力扣刷题笔记
有序数组的平方:
我的错误解法:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Solution s = new Solution(); int[] nums = {-5,-3,-2,-1}; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s.removeElement(nums)));; } } class Solution { public int[] removeElement(int[] nums) { int min = 0; int max = nums.length-1; while (min != max){ if(Math.abs(nums[min]) > Math.abs(nums[max])){ int temp = nums[max]; nums[max] = (int)Math.pow(nums[min],2); nums[min] = temp; max --; }else{ nums[max] = (int)Math.pow(nums[max],2); max --; } } nums[min] = (int)Math.pow(nums[min],2); return nums; } }
在我自己的这种解法中,在一些数组中并不适用。比如这里的例子-5,-3,-2,-1.
第一轮nums[3]=25,nums[0]=-1。而第二轮直接用-1和-2比较,中间的-3其实才是最大的数,所以错误。
这也是为什么解答答案中必须用一个新数组去记录的原因!
移除链表元素
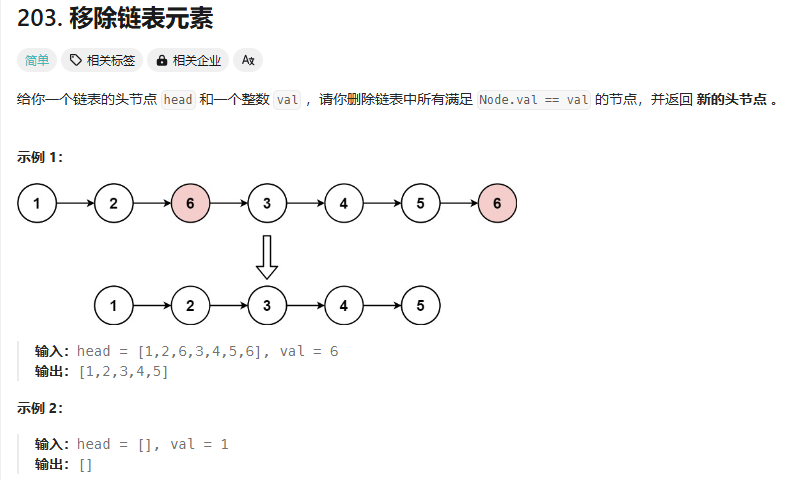
这里有两个地方要注意
1.怎么处理头节点,如果不加入虚拟头节点那么就要分两种情况去删除元素:判断是否为头节点
2.空指针异常的警告问题
我的错误代码:

在这里 我们应该写:
class Solution { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { while (head != null && head.val == val ){ head = head.next; } ListNode temp = head; while(temp != null && temp.next != null){ if (temp.next.val == val){ temp.next = temp.next.next; }else{ temp = temp.next; } } return head; } }
还一种带虚拟头节点的
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); dummy.next = head; ListNode temp = dummy; while (temp.next != null){ if (temp.next.val == val){ temp.next = temp.next.next; }else{ temp = temp.next; } } return dummy.next;
反转链表
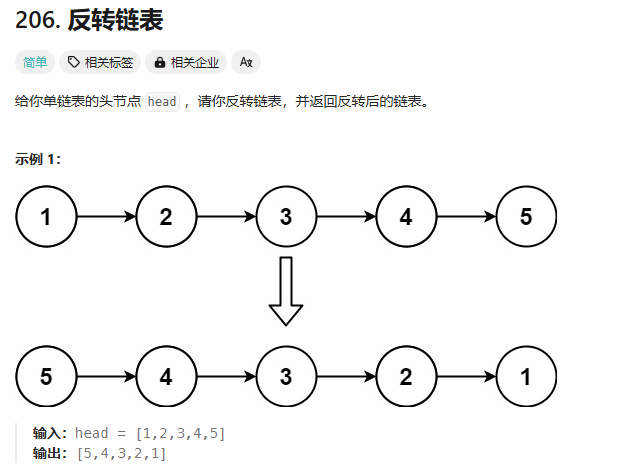
双指针的方法:
首先两个需要注意的点:
① 在最开始初始化的时候pre的赋值,这里应该是赋值null,因为最开始的头结点应该变成尾结点指向空
② 在改变了next指向的时候,需要增加一个temp来保留原先的next指向的结点,避免在改变了指向之后找不到原先的下一结点。
我写的代码:
class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null; ListNode cur = head; ListNode temp = cur.next; while (cur != null){ cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; if (temp.next != null){ temp = temp.next; } } return pre; } }
但这里我本来写的
cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; temp = temp.next;
这其实是有错误的,当我的temp本来指向的就是null之后,我是没有办法遍历它的next的,会出现空指针异常
需要更改的话,其实我可以将temp指针的赋值操作提到最前面,就不会有这个问题了。
正确写法如下:
class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null; ListNode cur = head; ListNode temp; while (cur != null){ temp = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; } return pre; } }
还有一种写法是写成递归的形式:
这一种形式最好是在写了双指针的解法之后去更改
这里也要注意一点就是空指针异常
temp的赋值要是在if判断之前就会出现空指针异常的问题,我们如果放在了下面就避免了我们去访问null的next的问题了。
class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){ ListNode pre = null; ListNode cur = head; return reverse(cur,pre); } public ListNode reverse(ListNode cur, ListNode pre){ if (cur == null){ return pre; } ListNode temp = cur.next; cur.next = pre; return reverse(temp,cur); } }
链表相交

