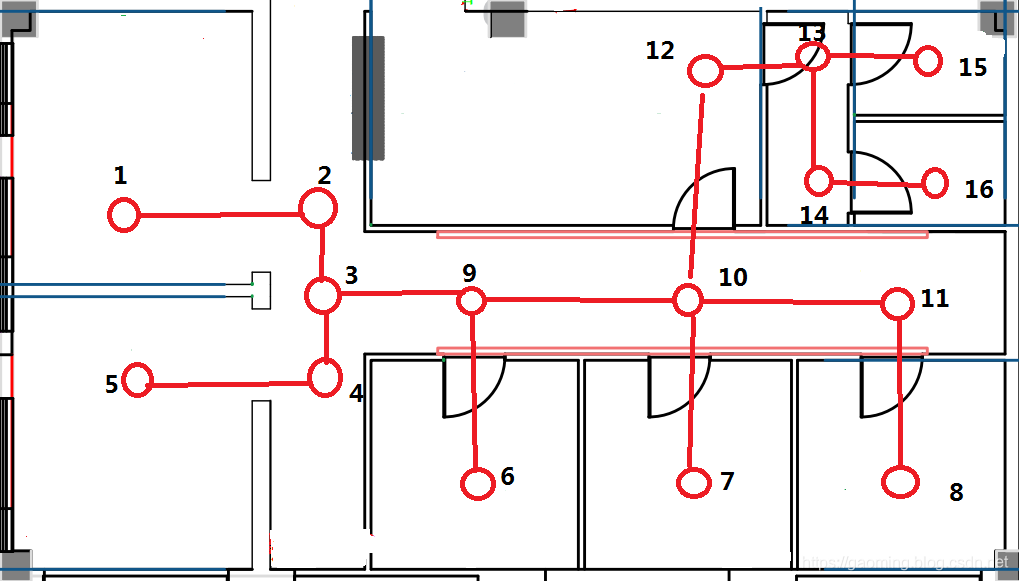
算法要求:
- 在一个无向连通图中求出两个给定点之间的所有路径;
- 在所得路径上不能含有环路或重复的点;
算法思想描述:
- 整理节点间的关系,为每个节点建立一个集合,该集合中保存所有与该节点直接相连的节点(不包括该节点自身);
- 定义两点一个为起始节点,另一个为终点,求解两者之间的所有路径的问题可以被分解为如下所述的子问题:对每一 个与起始节点直接相连的节点,求解它到终点的所有路径(路径上不包括起始节点)得到一个路径集合,将这些路径集合相加就可以得到起始节点到终点的所有路径;依次类推就可以应用递归的思想,层层递归直到终点,若发现希望得到的一条路径,则转储并打印输出;若发现环路,或发现死路,则停止寻路并返回;
- 用栈保存当前已经寻到的路径(不是完整路径)上的节点,在每一次寻到完整路径时弹出栈顶节点;而在遇到从栈顶节点无法继续向下寻路时也弹出该栈顶节点,从而实现回溯。
代码实现
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Node {
public String name = null;
public ArrayList<Node> relationNodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public ArrayList<Node> getRelationNodes() {
return relationNodes;
}
public void setRelationNodes(ArrayList<Node> relationNodes) {
this.relationNodes = relationNodes;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Test2 {
public static Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
public static ArrayList<Object[]> sers = new ArrayList<Object[]>();
public static boolean isNodeInStack(Node node) {
Iterator<Node> it = stack.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Node node1 = (Node) it.next();
if (node == node1)
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void showAndSavePath() {
Object[] o = stack.toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < o.length; i++) {
Node nNode = (Node) o[i];
if (i < (o.length - 1))
System.out.print(nNode.getName() + "->");
else
System.out.print(nNode.getName());
}
sers.add(o);
System.out.println("\n");
}
public static boolean getPaths(Node cNode, Node pNode, Node sNode, Node eNode) {
Node nNode = null;
if (cNode != null && pNode != null && cNode == pNode)
return false;
if (cNode != null) {
int i = 0;
stack.push(cNode);
if (cNode == eNode) {
showAndSavePath();
return true;
}
else {
nNode = cNode.getRelationNodes().get(i);
while (nNode != null) {
if (pNode != null && (nNode == sNode || nNode == pNode || isNodeInStack(nNode))) {
i++;
if (i >= cNode.getRelationNodes().size())
nNode = null;
else
nNode = cNode.getRelationNodes().get(i);
continue;
}
if (getPaths(nNode, cNode, sNode, eNode))
{
stack.pop();
}
i++;
if (i >= cNode.getRelationNodes().size())
nNode = null;
else
nNode = cNode.getRelationNodes().get(i);
}
stack.pop();
return false;
}
} else
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String nodeRalation[][] = { { "0" },
{ "2" },
{ "1", "3" },
{ "2", "4", "9" },
{ "3", "5" },
{ "4" },
{ "9" },
{ "10", "8" },
{ "7", "11" },
{ "3", "6", "10" },
{ "9", "7", "11" },
{ "10", "8" }
};
Node[] node = new Node[nodeRalation.length];
for (int i = 0; i < nodeRalation.length; i++) {
node[i] = new Node();
node[i].setName("node" + i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < nodeRalation.length; i++) {
ArrayList<Node> List = new ArrayList<Node>();
for (int j = 0; j < nodeRalation[i].length; j++) {
for (int z = 0; z < nodeRalation.length; z++) {
if (node[z].getName().equals("node" + nodeRalation[i][j])) {
List.add(node[z]);
break;
}
}
}
node[i].setRelationNodes(List);
List = null;
}
getPaths(node[1], null, null, node[8]);
}
}
node1->node2->node3->node9->node10->node7->node8
node1->node2->node3->node9->node10->node11->node8