voc数据集转换成coco数据集
1|0前言
作为本系列第一篇文章,我分享一个模型训练过程中常用到的工具,voc数据集转coco数据集。
在我做一些算法学习的时候,需要将voc数据集转coco放到yolo当中训练,但是在网上找了很多个都不是很好用,要不是会报错,要不是根本不能跑起来。为了节省在学习算法小伙伴的时间,我分享我在工作常常用的voc转coco的脚本。
2|0voc 格式分析
为了能够更好理解脚本,首先对voc数据集的格式做一个简单分析。
voc 全称 The PASCAL Visual Object Classes,它由Visual Object Classes(可视对象类)和挑战(Challenge)等竞赛项目开发, 开始于2005年,结束于2012年最后一届 。
VOC数据集包含许多不同类型的图像,每个图像都标注了一些可视对象,如人,汽车,狗等。这些标注包括每个对象的位置,大小和类别等信息。
常见的voc数据集是voc2007 和voc 2012,当然在模型训练过程肯定都会自己标注数据集,导出为voc格式。
voc 数据集的格式:
重要的信息包括:filename, size, object 等。除此之外,还有一个主要注意的点就是标注的坐标,xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax是标注的四个角,分别代表:
- xmin: 左上角x轴坐标
- ymin:左上角y周坐标
- xmax: 右下角x轴坐标
- ymax:右下角y轴坐标
3|0coco 格式分析
COCO的 全称是Common Objects in COntext,是微软团队提供的一个可以用来进行图像识别的数据集。MS COCO数 据集中的图像分为训练、验证和测试集。
假设有以下两个图像文件:
- image1.jpg
- image2.jpg
coco格式数据集:annotations.json
coco 数据集字段解析
coco 数据集是一个json文件,一共包括5个部分。
需要注意的是coco数据集标注的坐标。xmin ymin width height和voc有很大差异,分别代表:
- xmin 左上角x轴坐标
- ymin 左上角y轴坐标
- width 图片像素宽
- heidht 图片像素高
4|0脚本使用
通常在yolo模型检测训练时需要的数据集是coco格式或者yolo格式,那么就需要将voc转成coco。通常在生成任务中实用的voc数据集的文件和官方数据集格式略有差异。所以首先需要说明,使用该脚本之前需要将voc文件调整成如下格式:
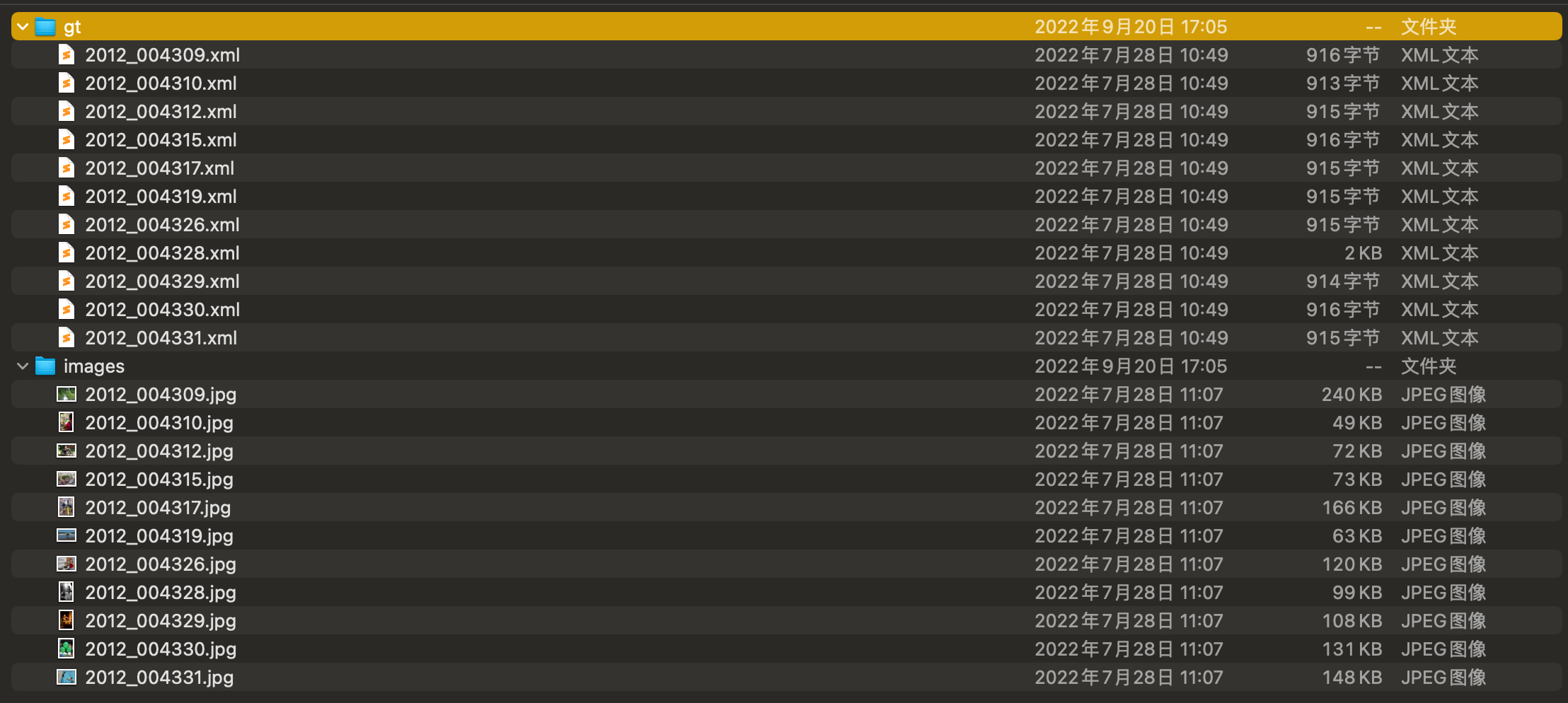
数据集包含两个文件夹,包括gt和images。gt是xml文件保存的目录,images是图片保存的目录。而且xml文件和images同名,只是后缀不一样。
脚本的主要逻辑:
- 遍历所有voc数据集
- 获取所有标签信息,去重保存在self.categories
- 获取所有图片元数据,保存在self.images
- 获取所有标注信息,保存在self.annotations
- 将以上三个容器保存到字典中,并将字典保存为一个json文件
__EOF__

本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/goldsunshine/p/18162555.html
关于博主:评论和私信会在第一时间回复。或者直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
2018-04-27 网站用户身份识别俩大招之django实现cookie