我的思路是算两个链表的长度之差mins,长度更长的链表先往前走mius步,然后再共同移动,每一步比较一下所指的节点是否一致。
还有一种看起来更快速的思路:

环形链表
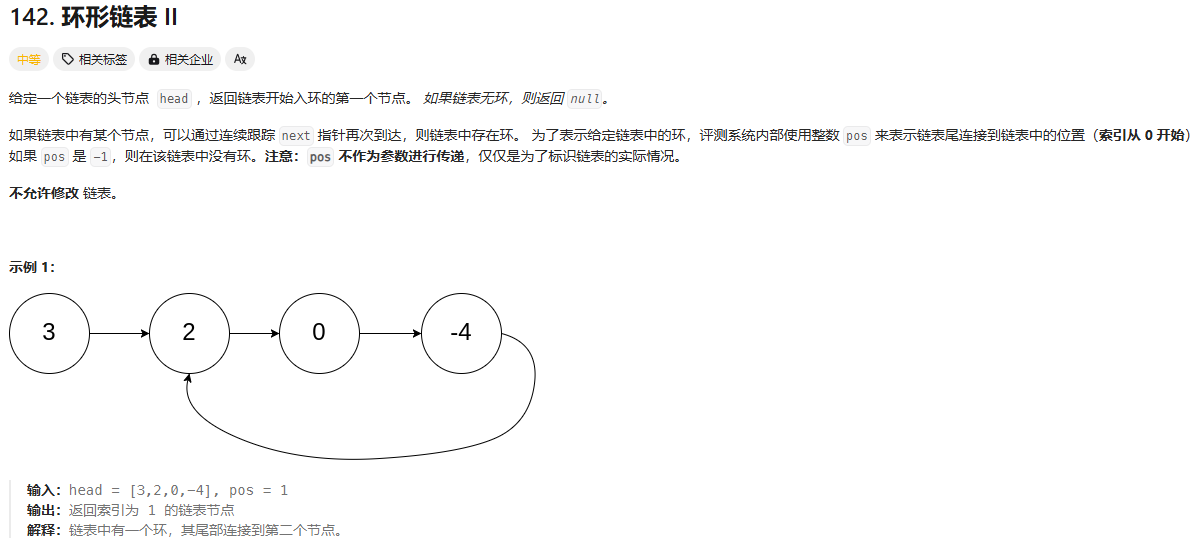
这个题目没写出来

我按照这个思路的代码是这样写的:
class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(int x) { val = x; next = null; } } public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while (fast != slow){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == null || fast.next == null){ return null; } } ListNode temp = head; while (slow != temp){ slow = slow.next; temp = temp.next; } return temp; } }
但其实这里有一个很严重的错误,在最开始我想要找到相遇结点时的程序是不正确的,最开始fast == slow就已经满足了,所以判断条件不能这样写
正确写法:
class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(int x) { val = x; next = null; } } public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == slow){ ListNode temp = head; while (slow != temp){ slow = slow.next; temp = temp.next; } return temp; } } return null; } }
两个数组的交集

