Vue14-vuex
Vue14-vuex
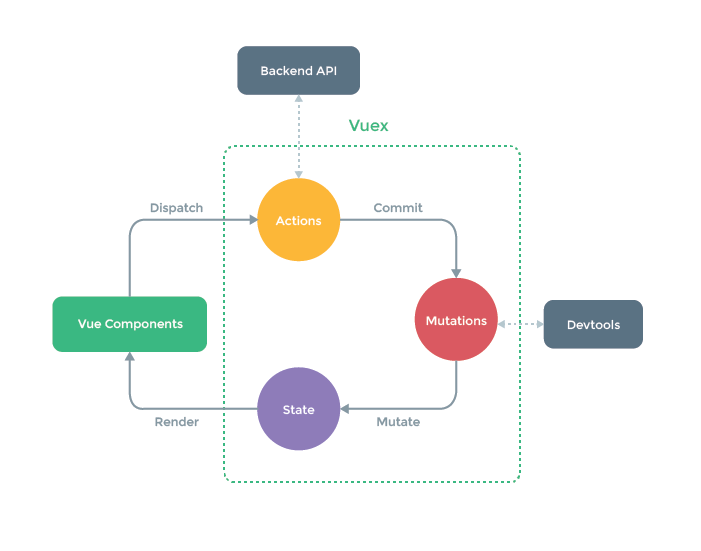
1.vuex简介
- vuex是vue中一个集中式状态(数据)管理的vue插件,可以对vue应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写);vuex也是一种组件间通信的方式,且适用于任意组件间通信。
- vuex的Github地址https://github.com/vuejs/vuex。
- vuex使用场景:多个组件依赖于同一状态;来自不同组件的行为需要变更同一状态。
2.求和案例-纯vue版
- App.vue。
<template>
<div>
<Count/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Count from "./components/Count";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {Count}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
- Count.vue。
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前和为:{{sum}}</h3>
<!-- value="2"会被当做字符串处理,有两种解决方式。
1 使用v-model.number强制转换为数字。
2 使用:value,这样2就是js表达式,2就为数字。
-->
<select v-model.number="num">
<option value="1">1</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
</select>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
<button @click="incrementOdd">当值为奇数时加</button>
<button @click="incrementWait">等等加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Count",
data() {
return {
sum: 0,
num: 1
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.sum += this.num;
},
decrement() {
this.sum -= this.num;
},
incrementOdd() {
if (this.sum % 2) {
this.sum += this.num;
}
},
incrementWait() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.sum += this.num;
}, 500);
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
button {
margin-left: 5px;
}
</style>
3.vuex的按照和使用
- 安装vuex,npm i vuex@3。注:vue2中只能使用vuex的3版本,vue3中只能使用vuex的4版本,当前vue最新的是3版本,所以直接使用npm i vuex安装的是vuex的4版本,直接使用会报错,所有使用vuex@3来按照vuex的3版本。
- main.js中引入和使用vuex。注:后续引入和使用的代码会移动到store/index.js中。
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 引入vuex后,new Vue时就会多出来一个store配置项。
Vue.use(Vuex);
- 准备store对象。
- src下创建store文件夹,在store中创建index.js。
- index.js中分别创建store中核心的三个概念,actions、mutations和state。
- index.js中创建store,store中包含actions、mutations和state。
- index.js中执行Vue.use(Vuex);,防止在main.js中执行报错。
- main.js中引入store,然后将其放入Vue配置对象中。
4.求和案例-vuex版
- store中的index.js。
// 该文件用于创建vuex中最为核心的store
/**
* 在store/index.js中执行Vue.use(Vuex);的原因。
* 1 在实例化store前必须前执行Vue.use(Vuex),
* 否则报错[vuex] must call Vue.use(Vuex) before creating a store instance.
