Java基础12
抽象类与抽象方法
abstract : 抽象的
abstract可以用来修饰:类、方法
abstract修饰类
> 此类称为抽象类
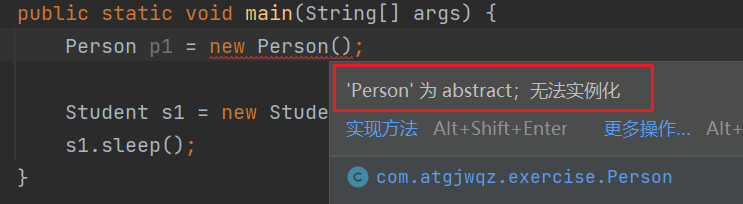
> 抽象类不能实例化
> 抽象类中是包含构造器的,因为子类对象实例化时,需要直接或间接的调用到父类的构造器
> 抽象类中可以没有抽象方法。反之,抽象方法所在的类,一定是抽象类。
抽象方法
> 此方法即为抽象方法
> 抽象方法只有方法的声明,没有方法体
> 抽象方法其功能是确定的(通过方法的声明即可确定),只是不知道如何具体实现(体现为:没有方法体)
> 子类必须重写父类中的所有抽象方法之后,方可实例化,否则此子类仍然是一个抽象类(还有抽象方法)
public abstract class Person { //抽象类 String name; int age; public Person(){ } public Person(String name, int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } public abstract void eat(); //抽象方法 public void sleep(){ System.out.println("人会睡觉"); } }
public class Student extends Person{ String school; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age, String school) { super(name, age); this.school = school; } public void eat(){ System.out.println("学生多吃有营养的食物"); } public void sleep() { System.out.println("学生要保证睡眠"); } }
public class AbstractTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // Person p1 = new Person(); Person设置为抽象类后不可以再创建对象 Student s1 = new Student(); s1.sleep(); } }
abstract不能使用的场景
abstract不能修饰: 属性、构造器、代码块等
abstract不能与哪些关键字共用:(自洽)
不能用abstract修饰私有方法、静态方法、final的方法、final的类。
> 私有方法不能重写
> 避免静态方法使用此类进行调用
> final的方法不能够被重写
> final修饰的类不能有子类
模板方法设计模式(TemplateMethod)
解决的问题:
- 当功能内部一部分实现是确定的,另一部分实现是不确定的。这时可以把不确定的部分暴露出去,让子类去实现。
- 换句话说,在软件开发中实现一个算法时,整体步骤很固定、通用,这些步骤已经在父类中写好了。但是某些部分易变,易变的部分可以抽象出来,供不同子类实现,这就是一种模板模式。
在此我们设计了一个模板方法,用于计算代码运行的时间,这里的code可以在后续子类中重写来计算code运行所需要花费的时间。
/** * 抽象应用案例: 模板方法的设计模式 */ public class TemplateTest { public static void main(String[] args) { PrintPrimeNumber p = new PrintPrimeNumber(); p.spendTime(); } } abstract class Template{ //计算某段代码执行需要花费的时间 public void spendTime(){ long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); code(); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("花费的时间为:" + (end -start)); } public abstract void code(); } class PrintPrimeNumber extends Template{ public void code(){ for (int i = 2; i <= 100000; i ++){ boolean isFlag = true; for (int j = 2; j <= Math.sqrt(i); j++){ if (i % j == 0){ isFlag = false; break; } } if (isFlag){ System.out.println(i); } } } }
案例
编写工资系统,实现不同类型员工(多态)的按月发放工资。如果当月出现某个Employee对象的生日,则将该雇员的工资增加100元
实验说明:
(1)定义一个Employee类,该类包含:
private成员变量name,number,birthday,其中birthday 为MyDate类的对象;
提供必要的构造器,
abstract方法earnings(),返回工资数额:
toString()方法输出对象的name,number和birthday。