解法一:
import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; class Solution { public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) { Set<Integer> arr = new HashSet<Integer>(); Set<Integer> rearr = new HashSet<Integer>(); for(int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i ++){ arr.add(nums1[i]); } for (int j = 0 ; j<nums2.length; j++){ if (arr.contains(nums2[j])){ rearr.add(nums2[j]); } } return rearr.stream().mapToInt(x -> x).toArray(); } }
快乐数

这道题目我开始想的是使用map,但是后来看答案我发现不用map,直接set判断这个数在不在里面就行了。我自己想的方法有一步特别麻烦的就是在计算一个数的各位平方之和的情况下,我还用了一个数组专门存放各个位上的数字,后来发现完全不需要这么复杂。
所以这道题很需要学习这种求各个位上平方之和的方法。
import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; class Solution { public boolean isHappy(int n) { Set <Integer> hashset = new HashSet<Integer>(); while (!hashset.contains(n)){ if (n == 1){ return true; } hashset.add(n); n = getnext(n); } return false; } public int getnext (int n){ int next = 0; while(n != 0){ next += (n%10) * (n%10); n = n / 10; } return next; } }
两数之和

这道题目我是用数组做的,借鉴了冒泡法的思想,我需要两层for循环去遍历,但其实这样时间复杂度会比较高一点。
这道题目也可以去用哈希法。我们可以用一个map存储数组中我们遍历过的元素,然后直接用contains判断我们需要的元素在不在map里面即可。这里的map可以存储key和value,正好满足了我们需要得到数组下标的需求。
我们遍历一遍数组中的元素,将遍历过的元素存储在map中,后续遍历后面的元素,我们通过target - nums[i]得到我们需要的数temp,然后直接搜索是否存在map中即可。
但需要注意的一点是,我们的key存放的是数,value存放的是下标。因为map只能通过key返回value,我们后续要的是下标值,所以应该吧下标值放在value中。
import java.util.HashMap; class Solution { public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { HashMap<Integer,Integer> hashmap = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); int[] arr = new int[2]; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i ++){ int temp = target - nums[i]; while (hashmap.containsKey(temp)){ arr[0] = hashmap.get(temp); arr[1] = i; return arr; } hashmap.put(nums[i],i); } return null; } }
四数相加

我最开始的想法:
import java.util.HashMap; class Solution { public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) { HashMap<Integer,Integer> hashMap1 = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); HashMap<Integer,Integer> hashMap2 = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); int num = 0; int member = 0; int n = nums1.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++){ for ( int j = 0; j < n; j ++){ hashMap1.put(++num,nums1[i]+nums2[j]); } } num = 0; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++){ for ( int j = 0; j < n; j ++){ hashMap2.put(++num,nums3[i]+nums4[j]); } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n*n; i ++){ for(int j = 0 ; j < n*n ;j ++){ if (hashMap1.get(i+1)+hashMap2.get(j+1)==0){ member++; } } } return member; } }
先将两个数组的两两之和用一个hashmap存储起来
key可以反应我获取和变来的下标(比如说1:00 ; 2:01; 3:10; 4:11)
但是后来我发现并不需要得到具体的数组的下标值。而且我这算法超出了时间限制,我发现最后的两层for循环去遍历其实是不需要的,我可以直接使用hashmap里自带的contains函数就可以找到hashmap2是否有-hashmap1的值就好。
但此时又有一个问题就是hashmap不能查找value值,我是将所有的存储在hashmap2的value里。如果我需要遍历一遍我的value我也没有办法获得这个value对应的次数,所以这个问题要换红方法解决。
那么我只能够将这些计算得到的和存储在key中,把这个值出现的次数放在value中,每当这个数字出现了一次,我的value值+1。
这里使用了一个很好用的函数getOrDefault。这个函数可以查找我需要的key值,此时我如果把所求的和存放在key里面,value就存放这个和出现的次数即可。
import java.util.HashMap; class Solution { public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) { HashMap<Integer,Integer> hashMap1 = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); HashMap<Integer,Integer> hashMap2 = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); int member = 0; int n = nums1.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++){ for ( int j = 0; j < n; j ++){ if (hashMap1.containsKey(nums1[i]+nums2[j])){ int num = hashMap1.get(nums1[i]+nums2[j]); hashMap1.put((nums1[i]+nums2[j]),++num); }else { hashMap1.put(nums1[i] + nums2[j], 1); } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { member += hashMap1.getOrDefault((-nums3[i] - nums4[j]), 0); } } return member; } }
四数之和

