多表查询两种方法
目录
一:多表查询的两种方法
1.为什么要用多表查询?
因为我们在涉及表的时候肯定不止一张表。
2.多表查询的两种方法:
连表操作 : 先将查询涉及到的表拼接成一张大表 之后基于单表查询
子查询 :其实就是分步操作,将一张表的查询结果当做另外一条SQL语句的查询条件

二:数据准备
1.建表
员工部门表
create table dep(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
);
员工详细信息表
create table emp(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male',
age int,
dep_id int
);
2.插入数据
员工部门表
insert into dep values
(200,'技术'),
(201,'人力资源'),
(202,'销售'),
(203,'运营'),
(205,'安保');
员工详细信息表
insert into emp(name,sex,age,dep_id) values
('jason','male',18,200),
('tony','female',48,201),
('kevin','male',18,201),
('nick','male',28,202),
('owen','male',18,203),
('jerry','female',18,204);
三:多表查询方法之连表操作
连表操作:
先将查询涉及到的表拼接成一张大表 之后基于单表查询
from emp,dep : 后面可以跟多个表名,逗号隔开,使两张表拼接起来
1.笛卡尔积(以下组合方式)
将员工与部门拼接在了一起,但是出现了重复
select * from emp,dep;
筛选两表id对应 错误(需要字段名前面加表名限制)
select * from emp,dep where dep_id=id;
查询两张表拼接 id之间的对应关系(只获得姓名与部门)
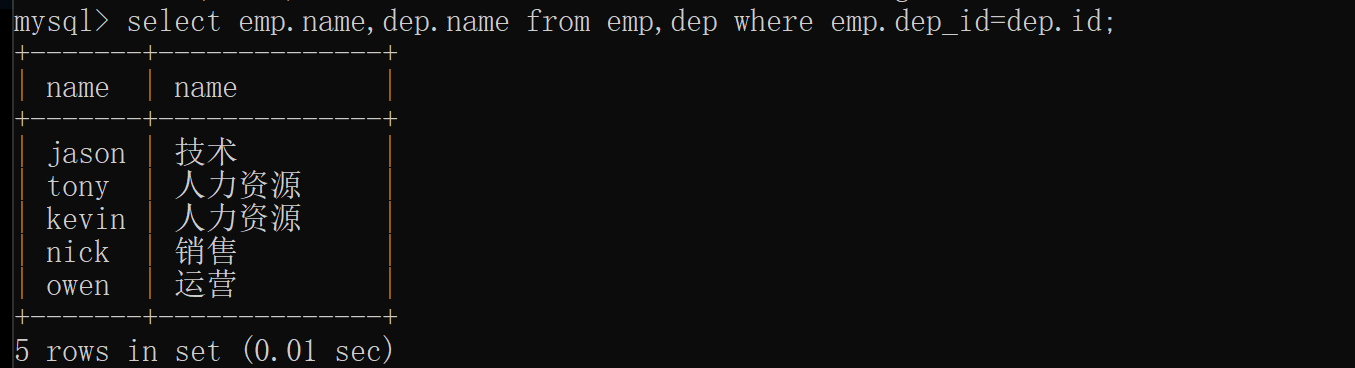
select emp.name,dep.name from emp,dep where emp.dep_id=dep.id;
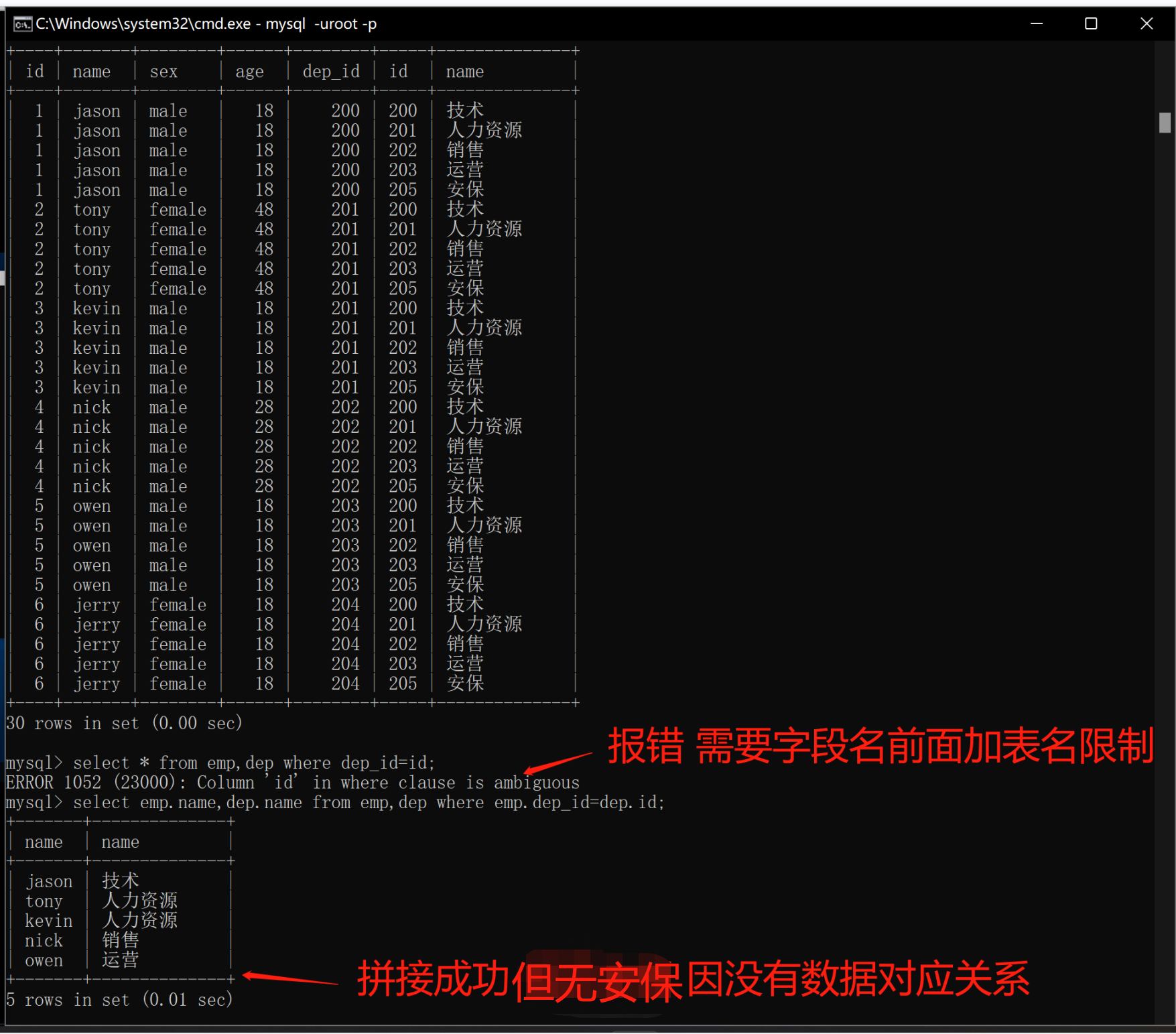
- 上述操作并不是合理的连表操作
"""
涉及到多表操作的时候 为了避免表字段重复
需要在字段名的前面加上表名限制
