Redis源码阅读(一)事件机制
Redis源码阅读(一)事件机制
Redis作为一款NoSQL非关系内存数据库,具有很高的读写性能,且原生支持的数据类型丰富,被广泛的作为缓存、分布式数据库、消息队列等应用。此外Redis还有许多高可用特性,包括数据持久化,主从模式备份等等,可以满足对数据完整性有一定要求的场景。
Redis的源码结构简单清晰,有大量材料可以参阅;通过阅读Redis源码,掌握一些常用技术在Redis中的实现,相信会对个人编程水平有很大帮助。这里记录下我阅读Redis源码的心得。从我自己比较关心的几个技术点出发,每个技术点都是来自个人使用Redis过程中产生的问题。这里也参考了黄建宏老师的《Redis设计与实现》部分内容,不得不说参考这本书再结合源码注释,看起来绝对事半功倍。
当初选用Redis的时候,很大程度上是由于Redis的并发性能很高,可以支持大量并发请求。那Redis是如何支持高并发请求的呢?这里就引入了第一个技术点,事件处理机制。在Redis中使用了单线程的Reactor模式,属于I/O多路复用的一种常见实现模式。这里简单介绍下Reactor模式。
1. Reactor模式
从网上切一个类图,简单描述一下Reactor模式的主体结构
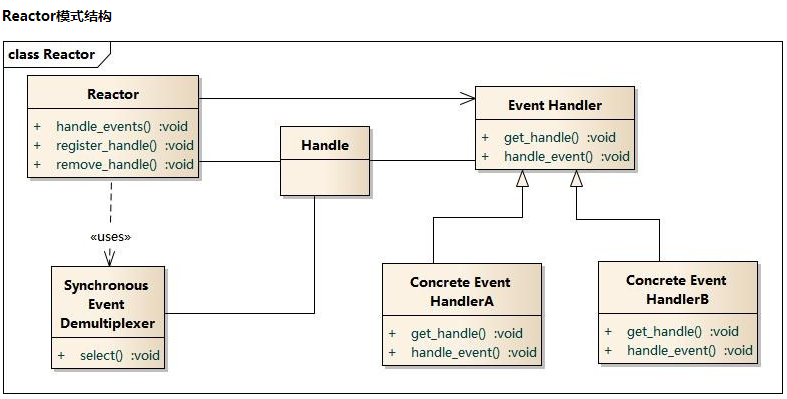
基本概念:
Handle:I/O操作的基本文件句柄,在linux下就是fd
Synchronous Event Demultiplexer :同步事件分离器,阻塞等待Handles中的事件发生(Redis中的事件分离器设置了超时,不会一直阻塞)。
Reactor: 事件分派器,负责事件的注册,删除以及对所有注册到事件分派器的事件进行监控, 当事件发生时会调用Event Handler接口来处理事件。
Event Handler: 事件处理器接口,这里需要Concrete Event Handler来实现该接口
Concrete Event Handler:真实的事件处理器,通常都是绑定了一个handle,实现对可读事件 进行读取或对可写事件进行写入的操作。
关键点:
I/O多路复用指的就是以事件驱动为基础,可实现单个线程侦听多个socket描述符的可读可写或异常状态,不需要为每个socket描述符单独创建一个线程来侦听描述符可读还是可写。在Reactor模式中,对多个描述符进行侦听的部件就是Synchronous Event Demultiplexer,通常是由操作系统提供的select/epoll/kqueue等函数实现。
Reactor模式大致的流程时序:主程序先向事件分派器注册要监听的事件,之后启动事件分派器,由事件分派器调用操作系统提供的同步事件分离器(如select/epoll)侦听事件,当事件发生时事件分派器会调用事件绑定好的处理函数handle_event()来处理事件。这里的同步并不是指阻塞,同步从API调用上来讲就是调用结束后一定能确知本次调用是否成功,如果API调用超时,那么使用者需要伺机再次发起调用才能达到目的(这里如果设置了超时,就是非阻塞的,因为进程不会卡在API调用上直到其获得结果);对于异步来讲,调用期望的结果不是在API调用结束后获取的,通常是由CPU自行处理完成后发送通知给调用者的。由此可以看出异步是天然非阻塞的。

事件分派器是单线程,这就要求每个事件的处理函数handle_event()不能是阻塞的,否则一旦有某个事件的处理函数阻塞住,程序就无法再调用其他事件的处理函数了。
2. 源码实现
在Redis中,事件分为两大类:文件事件和时间事件。文件事件就是指客户端的网络连接请求到达,客户端的发来的命令请求到达以及服务端发出命令应答这几类事件;时间事件主要是Redis内部的定时处理器。
看下Redis对事件机制的代码实现。按照正常的逻辑,Redis服务应该初始化一个事件分派器,然后将绑定了服务器IP,服务端口的连接套接字注册到事件分派器上,之后即可启动事件分派器。启动后客户端连接到Redis服务的请求就可以被事件分派器侦听。
Redis服务器初始化位于redis.c/initServer函数,贴出该函数中有关事件分派器初始化以及服务端口注册的代码:
void initServer() { int j; ...... createSharedObjects(); adjustOpenFilesLimit(); // 初始化事件分派器 server.el = aeCreateEventLoop(server.maxclients+REDIS_EVENTLOOP_FDSET_INCR); server.db = zmalloc(sizeof(redisDb)*server.dbnum); /* Open the TCP listening socket for the user commands. */ // 打开 TCP 监听端口,用于等待客户端的命令请求 if (server.port != 0 && listenToPort(server.port,server.ipfd,&server.ipfd_count) == REDIS_ERR) exit(1); /* Open the listening Unix domain socket. */ // 打开 UNIX 本地端口 if (server.unixsocket != NULL) { unlink(server.unixsocket); /* don't care if this fails */ server.sofd = anetUnixServer(server.neterr,server.unixsocket, server.unixsocketperm, server.tcp_backlog); if (server.sofd == ANET_ERR) { redisLog(REDIS_WARNING, "Opening