public abstract class Employee { private String name; private int number; private MyDate birthday; public Employee() { } public Employee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday) { this.name = name; this.number = number; this.birthday = birthday; } public abstract double earnings(); //抽象方法 返回工资数额 @Override public String toString() { return "name='" + name + "', number=" + number + ", birthday=" + birthday ; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(int number) { this.number = number; } public MyDate getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } }
(2) MyDate类包含:
private成员变量year,month,day;
提供必要的构造器;
toDateString()方法返回日期对应的字符串,xxxx年xx月xx日
public class MyDate { private int year; private int month; private int day; public MyDate() { } public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) { this.year = year; this.month = month; this.day = day; } @Override public String toString() { return year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日"; } public int getYear() { return year; } public void setYear(int year) { this.year = year; } public int getMonth() { return month; } public void setMonth(int month) { this.month = month; } public int getDay() { return day; } public void setDay(int day) { this.day = day; } }
3)定义SalariedEmployee类继承Employee类,实现按月计算工资的员工处理
该类包括: private成员变量monthlySalary;
提供必要的构造器;
实现父类的抽象方法earnings()该方法返回monthlySalary值;
toString()方法输出员工类型信息及员工的name,number,birthday。比如: SalariedEmployee[name = ' ' ,number = , birthday = xxxx年xx月xx日]
public class SalariedEmployee extends Employee{ private double monthlySalary; public SalariedEmployee() { } public SalariedEmployee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday, double monthlySalary) { super(name, number, birthday); this.monthlySalary = monthlySalary; } @Override public double earnings() { return monthlySalary; } @Override public String toString() { return "SalariedEmployee[ " + super.toString() + "]"; } public double getMonthlySalary() { return monthlySalary; } public void setMonthlySalary(double monthlySalary) { this.monthlySalary = monthlySalary; } }
(4)参照SalariedEmployee类定义HourlyEmployee类,实现按小时计算工资的员工处理。该类包括
private成员变量wage和hour;
提供必要的构造器;
实现父类的抽象方法earnings()该方法返回waqe*hour值;
toString0方法输出员工类型信息及员工的name, number, birthday。
public class HourlyEmployee extends Employee{ private double wage; private int hour; public HourlyEmployee() { } public HourlyEmployee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday, double wage, int hour) { super(name, number, birthday); this.wage = wage; this.hour = hour; } @Override public double earnings() { return wage * hour; } @Override public String toString() { return "HourlyEmployee = [" + super.toString() + "]"; } public double getWage() { return wage; } public void setWage(double wage) { this.wage = wage; } public int getHour() { return hour; } public void setHour(int hour) { this.hour = hour; } }