* 2 在main.js中import store from './store'时就会实例化store对象,
* 所以需要import store from './store'前执行Vue.use(Vuex);
* 但是vue脚手架在打包代码时,会将import汇总放在顶部,即import会先被执行,所以需要将
* Vue.use(Vuex);代码放在index.js中执行,防止报错。
*/
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import Vue from 'vue'
Vue.use(Vuex);
// 准备actions,用于响应组件中的动作
const actions = {
/**
* actions中的函数接受两个参数。
* context,store的上下文环境。
* value,$store.dispatch()时传递的参数。
*/
jia(context, value) {
// Actions中通过commit调用mutations中的JIA函数。
context.commit('JIA', value);
},
jian(context, value) {
context.commit('JIAN', value);
},
jiaOdd(context, value) {
if (context.state.num % 2) {
context.commit('JIA', value);
}
},
jiaWait(context, value) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('JIA', value);
}, 500)
},
};
// 准备mutations,用于操作数据(state)
const mutations = {
// mutations中的函数一般大写,用于和actions中的函数名区分。
// mutations中的函数接受两个参数。
// state对象,state中的属性会加上get和set。
// value,通过commit()函数调用传递的参数。
JIA(state, value) {
state.sum += value;
},
JIAN(state, value) {
state.sum -= value;
}
};
// 准备state,用于存储数据
const state = {
sum: 0
};
// 创建store
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions: actions,
mutations: mutations,
state: state
});
- main.js。
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
// 引入store。index.js是脚手架默认识别js,所以可以直接写为from './store',
// 相当与from './store/index.js'
import store from './store'
new Vue({
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App),
store: store,
beforeCreate() {
Vue.prototype.$bus = this;
}
});
- App.vue和原来保持一样。
- Count.vue。
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前和为:{{$store.state.sum}}</h3>
<select v-model.number="num">
<option value="1">1</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
</select>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
<button @click="incrementOdd">当值为奇数是加</button>
<button @click="incrementWait">等等加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Count",
data() {
return {
num: 1
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
// 通过dispatch调用Actions中的jia函数,并且传递参数num。
this.$store.dispatch('jia', this.num);
},
decrement() {
// 当Actions中没有业务操作的时候,可以直接通过commit调用mutations来操作数据。
this.$store.commit('JIAN', this.num);
},
incrementOdd() {
this.$store.dispatch('jiaOdd', this.num);
},
incrementWait() {
this.$store.dispatch('jiaWait', this.num);
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
button {
margin-left: 5px;
}
</style>
5.求和案例-getters
- 当state中的数据需要经过加工后在使用时,可以在getters中加工。
- main.js和App.vue代码保持不变。
- 添加getters后的store/index.js。
... actions、mutations和state省略
const getters = {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum * 10;
}
};
// 创建store
const store = new Vuex.Store({
actions: actions,
mutations: mutations,
state: state,
getters: getters
});
- Count.vue中使用getters。
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前和10倍为:{{$store.getters.bigSum}}</h3>
</div>
</template>
6.求和案例-mapState和mapGetters
- mapState用于将state中的数据映射为计算属性;mapGetters用于将getters中的数据映射为计算属性。
- store/index.js、main.js、App.vue代码保持不变。
- Count.vue。
<template>
<div>
<!-- 使用mapGetters简化getters后的写法。 -->
<h3>当前和为:{{bigSum}}</h3>
<!-- 每次插值语法中都需要写$store.state.xxx,可以使用计算属性,简化这种写法。 -->
<!-- 使用mapState简化读取state数据的写法。 -->
<h3>姓名 {{xingming}}</h3>
<h3>学校 {{xuexiao}}</h3>
<h3>年龄 {{age}}</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState, mapGetters} from 'vuex'
export default {
... name data methods属性省略。
computed: {
// 1 使用计算属性访问state中数据的访问。
// 可以看到计算属性访问state中的数据后,return this.$store.state.xxx都是相同的代码,
// 所以可以使用mapState来生成这段代码。
xingming() {
return this.$store.state.name;
},
// 2 借助mapState生成计算属性,从state中读取数据,对象写法。
// 使用mapState生成xuexiao和age的计算属性,xuexiao和age去访问state中school和age属性。
// 生成的计算属性的代码和上面的xingming计算属性作用相同。
// ...mapState({}),将...mapState({})生成的对象展开,然后放到computed中。
...mapState({xuexiao: 'school'}),
// 如果计算属性名和state中的属性重名,不能使用属性的简写,
// 因为简写会将school当做变量来处理,而这里的school是一个字符串。
// ...mapState({school, age})
// 3 借助mapState生成计算属性,从state中读取数据,数组写法。
// 计算属性名和state中的属性重名时可以采用数组写法。
...mapState(['age']),
// 4 借助mapGetters生成getters中的计算属性,对象写法。
...mapGetters({bigSum: 'bigSum'}),
// 5 借助mapGetters生成getters中的计算属性,数组写法。
...mapGetters(['bigSum']),
},
</script>
7.求和案例-mapActions和mapMutations
-
mapActions生成和actions对话的方法;mapMutations生成和mutations对话的方法。
-
mapActions和mapMutations在使用时需要注意:如果需要传递参数,就需要在模板中绑定事件时将参数传递好,否则传递的参数就是事件对象。
-
Count.vue。
<template>
<div>
<!-- 当使用mapMutation和mapAction生成代码后,方法的调用需要传递参数。 -->
<button @click="decrement(num)">-</button>
<button @click="JIAN(num)">-</button>
