Linux C/C++服务器
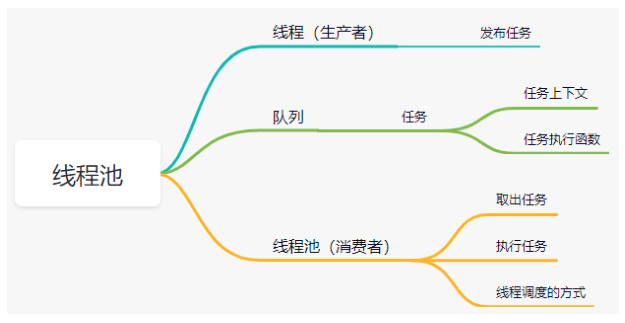
线程池
- 为什么需要线程池? 某类任务非常耗时(磁盘io、网络io或cpu密集任务),严重影响该线程处理其他任务
解决办法就是把这些耗时任务放到其他线程异步去执行,线程资源的开销与cpu核心之间做平衡选择 - 线程池的作用:复用线程资源,减少线程创建和销毁的开销;充分利用系统资源;异步执行耗时任务,在网络应用中使用较多
- 线程池线程数量:对于io密集型的耗时任务通常使用2 * (n+1)个线程,n为cpu核心数;对于cpu密集型的耗时任务使用n个线程;对于既有io密集又有cpu密集的耗时任务,通常使用的线程数量为(io等待时间+cpu运算时间) * 核心数/cpu运算时间
线程池的实现
线程池中的线程有两种,生产者线程,主要用于发布耗时任务,消费者线程,用于处理这些耗时任务,任务存放在消息队列中,消息队列中会存放任务上下文环境和任务的回调函数
通过mutex+condition实现线程的休眠与唤醒
线程池中的相关函数
在实现线程池之前,先了解下需要用到的相关函数
//线程创建与关闭
pthread_create(threadid, NULL, callback_func, void *arg)
pthread_join() //等待所有线程回调函数返回,即等待所有线程执行完
pthread_exit()
//线程互斥锁
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_mutex_lock()
pthread_mutex_unlock()
pthread_mutex_destroy()
//条件变量,线程的休眠与唤醒
pthread_cond_t condition;
pthread_cond_wait() //线程休眠,等待被唤醒
pthread_cond_signal() //唤醒单个线程
pthread_cond_broadcast() //唤醒所有线程
pthread_cond_destroy() //回收条件变量
- pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->condition), &(pool->mutex))
pthread_cond_wait接口内部会调用pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex)),释放锁;然后阻塞在 condition 条件变量
当我们发布任务时会调用pthread_cond_signal()接口,唤醒pthread_cond_wait,解除 condition 阻塞,然后加锁pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex))
线程池的实现思路
线程池由生产者线程、消费者线程和线程队列组成
生产者线程用来创建线程池和发布任务,消费者线程执行耗时任务,线程队列中包含任务的上下文及任务函数的函数指针
- 线程队列
typedef struct thread_pool_t thread_pool_t;
typedef void (*handler_pt) (void *); //函数指针类型定义的通用写法
//任务
typedef struct task_t {
handler_pt func; //回调函数名
void * arg; //回调函数参数
} task_t;
//任务队列
typedef struct task_queue_t {
uint32_t head; //取出任务位置
uint32_t tail; //插入任务位置
uint32_t count; //队列有多少数据
task_t *queue; //任务数组指针
} task_queue_t;
//线程的上下文环境
struct thread_pool_t {
pthread_mutex_t mutex; //线程锁
pthread_cond_t condition; //条件变量,休眠与唤醒线程
pthread_t *threads; //线程数组指针
task_queue_t task_queue; //任务队列数组
int closed; //线程池退出标记
int started; //当前运行的线程数
int thrd_count; //线程数量
int queue_size; //队列大小
};
- 线程池的创建与调度
thread_pool_create(){
...