socket: %s", server.neterr); exit(1); } anetNonBlock(NULL,server.sofd); } /* Abort if there are no listening sockets at all. */ if (server.ipfd_count == 0 && server.sofd < 0) { redisLog(REDIS_WARNING, "Configured to not listen anywhere, exiting."); exit(1); } ...... updateCachedTime(); /* Create the serverCron() time event, that's our main way to process * background operations. */ // 为 serverCron() 创建时间事件 if(aeCreateTimeEvent(server.el, 1, serverCron, NULL, NULL) == AE_ERR) { redisPanic("Can't create the serverCron time event."); exit(1); } /* Create an event handler for accepting new connections in TCP and Unix * domain sockets. */ // 为 TCP 连接关联连接应答(accept)处理器 // 用于接受并应答客户端的 connect() 调用 for (j = 0; j < server.ipfd_count; j++) { if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.ipfd[j], AE_READABLE, acceptTcpHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR) { redisPanic( "Unrecoverable error creating server.ipfd file event."); } } // 为本地套接字关联应答处理器 if (server.sofd > 0 && aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,server.sofd,AE_READABLE, acceptUnixHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR) redisPanic("Unrecoverable error creating server.sofd file event."); ...... }
aeCreateFileEvent函数相当于Reactor模型中的事件注册函数register_handle(),这里对Redis配置文件中每组IP绑定的server.ipfd[i]都创建了侦听事件,侦听事件对应的处理器为连接应答处理器,即networking.c/acceptTcpHandler函数。侦听事件处理器中调用了accept来处理用户的连接请求;当客户端调用connect发起连接请求时,Redis服务端的侦听事件即变成可处理的状态,Redis通过select/epoll检查到侦听事件可处理,就会调用其对应的处理器acceptTcpHandler函数来处理客户端的连接请求。
acceptTcpHandler源码如下:
void acceptTcpHandler(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) { int cport, cfd, max = MAX_ACCEPTS_PER_CALL; char cip[REDIS_IP_STR_LEN]; REDIS_NOTUSED(el); REDIS_NOTUSED(mask); REDIS_NOTUSED(privdata); redisClient *c; while(max--) { // accept 客户端连接 cfd = anetTcpAccept(server.neterr, fd, cip, sizeof(cip), &cport); if (cfd == ANET_ERR) { if (errno != EWOULDBLOCK) redisLog(REDIS_WARNING, "Accepting client connection: %s", server.neterr); return; } // snprintf() // 为客户端创建客户端状态(redisClient) c = acceptCommonHandler(cfd,0); if(c != NULL) { snprintf(c->cip, sizeof(c->cip), "%s", cip); c->cport = cport; } redisLog(REDIS_VERBOSE,"Accepted %s:%d %s:%d ", cip, cport, c->cip, c->cport); } }
anetTcpAccept函数内部使用accept创建好与客户端的连接,返回cfd,后续与客户端的消息收发都是建立在cfd上的。这里很自然的就需要将cfd也注册到Redis的事件分派器上。我们注意到cfd的读事件对应着客户端发来了命令请求,需要服务端读取后处理;写事件对应着Redis服务端发出的命令处理应答,写给客户端。在刚刚建立连接的时候,服务端很显然是要接收用户的命令,所以这里只能先注册cfd的读事件。
代码中可以看到acceptTcpHandler函数里会调用networking.c/acceptCommonHandler创建客户端,acceptCommonHandler中的createClient执行了对通信fd可读事件的注册