<button @click="incrementOdd(num)">当值为奇数是加</button>
<button @click="jiaWait(num)">等等加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
... 省略name data computed
methods: {
increment() {
// 通过dispatch调用Actions中的jia函数,并且传递参数num。
this.$store.dispatch('jia', this.num);
},
// 1 使用mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法中会调用commit来联系mutations,对象式写法。
// 使用mapMutations生成代码,生成代码需要传递一个对象,
// 对象的key为方法名,对象的value为mutations中的方法名。
// 默认生成的代码为:
/*
decrement(value) {
this.$store.commit('jia', value);
},
*/
// 2 默认生成decrement方法使用@click="decrement"调用,vue中事件触发会将事件作为方法的参数传递,即value是事件event。
// 所以调用mapMutations生成的方法需要指定参数,如@click="decrement(num)"
...mapMutations({decrement: 'JIAN'}),
// 3 使用mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法中会调用commit来联系mutations,数组写法。
// 数组写法需要注意,数组中的值为mutations中定义函数的函数名;
// 当生成的方法名和mutations中的函数名相同时使用数组写法。
...mapMutations(['JIAN']),
// 4 使用mapActions生成的方法会调用dispatch来联系actions,对象写法。
...mapActions({incrementOdd: 'jiaOdd'}),
// 5 使用mapActions生成的方法会调用dispatch来联系actions,数组写法。
...mapActions(['jiaWait']),
}
}
</script>
8.求和案例-vuex模块化和命名空间
- 模块化。求和案例出现两个组件:Count求和组件和Person人员组件。模块化会将服务与Count组件的数据定义到store/count.js中;将服务与Person组件的数据定义到person.js中。然后在store/index.js中统一引入。
- 模块化让代码更好的维护,让多种数据分类更加明确。
- count.js。
export default {
namespaced: true,
// 省略actions mutations getters中的内容。
actions: {},
mutations: {},
getters: {},
};
- person.js。
import axios from 'axios'
import {nanoid} from 'nanoid'
// 导出
export default {
// 使用mapXxx引入模块,需要在模块中定义名称空间。
namespaced: true,
actions: {
addPersonWang(state, value) {
if (value.name.indexOf('王') === 0) {
state.commit('ADD_PERSON', value);
} else {
alert('添加的人必须姓王!');
}
},
addPersonServer(state) {
// http://api.uixsj.cn/hitokoto/get?type=social获取励志语言。
axios.get(`http://api.uixsj.cn/hitokoto/get?type=social`).then(
response => {
state.commit('ADD_PERSON', {id: nanoid(), name: response.data});
},
error => {
alert(error.message);
}
)
}
},
mutations: {
ADD_PERSON(state, value) {
console.log('Mutations中的ADD_PERSON被调用了');
state.personList.unshift(value);
}
},
state: {
personList: [
{id: '001', name: '张三'}
]
},
getters: {
// 返回第一个人的姓名
firstPersonName(state) {
return state.personList[0].name;
}
},
};
- index.js。
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import Vue from 'vue'
// 分别引入count.js/person.js
import countOptions from './count'
import personOptions from './person'
Vue.use(Vuex);
export default new Vuex.Store({
// 将countOptions和personOptions作为模块传入。
modules: {
a: countOptions,
b: personOptions,
}
});
- Person.vue中使用模块化,模块化后原生写法。
<template>
<div>
<h3>第一个人的名字:{{firstPersonName}}</h3>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入姓名" v-model="name">
<button @click="add">提交</button>
<button @click="addPersonWang">提交</button>
<button @click="addPersonServer">添加一个人,名字随机</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="person in personList" :key="person.id">{{person.name}}</li>
</ul>
<h3 style="color: red">上面组件和为 {{sum}}</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {nanoid} from 'nanoid'
export default {
methods: {
add() {
const personObj = {id: nanoid(), name: this.name};
// 如果使用store原生的commit写法,模块后,调用模块中的方法,需要使用b/ADD_PERSON
this.$store.commit('b/ADD_PERSON', personObj);
},
addPersonWang() {
const personObj = {id: nanoid(), name: this.name};
// 如果使用store原生的dispatch写法,模块后,调用模块中的方法,需要使用b/ADD_PERSON
this.$store.dispatch('b/addPersonWang', personObj);
},
addPersonServer() {
return this.$store.dispatch('b/addPersonServer')
}
},
computed: {
personList() {
return this.$store.state.b.personList;
},
sum() {
return this.$store.state.a.sum;
},
firstPersonName() {
// 如果使用store原生调用getters写法,
// 模块化后需要使用 this.$store.getters['b/firstPersonName']
return this.$store.getters['b/firstPersonName']
},
}
}
</script>
- Count.vue中使用模块化,模块化后mapXxx写法。
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前和为:{{a.sum}}</h3>
<h3>当前和为:{{bigSum}}</h3>
<h3>姓名 {{a.name}}</h3>
<button @click="jia(num)">+</button>
<h3 style="color: red">下方组件人数为 {{personList.length}}</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
methods: {
...mapMutations('a', ['JIAN']),
...mapActions('a', ['jiaWait', 'jiaOdd', 'jia']),
},
computed: {
// 1 对象方式引入a模块,a中每个属性或方法的调用都需要使用a.xxx。
...mapState({a: 'a'}),
...mapState('b', ['personList']),
// 2 通过namespaced名称空间引入,需要在组件中加namespaced: true。
// 3 通过namespaced名称空间引入后,调用方式可以直接写为xxx,而不是a.xxx。
...mapGetters('a', ['bigSum']),
}
}
</script>




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构