这道题目最难的地方我觉得就是不能重复的四元组,你要保证你所获取的所有的元组是之前没有取到的,就需要一个去重的操作。
上一道题目是三数之和,思想有部分是一样的:

import java.util.*; class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> lists = new ArrayList<>(); Arrays.sort(nums); for ( int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ if (nums[i] > 0){ return lists; }else if( i >0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]){ continue; } int left = i + 1; int right = nums.length-1; while (left < right){ int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right]; if (sum > 0){ right --; }else if(sum < 0){ left++; }else{ lists.add(new LinkedList<>(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[left],nums[right]))); while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left+1]) left++; while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right-1]) right--; left++;right--; } } } return lists; } }
为了后续的操作,这里一定第一步就是进行数组排序操作。
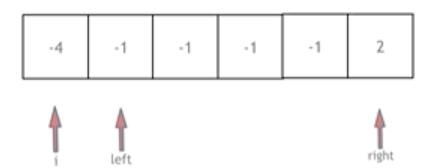

这中间比较重要的就是去重操作。首先对外层的i,当nums[i]和前一个位置的数相等时,我们就要向后移动一位,这里不能够和后一位去判断,我们时要防止和前面的取到的元组一样,所以和前面一位去判断。
四数之和就是外层再增加了一层循环。但是外层要注意的一点就是nums[k]>target并不能作为break的判断语句,大于了目标值并不代表后续移动中没有满足的条件了,如果时-4,-1,0,0.那么nums[k]= -4, nums[i]= -1。这个时候我们俩个负数相加其实变小了,所以仍然可能满足条件。
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) { Arrays.sort(nums); List<List<Integer>> lists = new ArrayList<>(); for (int k = 0; k < nums.length; k++){ if (nums[k] >= 0 && nums[k] > target){break;} if (k > 0 && nums[k] == nums[k-1]){continue;} for ( int i = k + 1; i < nums.length; i++){ if (i > k+1 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]){continue;} if (nums[k]+nums[i]>target && nums[k]+nums[i]>=0){break; } int left = i + 1; int right = nums.length-1; while (left<right){ long sum =(long) nums[i] + nums[k] + nums[left] + nums[right]; if (sum<target){ left++; }else if(sum>target){ right--; }else { lists.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[k],nums[left],nums[right])); while (left < right && nums[left]==nums[left+1]){left++;} while (right> left && nums[right]==nums[right-1]){right--;} right--; left++; } } } } return lists; } }
反转字符串

这里我想到的就是a=a+b;b=a-b;a=a-b;
给出的答案里面有一种异或运算的方法:
class Solution { public void reverseString(char[] s) { int l = 0; int r = s.length - 1; while (l < r) { s[l] ^= s[r]; //构造 a ^ b 的结果,并放在 a 中 s[r] ^= s[l]; //将 a ^ b 这一结果再 ^ b ,存入b中,此时 b = a, a = a ^ b s[l] ^= s[r]; //a ^ b 的结果再 ^ a ,存入 a 中,此时 b = a, a = b 完成交换 l++; r--; } } } // 第二种方法用temp来交换数值更多人容易理解些 class Solution { public void reverseString(char[] s) { int l = 0; int r = s.length - 1; while(l < r){ char temp = s[l]; s[l] = s[r]; s[r] = temp; l++; r--; } } }