(5)定义PayrollSystem类,创建Employee变量数组并初始化,该数组存放各类员对象的引用。
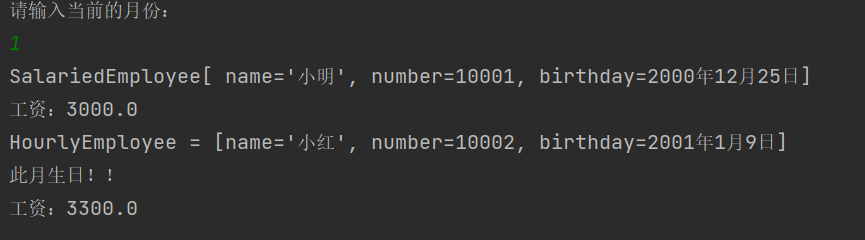
利用循环结构遍历数组元素,输出各个对象的类型,name,number,birthday,以及该对象生日。
当键盘输入本月月份值时,如果本月是某个Employee对象的生日,还要输出增加工资信息。
import java.util.Scanner; public class PayrollSystem { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); Employee[] employees = new Employee[2]; employees[0] = new SalariedEmployee("小明",10001,new MyDate(2000,12,25),3000); employees[1] = new HourlyEmployee("小红",10002,new MyDate(2001,1,9),100,32); System.out.println("请输入当前的月份:"); int month = scan.nextInt(); for (int i = 0; i < employees.length; i++){ System.out.println(employees[i].toString()); if (month == employees[i].getBirthday().getMonth()){ System.out.println("此月生日!!"); System.out.println("工资:" + (employees[i].earnings() + 100)); }else{ System.out.println("工资:" + employees[i].earnings()); } } } }
接口
接口的理解: 接口的本质是 契约、标准、规范。就像法律一样,制定好以后大家都要遵守
定义接口的关键字:interface
接口内部结构的说明:
> 可以声明:
属性: 必须使用public static final修饰(可以省略)
方法:jdk8之前:声明抽象方法,修饰为public abstract(可以省略)
jdk8:声明静态方法、默认方法
jdk9:声明私有方法
> 不可以声明: 构造器、代码块等
接口与类的关系 : 实现关系
格式: class A extends SuperA implements B,C{ }
A相较于SuperA来讲,叫做子类。
A相较于B,C来讲,叫做实现类。
满足此关系后,说明:
> 类可以实现多个接口。
> 类针对于接口的多实现,一定程度上就弥补了类的单继承的局限性。
> 类必须将实现的接口中的所有的抽象方法都重写(或实现),方可实例化。否则,此实现类必须声明为抽象类。
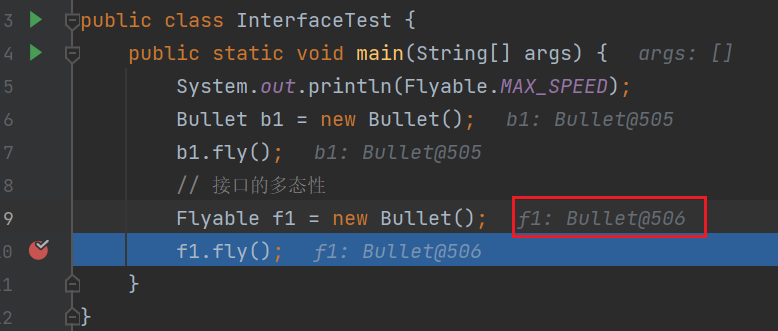
public class InterfaceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Flyable.MAX_SPEED); Bullet b1 = new Bullet(); b1.fly(); } } interface Flyable{ //接口 // 全局常量 public static final int MIN_SPEED = 0; //这里的public static final可以省略 int MAX_SPEED = 7900; // 方法 (可以省略public abstract) void fly(); } interface Attackable{ //接口 public abstract void attack(); } abstract class Plane implements Flyable{ //因为接口里面有抽象方法 所以要声明为抽象类 // 除非重写抽象类Flyable里面的抽象方法 就可以不需要加abstract修饰 } class Bullet implements Flyable,Attackable{ //这里接口两个,所以两个抽象方法都要重写 @Override public void fly() { System.out.println("子弹飞一会"); } @Override public void attack() { System.out.println("子弹可以击穿身体!"); } }
接口与接口的关系
// 测试接口的多继承关系 interface AA{ void method1(); } interface BB{ void method2(); } interface CC extends AA,BB{ //接口可以多继承 } class DD implements CC{ //必须要重写接口里面的方法,否则仍然是抽象类要abstract修饰 @Override public void method1() { } @Override public void method2() { } }
接口的多态性
接口的多态性: 接口名 变量名 = new 实现类对象;
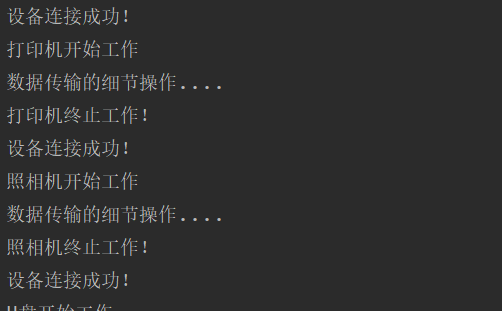