"""
2.连表操作
3.inner join 内连接
inner join 内连接:只连接两表中都存在(有对应关系)的数据
select * from emp inner join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id;
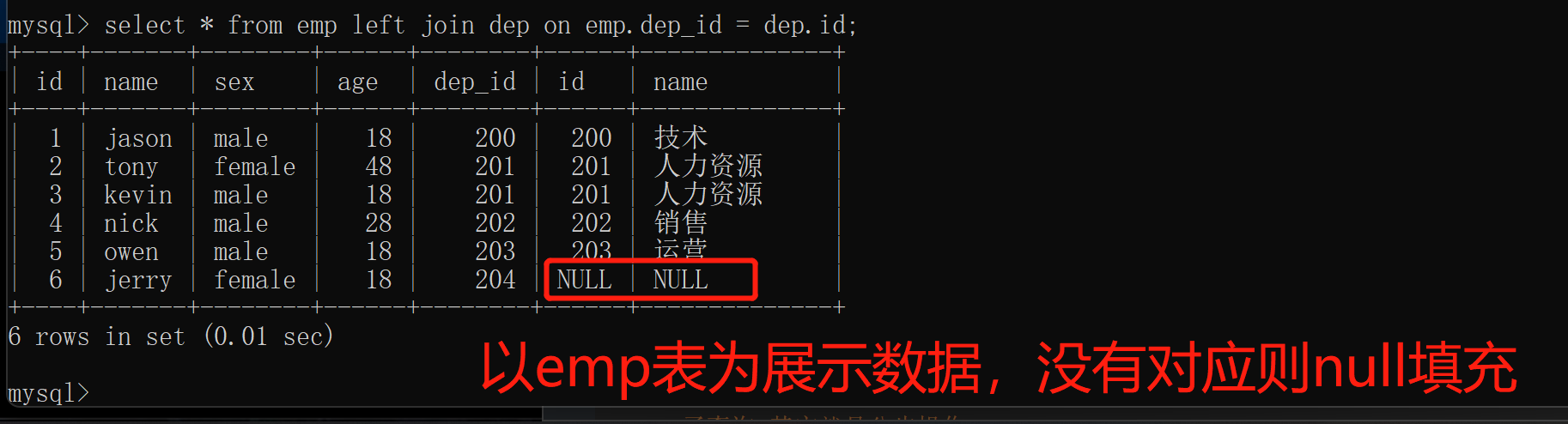
4.left join 左连接
left join 左连a接:以左表为基准展示左表所有的数据没有对应则NULL填充
select * from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id;
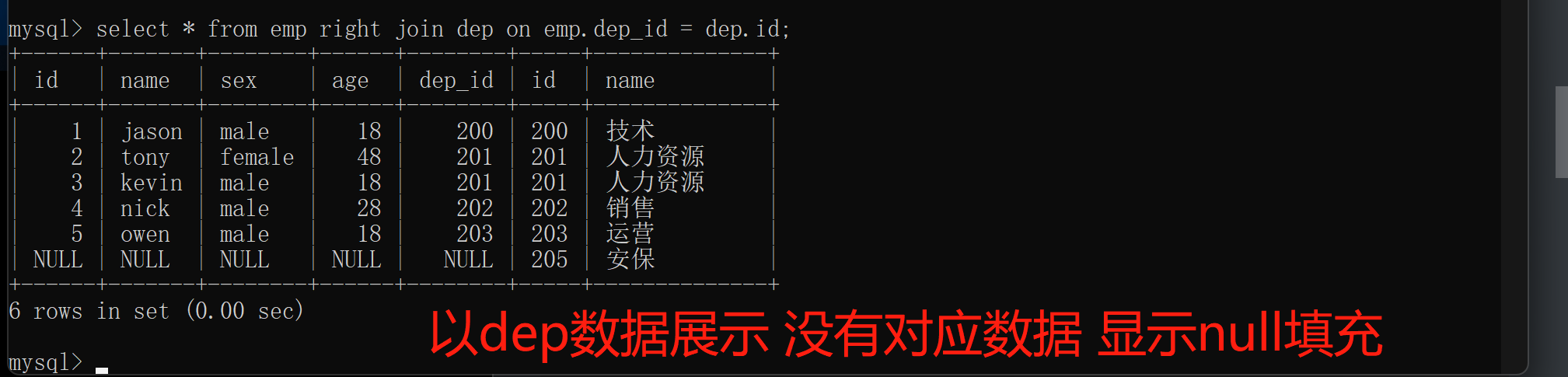
5.right join 右连接
right join 右连接:以右表为基准展示右表所有的数据没有对应则NULL填充
select * from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id;
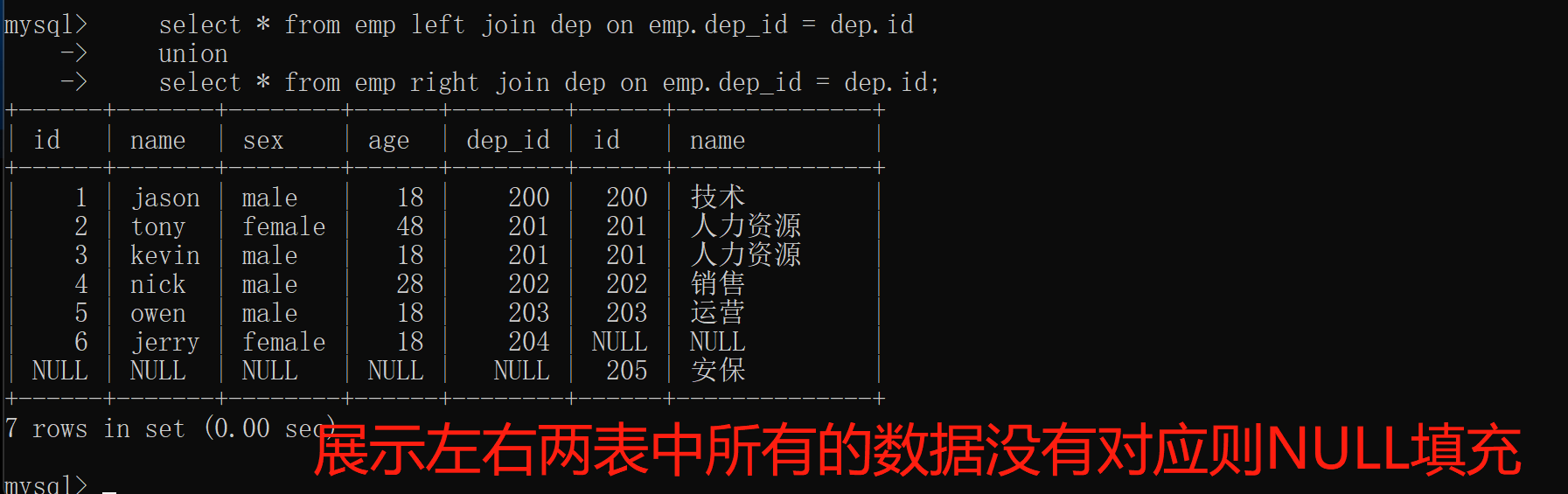
6.union 全连接
