Java二叉树
二叉树存储方式
二叉树可以链式存储,也可以顺序存储。
那么链式存储方式就用指针, 顺序存储的方式就是用数组。
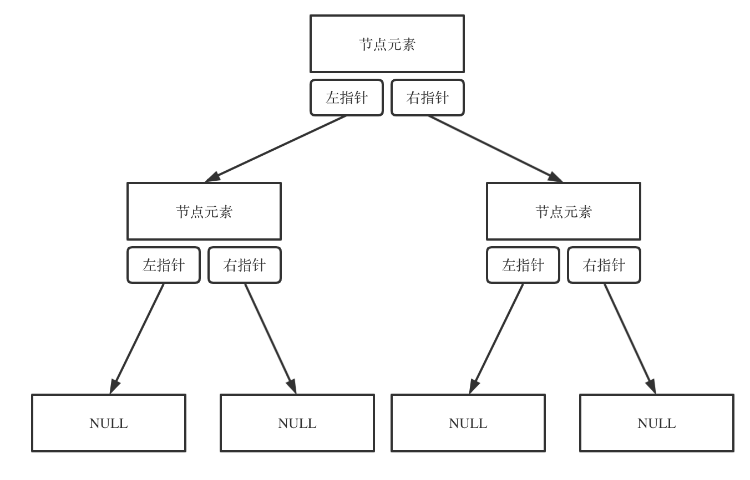
构造二叉树
public class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode() {} TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { this.val = val; this.left = left; this.right = right; } }
前序遍历
class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>(); preorder(root, result); return result; } public void preorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) { if (root == null) { return; } result.add(root.val); preorder(root.left, result); preorder(root.right, result); } }
中序遍历
class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); inorder(root, res); return res; } void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) { if (root == null) { return; } inorder(root.left, list); list.add(root.val); // 注意这一句 inorder(root.right, list); } }
后序遍历
class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); postorder(root, res); return res; } void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) { if (root == null) { return; } postorder(root.left, list); postorder(root.right, list); list.add(root.val); // 注意这一句 } }
如果不用递归如何去实现前中后序遍历
基本上递归都可以用栈的方式去实现
- 前序遍历: 中左右
class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); TreeNode temp = new TreeNode(); stack.push(root); //先将根节点入栈 List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null){ return list; } while (stack.size() != 0){ //遍历完全的判断是:如果栈内没结点了就说明遍历完了 temp = stack.pop(); list.add(temp.val); if(temp.right != null){ stack.push(temp.right); // 注意我们的中序遍历是:中左右, 所以我们如果入栈应该是先右再左,这样出栈的时候才是左再右 } if(temp.left != null){ stack.push(temp.left); } } return list; } }
- 中序遍历:左中右

class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); TreeNode temp = root; if(root == null){ return list; } while (temp != null || stack.size() != 0){ //只要当前节点 cur 不为空或栈 stack 不为空,就继续遍历 if (temp != null){ stack.push(temp); temp = temp.left; }else { temp = stack.pop(); list.add(temp.val); temp = temp.right; } } return list; } }
后序遍历
后序遍历顺序 左-右-中 入栈顺序:中-左-右 出栈顺序:中-右-左, 最后翻转结果class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); TreeNode temp = root; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); if (root != null){ stack.push(root); } while (stack.size() != 0){ temp = stack.pop(); list.add(temp.val); if(temp.left != null){ stack.push(temp.left); } if (temp.right != null){ stack.push(temp.right); } } Collections.reverse(list); return list; } }
层序遍历
我写的是利用的列表去记录的,标准写法是用的队列