第一步
a = a ^ b; 完成后 a变量的结果为a ^ b
第二步:
b = a ^ b; 此时赋值号右边的a保存的是a ^ b的值,那么将赋值号右边的a用a ^ b替换,
得到(a ^ b) ^ b=a ^ (b ^ b)=a ^0=a, 即经过第二步运算后b中的值为a,即b=a,将a换到了b里
第三步: a = a ^ b;
此时赋值号右边的a保存的仍然是a ^ b的值,不变,而赋值号右边的b已经是a 了,将赋值号右边的a,b分别进行替换,
即此时赋值号右边a ^ b=(a ^ b)^ a=a ^ b^ a=a ^ a^ b=0^ b=b, 该值赋值给a,即a=b
即经过第三步运算后a中的值为b,即a=b,将b换到了a里
实现strStr()

这里我的写法是暴力搜索时间消耗很大,这个看到答案之后知道是KMP问题,可以通过找到next数组帮助。
我的写法:
class Solution { public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) { char[] a = haystack.toCharArray(); char[] b = needle.toCharArray(); int j = 0; for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i ++){ if (a[i] == b[0]){ int num = i; for(j =0 ; j < b.length; j++){ if (num + b.length > a.length){return -1;} if(a[i] != b[j]){ break; } i++; } if(j == b.length){ return i-b.length; }else{ i = num; } } } return -1; } }
首先学一下怎么获得next数组
public void findNext(String s, int[] next){ next[0] = -1; char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); for (int i =1, j = -1; i < s.length(); i++){ while (j >= 0 && chars[i] != chars[j +1]){j = next[j];} if ( chars[i] == chars[j + 1]){ j++;} next[i] = j; } }
不懂就自己去IDEA里遍历一遍就知道啦,不太好说
class Solution { public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) { int[] next = new int[needle.length()]; int j = -1; findNext(needle,next); for (int i = 0; i < haystack.length(); i++){ while (j >= 0 && haystack.charAt(i) != needle.charAt(j + 1)){j = next[j];} if (haystack.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j + 1)){ j ++; } if (j == needle.length() -1){ return (i - needle.length())+1; } } return -1; } public void findNext(String s, int[] next){ next[0] = -1; char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); for (int i =1, j = -1; i < s.length(); i++){ while (j >= 0 && chars[i] != chars[j +1]){j = next[j];} if ( chars[i] == chars[j + 1]){ j++;} next[i] = j; } } }
这里我们算的是needle的next数组,因为我们借助needle的next数组可以帮助我们在haystack[i] != needle[j]的时候,不用从头重新遍历一次needle,这样减少了复杂度!
class Solution { public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) { int[] next = new int[needle.length()]; int j = -1; findNext(needle,next); for (int i = 0; i < haystack.length(); i++){ while (j >= 0 && haystack.charAt(i) != needle.charAt(j + 1)){j = next[j];} if (haystack.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j + 1)){ j ++; } if (j == needle.length() -1){ return (i - needle.length())+1; } } return -1; } public void findNext(String s, int[] next){ next[0] = -1; char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); for (int i =1, j = -1; i < s.length(); i++){ while (j >= 0 && chars[i] != chars[j +1]){j = next[j];} if ( chars[i] == chars[j + 1]){ j++;} next[i] = j; } } }
重复的子字符串