public class USBTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建接口实现类的对象 Computer computer = new Computer(); Printer p1 = new Printer(); computer.transferData(p1); // 创建接口实现类的匿名对象 computer.transferData(new Camera()); // 创建接口匿名实现类的对象 USB usb1 = new USB(){ public void start(){ System.out.println("U盘开始工作"); } @Override public void stop() { System.out.println("U盘结束工作"); } }; computer.transferData(usb1); // 创建接口匿名实现类的匿名对象 computer.transferData(new USB(){ @Override public void start() { System.out.println("扫描仪开始工作"); } @Override public void stop() { System.out.println("扫描仪结束工作"); } }); } } class Computer { public void transferData(USB usb){//多态: USB usb = new Printer(); System.out.println("设备连接成功!"); usb.start(); System.out.println("数据传输的细节操作...."); usb.stop(); } } interface USB{ //声明常量 //USB的长、宽、高..... //方法 void start(); void stop(); } class Printer implements USB{ @Override public void start() { System.out.println("打印机开始工作"); } @Override public void stop() { System.out.println("打印机终止工作!"); } } class Camera implements USB{ @Override public void start() { System.out.println("照相机开始工作"); } @Override public void stop() { System.out.println("照相机终止工作!"); } }
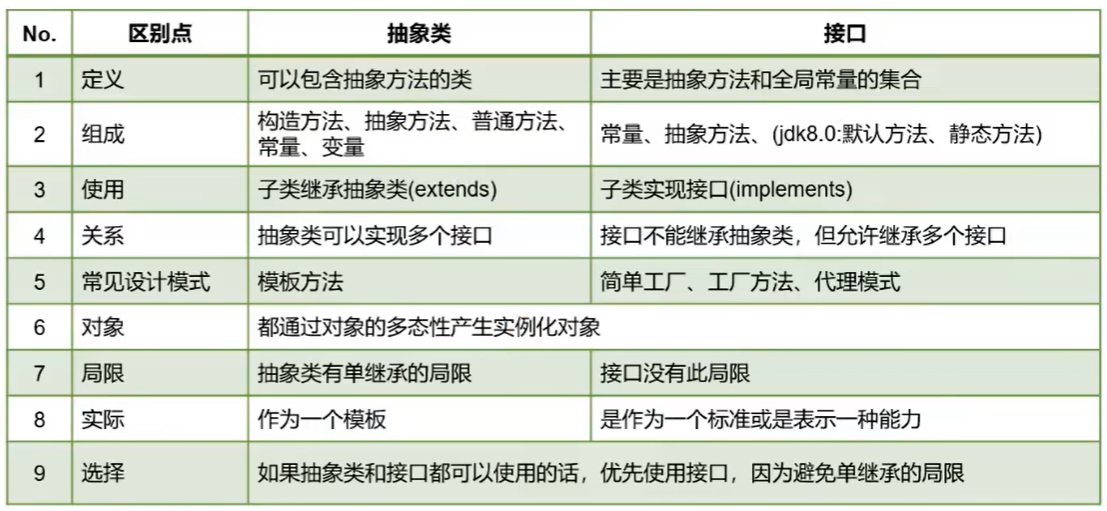
面试题:区分抽象类与接口
> 共性: 都可以声明抽象方法
都不能实例化
> 不同: ① 抽象类一定有构造器。接口没有构造器
② 类与类之间继承关系,类与接口之间是实现关系,接口与接口之间是多继承关系
练习
定义一个circle类,声明radius属性,提供getter和setter方法
定义一个ComparableCircle类,继承Circle类并且实现Compare0bject接口。
在ComparableCircle类中给出接口中方法compareTo的实现体,用来比较两个圆的半径大小。
定义一个测试类InterfaceTest,创建两个ComparableCircle对象,调用compareTo方法比较两个类的半径大小
拓展: 参照上述做法定义矩形类Rectangle和ComparableRectangle类,在ComparableRectangle类
中给出compareTo方法的实现,比较两个矩形的面积大小。
public class InterfaceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ComparableCircle c1 = new ComparableCircle(2); ComparableCircle c2 = new ComparableCircle(3); int comparaValue = c1.compareTo(c2); if(comparaValue > 0){ System.out.println("c1对象大"); }else if(comparaValue < 0){ System.out.println("c2对象大"); }else{ System.out.println("c1和c2一样大"); } } } class Circle { private double radius; public Circle() { } public Circle(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } } interface CompareObject{ int compareTo(Object o); } class ComparableCircle extends Circle implements CompareObject{ public ComparableCircle() { } public ComparableCircle(double radius) { super(radius); } @Override public int compareTo(Object o) { if (o instanceof ComparableCircle) { ComparableCircle c = (ComparableCircle) o; //错误写法: 这样如果整数部分相同只是小数部分不同 返回值会错误 // return (int) (this.getRadius() - c.getRadius()); // 正确写法1 if (this.getRadius() > c.getRadius()){ return 1; }else if(this.getRadius() < c.getRadius()){ return -1; }else{ return 0; } //正确写法2: // return Double.compare(this.getRadius(),c.getRadius()); }else{ throw new RuntimeException("输入的类型不匹配!"); //抛出异常 } } }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具