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<>(); // 记录出栈的正确顺序 List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null){ return result; } stack.push(root); while (stack.size() != 0){ List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); int len = stack.size(); //这里一定要记录一下长度 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){ //这里不能够直接写i < stack.size() 因为随着pop操作,size一直在变化 list1.add(stack.peek().val); // 这一层全部加入到该层的结果中 list.add(stack.pop()); // 记录这一层的结点 方便遍历下一层 } result.add(list1); for(int j = list.size(); j > 0; j--){ // 遍历下一层 if(list.get(j-1).right != null){ stack.push(list.get(j-1).right); } if(list.get(j-1).left != null){ stack.push(list.get(j-1).left); } } list.clear(); // 清空 防止后面重复 } return result; } }
但其实这里很复杂,我用了栈和列表,后来发现队列会方便很多
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode1 root) { Queue<TreeNode1> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // 队列用来存储遍历的结点 List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); // 记录每一层的结点结果 if (root == null){ return result; } queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int len = queue.size(); // 记录每一层的个数 List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); // 记录每一层的结点 while (len > 0){ // 遍历每一层 if (queue.peek().left != null){ queue.offer(queue.peek().left); } if (queue.peek().right != null){ queue.offer(queue.peek().right); } list.add(queue.poll().val); len --; } result.add(list); } return result; } }
翻转二叉树
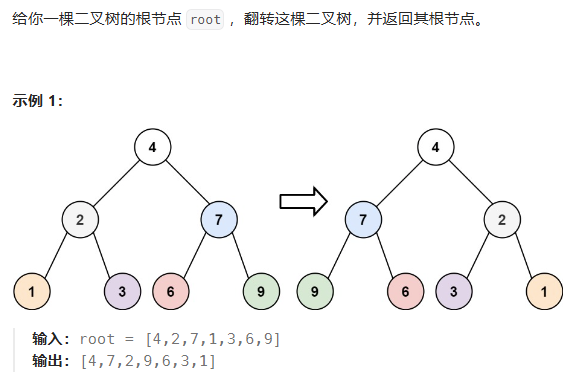
class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) { if (root == null){ return root; } TreeNode temp = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = temp; invertTree(root.left); invertTree(root.right); return root; } }
对称二叉树
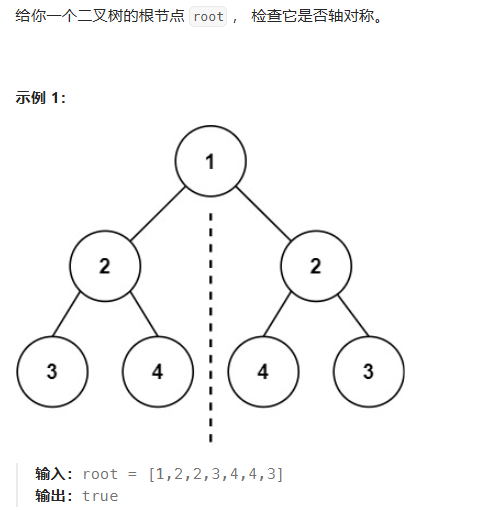
要遍历两棵树而且要比较内侧和外侧节点,所以准确的来说是一个树的遍历顺序是左右中,一个树的遍历顺序是右左中。
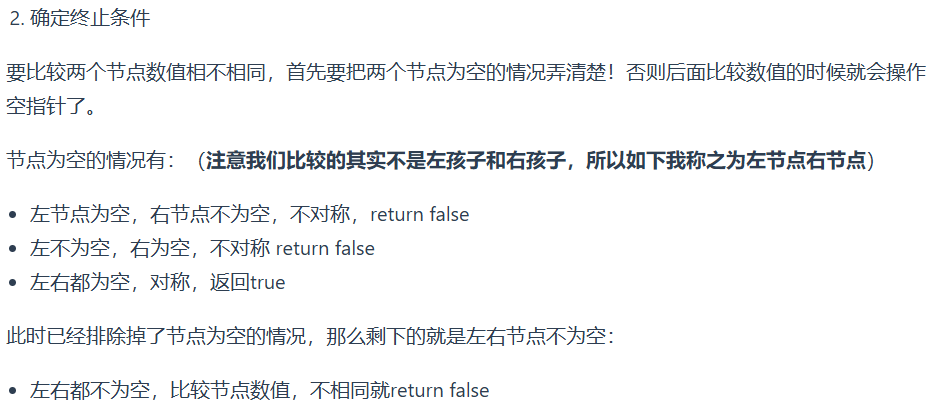
class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return false; } return sort(root.left, root.right); } public boolean sort (TreeNode l, TreeNode r){ if (l == null && r == null){ return true; } if (l == null && r != null){ return false; } if (l != null && r == null){ return false; } if (l.val != r.val){ return false; } boolean outside = sort(l.left, r.right); boolean inside = sort(l.right, r.left); return outside && inside; } }
节点个数
普通二叉树
用递归遍历去遍历一遍,这里用后序遍历是最快的。
class Solution { public int countNodes(TreeNode1 root) { int num = 0; if(root == null){return num;} num ++; int num_left = countNodes(root.left); // 左 int num_right = countNodes(root.right); // 右 num += countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right); // 中 return num; } // 上面的代码精简版: public int countNodes1(TreeNode1 root) { if (root == null){return 0;} return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1; } }
完全二叉树
这里如果是完全二叉树,我们不应该再用一般的方法对其进行计算,因为会消耗很多的资源,我们可以利用其特性进行计算。
对于满二叉树我们可以直接根据公式得到。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2^(h-1) 个节点。
对于最后一层叶子节点没有满,分别递归左孩子,和右孩子,递归到某一深度一定会有左孩子或者右孩子为满二叉树,然后依然可以按照满二叉树来计算。