union 全连接:展示左右两表中所有的数据没有对应则NULL填充
select * from emp left join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id
union
select * from emp right join dep on emp.dep_id = dep.id;
四:多表查询方法之子查询
子查询:其实就是分步操作
将一张表的查询结果当做另外一条SQL语句的查询条件
1.子查询
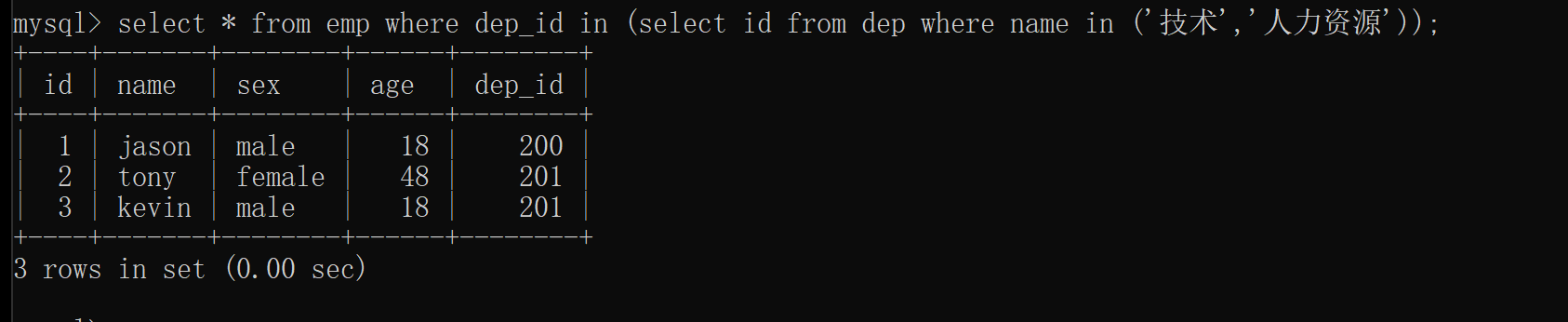
1.查询部门是技术或者人力资源的员工信息
1.先查询技术和人力资源的部门编号
select id from dep where name in ('技术','人力资源');
2.根据部门编号去员工表中筛选出对应的员工数据
select * from emp where dep_id in (200,201);
3.子查询:将SQL语句括号括起来即可充当查询条件
select * from emp where dep_id in (select id from dep where name in ('技术','人力资源'));