redisClient *createClient(int fd) { //createClient,主 备全量同步完成后,备创建一个client来接收主到备的实时KV // 分配空间 redisClient *c = zmalloc(sizeof(redisClient)); /* passing -1 as fd it is possible to create a non connected client. * This is useful since all the Redis commands needs to be executed * in the context of a client. When commands are executed in other * contexts (for instance a Lua script) we need a non connected client. */ if (fd != -1) { // 非阻塞 anetNonBlock(NULL,fd); // 禁用 Nagle 算法 anetEnableTcpNoDelay(NULL,fd); // 设置 keep alive if (server.tcpkeepalive) anetKeepAlive(NULL,fd,server.tcpkeepalive); // 绑定读事件到事件 loop (开始接收命令请求) //accept接收到客户端连接的时候调用该函数把fd加入事件集中 if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_READABLE, readQueryFromClient, c) == AE_ERR) { close(fd); zfree(c); return NULL; } } ... ... // 返回客户端 return c; }
那么cfd的写事件是在什么时候注册的呢? cfd可写事件是服务器对客户端发送命令应答的事件,应该在服务器执行了客户端的命令之后再注册上去。Redis也是在每个命令处理器处理完成时调用addReply函数来注册cfd写事件的。客户端准备好接收应答时就会产生cfd的写事件,如果Redis注册写事件在客户端准备好接收应答之后也没有关系,Redis注册写事件之后,即发现该事件可以处理,在下一个事件分派器轮询周期即可被处理。命令应答处理器的函数是networking.c/sendReplyToClient,应答完成后就调用aeDeleteFileEvent函数释放掉通信fd的应答事件监控。
void sendReplyToClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) { redisClient *c = privdata; int nwritten = 0, totwritten = 0, objlen; size_t objmem; robj *o; REDIS_NOTUSED(el); REDIS_NOTUSED(mask); // 一直循环,直到回复缓冲区为空 // 或者指定条件满足为止 while(c->bufpos > 0 || listLength(c->reply)) { if (c->bufpos > 0) { // c->bufpos > 0 // 写入内容到套接字 // c->sentlen 是用来处理 short write 的 // 当出现 short write ,导致写入未能一次完成时, // c->buf+c->sentlen 就会偏移到正确(未写入)内容的位置上。 nwritten = write(fd,c->buf+c->sentlen,c->bufpos-c->sentlen); // 出错则跳出 if (nwritten <= 0) break; // 成功写入则更新写入计数器变量 c->sentlen += nwritten; totwritten += nwritten; /* If the buffer was sent, set bufpos to zero to continue with * the remainder of the reply. */ // 如果缓冲区中的内容已经全部写入完毕 // 那么清空客户端的两个计数器变量 if (c->sentlen == c->bufpos) { c->bufpos = 0; c->sentlen = 0; } } else { // listLength(c->reply) != 0 // 取出位于链表最前面的对象 o = listNodeValue(listFirst(c->reply)); objlen = sdslen(o->ptr); objmem = getStringObjectSdsUsedMemory(o); // 略过空对象 if (objlen == 0) { listDelNode(c->reply,listFirst(c->reply)); c->reply_bytes -= objmem; continue; } // 写入内容到套接字 // c->sentlen 是用来处理 short write 的 // 当出现 short write ,导致写入未能一次完成时, // c->buf+c->sentlen 就会偏移到正确(未写入)内容的位置上。 