pthread_create(&(pool->threads[i]), NULL, thread_worker, (void*)pool);
}
static void * thread_worker(void *thrd_pool) { //线程创建回调函数 内部函数,不对用户开放
thread_pool_t *pool = (thread_pool_t*)thrd_pool;
task_queue_t *que;
task_t task;
for (;;) { //一直循环执行任务
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex));
que = &pool->task_queue;
// 为什么使用while,while(que->count == 0 && pool->closed == 0)
// 虚假唤醒 linux pthread_cond_signal
// linux 可能被信号唤醒
// 业务逻辑不严谨,被其他线程抢了该任务
while (que->count == 0 && pool->closed == 0) { //队列为空 && 线程池没有退出
// pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex))
// 阻塞在 condition
// pthread_cond_signal()===========notify=============
// 解除阻塞
// pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex));
pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->condition), &(pool->mutex));
}
if (pool->closed == 1) break;
task = que->queue[que->head];
que->head = (que->head + 1) % pool->queue_size;
que->count--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));
(*(task.func))(task.arg); //执行任务
}
pool->started--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));
pthread_exit(NULL);
return NULL;
}
//发布任务 唤醒线程
int thread_pool_post(thread_pool_t *pool, handler_pt func, void *arg) {
if (pool == NULL || func == NULL) {
return -1;
}
task_queue_t *task_queue = &(pool->task_queue);
if (pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->mutex)) != 0) {
return -2;
}
if (pool->closed) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));
return -3;
}
if (task_queue->count == pool->queue_size) { //任务队列满了,发布失败
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));
return -4;
}
//往任务队列中插入任务
task_queue->queue[task_queue->tail].func = func;
task_queue->queue[task_queue->tail].arg = arg;
task_queue->tail = (task_queue->tail + 1) % pool->queue_size;
task_queue->count++;
if (pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->condition)) != 0) { //唤醒一个休眠的线程
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex)); //没有休眠的线程,释放锁
return -5;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->mutex));
return 0;
}
线程池实现demo
gcc -o mian main.c thrd_poll.c -pthread
./main 8 256
nginx线程池
作用:处理文件缓冲(磁盘io密集型)
nginx线程池用于优化读取静态磁盘文件耗时大的问题,对每个连接的compute耗时运算(静态网页文件缓存读取)放到线程池中异步处理
nginx一般推荐使用sendfile(小文件)和sendfile_max_chunk(大文件)直接将磁盘文件映射至内核缓冲区,但也可使用线程池进行磁盘io读取优化

reactor结构
众所周知,网络io基本都是reactor结构,我们先把结构图贴出来,以便后面nginx、redis、skynet中使用
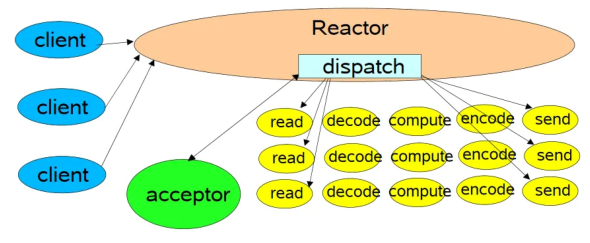
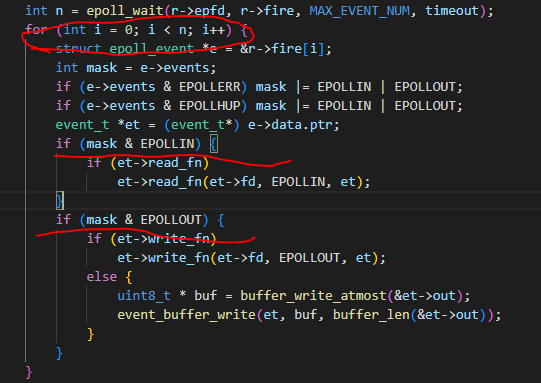
结合上边代码,如果同时有3个io读事件被检测,后边的for循环是依次处理,每个读事件如果有耗时的计算任务,那将严重影响服务器对其他消息的回复时间;如果把每个读事件的处理都放在线程池中进行异步处理,那么服务器响应时间将大大加快
nginx线程池结构
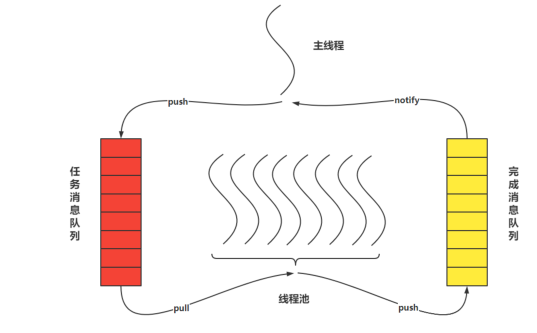
redis线程池
作用:读写 io 处理以及数据包解析、压缩(网络密集型)
redis线程池主要用于处理网络io中每个连接的读写解析和压缩过程,将单线程for循环执行变为线程池异步同时执行,用于提升处理网络io的速度

值得一提的是redis设计的线程调度非常的巧妙,没有使用condition条件变量,而是全部使用互斥锁
那如何让线程池中的线程休眠?主线程持有其他线程的锁,主线程将其他线程加锁,其他线程就在加锁处休眠等待主线程释放锁