class Solution { public int countNodes(TreeNode root) { if (root == null){return 0;} int num_left = 0; int num_right = 0; TreeNode temp_left = root.left; TreeNode temp_right = root.right; while (temp_left != null){ //看左边的层次 num_left ++; temp_left = temp_left.left; } while (temp_right != null){ //看右边的层次 num_right ++; temp_right = temp_right.right; } if (num_left == num_right){ //最左边的层次等于最右边的层次则认为是满二叉树 return (2 << num_left) -1 ; // 2 << num_left :实际上相当于 2 * (2^num_left) 注意这里的num_left实际上是层数-1,所以要再乘以2相当于 2^(num_left + 1) - 1 } else { return countNodes(root.right) + countNodes(root.left) +1; // 这里的加1是因为在这一层的根节点要算上 } } }
平衡二叉树
我的写法是暴力计算,但是可以发现会有很多的重复计算高度。
class Solution { public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) { if (root == null){return true;} if(Math.abs(depth(root.left)-depth(root.right)) < 2){ return isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right); } return false; } public int depth(TreeNode root){ if (root == null){return 0;} return Math.max(depth(root.left), depth(root.right)) + 1; } }
但是这里用很巧妙的方法帮助我不用去计算已经不是平衡树的时候的高度。
class Solution { /** * 递归法 */ public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) { return getHeight(root) != -1; } private int getHeight(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left); if (leftHeight == -1) { // 如果子树已经不是平衡树了就直接返回-1 不要去计算高度了,网上递归的时候上面的树必然也不会是平衡树 return -1; } int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right); if (rightHeight == -1) { return -1; } // 左右子树高度差大于1,return -1表示已经不是平衡树了 if (Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) { return -1; } return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1; //如果是平衡树,那么这一层的高度是左右子树的最大高度加上本层 } }
二叉树的所有路径
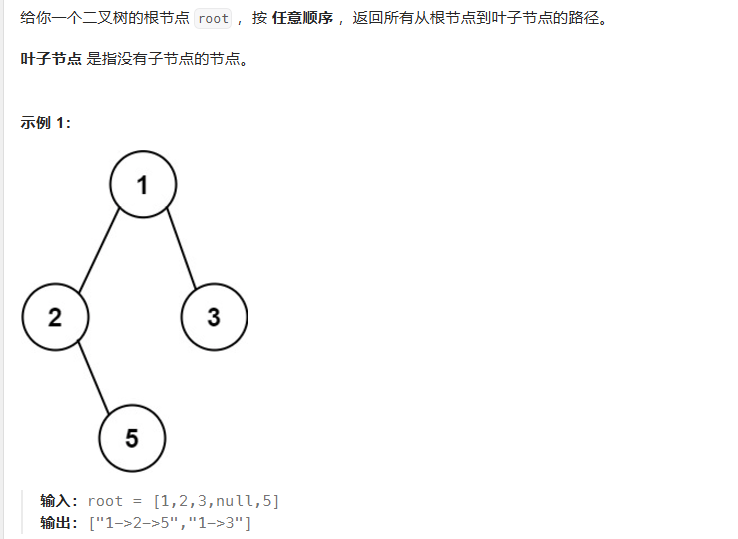
其实我一看到题目就想到了前序遍历。
但是卡在了怎么去回溯,我输出路径之后怎么返回上面去?
class Solution { public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) { List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null){return result;} List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); travelsal(root,list,result); return result; } public void travelsal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list, List<String> result){ list.add(root.val); if (root.left == null && root.right == null){ //结束条件。满足了就应该把这个路径输出 StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < list.size() - 1; i++){ str.append(list.get(i)).append("->"); } str.append(list.get(list.size()-1)); result.add(str.toString()); return; } if(root.left != null){ travelsal(root.left,list,result); //递归 list.remove(list.size()-1); //回溯的过程,当我把路径记下来之后再回到这里我就要删除 } if(root.right != null){ travelsal(root.right,list,result); //回溯的过程,当我把路径记下来之后再回到这里我就要删除 list.remove(list.size()-1); } } }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具