torch.Size([27783, 7])
"""
x = x [ xc [ xi ]] # confidence
"""
(Pdb) pp x.shape
torch.Size([17788, 7])
"""
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len ( labels [ xi ]):
lb = labels [ xi ]
v = torch . zeros (( len ( lb ), nc + nm + 5 ), device = x . device )
v [:, : 4 ] = lb [:, 1 : 5 ] # box
v [:, 4 ] = 1.0 # conf
v [ range ( len ( lb )), lb [:, 0 ]. long () + 5 ] = 1.0 # cls
x = torch . cat (( x , v ), 0 )
# If none remain process next image
if not x . shape [ 0 ]:
continue
"""
(Pdb) x[0]
tensor([6.89062e+00, 1.11172e+01, 2.53906e+01, 2.80781e+01, 1.03188e-03, 1.96777e-01, 2.99805e-01], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float16)
(Pdb) n
> /home/lijinkui/Documents/code/yolov5/utils/general.py(922)non_max_suppression()
-> box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4]) # center_x, center_y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
(Pdb) x[0]
tensor([6.89062e+00, 1.11172e+01, 2.53906e+01, 2.80781e+01, 1.03188e-03, 2.03013e-04, 3.09467e-04], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float16)
"""
# Compute conf
x [:, 5 :] *= x [:, 4 : 5 ] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box/Mask
"""
(Pdb) pp box[0]
tensor([-5.80469, -2.92188, 19.59375, 25.15625], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float16)
"""
box = xywh2xyxy ( x [:, : 4 ]) # center_x, center_y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
mask = x [:, mi :] # zero columns if no masks
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label :
"""
x[:, 5:mi] > conf_thres: 大于阈值的结果
i:bbox的横坐标
j: bbox的纵坐标
box[i]:xywh
x[i, 5 + j, None]: 获得了所有大于阈值的bbox结果
j[:, None]: 类别ID
"""
i , j = ( x [:, 5 : mi ] > conf_thres ). nonzero ( as_tuple = False ). T
x = torch . cat (( box [ i ], x [ i , 5 + j , None ], j [:, None ]. float (), mask [ i ]), 1 )
"""
(Pdb) pp x.shape
torch.Size([17039, 6])
"""
else : # best class only
conf , j = x [:, 5 : mi ]. max ( 1 , keepdim = True )
x = torch . cat (( box , conf , j . float (), mask ), 1 )[ conf . view (- 1 ) > conf_thres ]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None :
x = x [( x [:, 5 : 6 ] == torch . tensor ( classes , device = x . device )). any ( 1 )]
# Apply finite constraint
# if not torch.isfinite(x).all():
# x = x[torch.isfinite(x).all(1)]
# Check shape
n = x . shape [ 0 ] # number of boxes
if not n : # no boxes
continue
# 对置信度排序,并去掉超出范围的结果
x = x [ x [:, 4 ]. argsort ( descending = True )[: max_nms ]] # sort by confidence and remove excess boxes
# Batched NMS
c = x [:, 5 : 6 ] * ( 0 if agnostic else max_wh ) # classes
# 获取boxes 和 scores
boxes , scores = x [:, : 4 ] + c , x [:, 4 ] # boxes (offset by class), scores
"""
(Pdb) pp boxes.shape
torch.Size([17039, 4])
(Pdb) pp scores.shape
torch.Size([17039])
"""
# 遍历score,通过IOU 筛选bbox。返回最终的bbox的index
i = torchvision . ops . nms ( boxes , scores , iou_thres ) # NMS
"""
(Pdb) i.shape
torch.Size([300])
"""
i = i [: max_det ] # limit detections
if merge and ( 1 < n < 3E3 ): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
# update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou ( boxes [ i ], boxes ) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores [ None ] # box weights
x [ i , : 4 ] = torch . mm ( weights , x [:, : 4 ]). float () / weights . sum ( 1 , keepdim = True ) # merged boxes
if redundant :
i = i [ iou . sum ( 1 ) > 1 ] # require redundancy
# 获取某一个网格的最终结果
output [ xi ] = x [ i ]
"""
(Pdb) p output[xi].shape
torch.Size([300, 6])
"""
if mps :
output [ xi ] = output [ xi ]. to ( device )
if ( time . time () - t ) > time_limit :
LOGGER . warning ( f 'WARNING ⚠️ NMS time limit {time_limit:.3f}s exceeded' )
break # time limit exceeded
return output
__EOF__





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
2023-07-17 subprocess Python执行系统命令最优选模块