nwritten = write(fd, ((char*)o->ptr)+c->sentlen,objlen-c->sentlen); // 写入出错则跳出 if (nwritten <= 0) break; // 成功写入则更新写入计数器变量 c->sentlen += nwritten; totwritten += nwritten; /* If we fully sent the object on head go to the next one */ // 如果缓冲区内容全部写入完毕,那么删除已写入完毕的节点 if (c->sentlen == objlen) { listDelNode(c->reply,listFirst(c->reply)); c->sentlen = 0; c->reply_bytes -= objmem; } } /* Note that we avoid to send more than REDIS_MAX_WRITE_PER_EVENT * bytes, in a single threaded server it's a good idea to serve * other clients as well, even if a very large request comes from * super fast link that is always able to accept data (in real world * scenario think about 'KEYS *' against the loopback interface). * * 为了避免一个非常大的回复独占服务器, * 当写入的总数量大于 REDIS_MAX_WRITE_PER_EVENT , * 临时中断写入,将处理时间让给其他客户端, * 剩余的内容等下次写入就绪再继续写入 * * However if we are over the maxmemory limit we ignore that and * just deliver as much data as it is possible to deliver. * * 不过,如果服务器的内存占用已经超过了限制, * 那么为了将回复缓冲区中的内容尽快写入给客户端, * 然后释放回复缓冲区的空间来回收内存, * 这时即使写入量超过了 REDIS_MAX_WRITE_PER_EVENT , * 程序也继续进行写入 */ if (totwritten > REDIS_MAX_WRITE_PER_EVENT && //最多写64M (server.maxmemory == 0 || zmalloc_used_memory() < server.maxmemory)) break; } // 写入出错检查 if (nwritten == -1) { if (errno == EAGAIN) { nwritten = 0; } else { redisLog(REDIS_VERBOSE, "Error writing to client: %s", strerror(errno)); freeClient(c, NGX_FUNC_LINE); return; } } if (totwritten > 0) { /* For clients representing masters we don't count sending data * as an interaction, since we always send REPLCONF ACK commands * that take some time to just fill the socket output buffer. * We just rely on data / pings received for timeout detection. */ if (!(c->flags & REDIS_MASTER)) c->lastinteraction = server.unixtime; } if (c->bufpos == 0 && listLength(c->reply) == 0) { c->sentlen = 0; // 删除 write handler aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,c->fd,AE_WRITABLE); /* Close connection after entire reply has been sent. */ // 如果指定了写入之后关闭客户端 FLAG ,那么关闭客户端 if (c->flags & REDIS_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY) freeClient(c, NGX_FUNC_LINE); } }
Redis中的文件事件处理流程已经大体列出了,还有一个比较重要的环节就是Synchronous Event Demultiplexer的实现。在Redis中是根据操作系统支持的情况选用效率最高的实现。同步事件分离器是封装在ae.h/ae.c中的,使用统一的API供Redis来调用。分离器的具体实现是选用不同操作系统下效率最高的事件分离器,各实际的事件分离器实现在ae_epoll.c/ae_select.c/ae_evport.c/ae_kqueue.c中。
看下选取不同类型事件分离器的代码(ae.c):
/* Include the best multiplexing layer supported by this system. * The following should be ordered by performances, descending. */ #ifdef HAVE_EVPORT #include "ae_evport.c" #else #ifdef HAVE_EPOLL #include "ae_epoll.c" #else #ifdef HAVE_KQUEUE #include "ae_kqueue.c" #else #include "ae_select.c" #endif #endif #endif