第一种想法是:
![]()
class Solution { public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern(String s) { String copy = s+s; copy = copy.substring(1,copy.length()-1); if (copy.contains(s)){return true;} return false; } }
这道题还是可以用上面的KMP来算,但是有一个要知道的规律:

class Solution { public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern(String s) { int len = s.length(); int[] next = new int[s.length()]; next[0] = -1; for ( int i = 1, j = -1; i < s.length(); i++){ while ( j >= 0 && s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j + 1)){ j = next[j]; } if(s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j + 1)){ j++; } next[i] = j; } if (next[len - 1] != -1 && len % (len - ((next[len - 1]) + 1)) == 0){ return true; } return false; } }
滑动窗口最大值

1.双端队列维护窗口中的最大值:
使用双端队列(Deque)来高效维护滑动窗口中的元素:
- 队列存储下标,而不是直接存储数值。这样我们可以根据下标来判断哪些元素已经滑出窗口。
- 队列中的元素保持单调递减,队列头部总是当前窗口的最大值。
2. 如何维护队列:
在遍历数组时,我们对每个元素做以下操作:
-
移除队列头部过期的下标:如果队列头部的元素不在当前窗口范围内(即小于
i - k + 1),就将其从队列中移除。 -
保持单调性:如果当前元素大于队列尾部的元素,就将队列尾部的元素移除,直到找到比当前元素大的或队列为空。这样可以保证队列中的元素单调递减。
-
将当前元素下标加入队列:把当前下标放入队列尾部。
-
记录最大值:当
i >= k - 1时,窗口已经成型,队列头部的下标对应的元素就是当前窗口的最大值,将其加入结果数组。
3. 时间复杂度优化:
- 每个元素最多进队和出队一次,因此时间复杂度为
O(n),比暴力解法的O(n*k)更高效。
import java.util.ArrayDeque; class Solution { public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) { ArrayDeque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>(); int n = nums.length; int[] res = new int[n - k + 1]; int idx = 0; for ( int i =0; i< n; i++){ while (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peek() < i-k+1){ // 当队列的头节点不在我们需要的[i - k + 1, i]范围内,删除 deque.poll(); } while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] < nums[i]){ // 当队列的尾结点小于当前加入的值,删除 deque.pollLast(); } deque.offer(i); // 加入下标 if(i >= k - 1){ // 说明一定构成了一个窗口 则可以取最大值记录下来 res[idx ++] = nums[deque.peek()]; //不是弹出,是访问 } } return res; } }
前K个高频元素

这里利用了一个优先级队列进行排序操作,使得频率出现高的一直被保留在pq队列里面。这里使用的是小顶堆。
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq
- 这是创建了一个存储
int[]类型数组的优先队列pq。 PriorityQueue是一个基于堆的优先队列,默认是最小堆,也就是说它总是优先取出队列中最小的元素。
2. new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1[1] - o2[1])
- 这里使用了一个自定义的比较器来定义优先级规则。
PriorityQueue默认按照自然顺序进行排序(对于数值型,默认从小到大),但这里我们通过一个 lambda 表达式自定义了比较规则。
解释比较器 (o1, o2) -> o1[1] - o2[1]:
o1和o2是优先队列中的两个int[]数组。- 比较器根据每个数组的第二个元素 (
o1[1]和o2[1]) 来比较两个数组的大小。 - 如果
o1[1] - o2[1]的结果为负值,说明o1[1]小于o2[1],则o1的优先级更高(排在前面);如果结果为正值,o2的优先级更高。
如果要使用大顶堆:(o1,o2) -> o2[1] - o1[1];
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.PriorityQueue; class Solution { public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1[1] - o2[1]); //小顶堆 int[] res = new int[k]; //这里用来保留我们要选取的前k个高频的结果 Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // key用来存储值,value用来存储出现的频率 for(int num : nums){ map.put(num,map.getOrDefault(num,0)+1); //每次频率+1 } for(var x : map.entrySet()){ //遍历map里的每一个键值对 int[] temp = new int[2]; temp[0] = x.getKey(); temp[1] = x.getValue(); pq.offer(temp); if(pq.size() > k){ // 我们只保存前k个高频率的值 pq.poll(); // 删除队头频率低的值 } } for(int i =0; i < k; i++){ res[i] = pq.poll()[0]; } return res; } }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具