Java基础10
Object类
类java.lang.Object是类层次结构的根类,即所有其它类的父类。每个类都使用Object作为超类。
注意:
> Object类中声明的结构(属性、方法等)就具有通用性。
> Object类中没有声明属性
> Object类提供了一个空参的构造器
> 重点关注: Object类中声明的方法
常用方法
重点方法: equals() \ toString()
了解方法: clone() \ finalize()
后续了解的方法:getClass() \ hashCode() \ notify() \ notifyAll() \ wait() \ wait(xx) \ wait(xx,yy)
clone()
clone()方法是用来创建并返回此对象的一个副本的。换句话说,它可以帮助我们复制一个对象。
前提:只有实现了Cloneable接口的类才能被复制,否则调用clone()方法时会抛出CloneNotSupportedException异常
// 定义一个实现了Cloneable接口的类 class MyClass implements Cloneable { int value; public MyClass(int value) { this.value = value; } // 重写Object类的clone()方法 @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } @Override public String toString() { return "MyClass{" + "value=" + value + '}'; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { try { MyClass obj1 = new MyClass(10); MyClass obj2 = (MyClass) obj1.clone(); // 复制对象 System.out.println("obj1: " + obj1); // 输出:obj1: MyClass{value=10} System.out.println("obj2: " + obj2); // 输出:obj2: MyClass{value=10} System.out.println("obj1 == obj2: " + (obj1 == obj2)); // 输出:obj1 == obj2: false,说明两个对象在内存中的地址不同 } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
定义了一个实现了Cloneable接口的类MyClass,并重写了clone()方法。
在main方法中,我们创建了一个MyClass对象obj1,并使用clone()方法复制了obj1得到了obj2。通过输出我们可以看到,obj1和obj2的值是一样的,但是它们在内存中的地址是不同的,说明它们是两个不同的对象。
finalize()
当垃圾回收器确定不存在对该对象的更多引用时,对象的垃圾回收器将调用此方法
注意:finalize()方法并不能保证一定会被执行,也不能保证何时被执行。因此,我们不能依赖finalize()方法来执行一些重要的清理工作,比如关闭文件、断开网络连接等
class MyClass { @Override protected void finalize() throws Throwable { System.out.println("MyClass对象被垃圾回收器回收了"); super.finalize(); // 调用父类的finalize()方法 } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { MyClass obj = new MyClass(); obj = null; // 将obj引用置为null,使得原来的MyClass对象可以被垃圾回收器回收 // 在这里,我们并不能确定MyClass对象的finalize()方法是否已经被执行,因为垃圾回收器的行为是不可预测的 } }
定义了一个类MyClass,并重写了finalize()方法。在main方法中,我们创建了一个MyClass对象obj,然后立即将obj引用置为null,使得原来的MyClass对象可以被垃圾回收器回收。但是,我们不能确定MyClass对象的finalize()方法是否已经被执行,因为垃圾回收器的行为是不可预测的。
equals()
java.lang.Object类中equals()的定义:
public boolean equals(Object obj){ return (this == obj); }
说明
> 自定义的类在没有重写Object中的equals()方法的情况下,调用的就是Object类中声明的equals(),比较两个对象的引用地址是否相同。(或比较两个对象是否指向了堆空间中的同一个对象实体)
> 对于像String、File、Data和包装类等,它们都重写了Object类中的equals()方法,用于比较两个对象的实体内容是否相等。
package com.atgjwqz.exercise; public class UserTest { public static void main(String[] args) { User u1 = new User("Tom", 12); User u2 = new User("Tom",12); System.out.println(u1.equals(u2)); //输出:false 判断的是地址值 String str1 = new String("hello"); String str2 = new String("hello"); System.out.println(str1 == str2);// false System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); //true } } class User{ String name; int age; public User() { } public User(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } }
开发中的使用说明
> 实际开发中,针对于自定义的类,常常会判断两个对象是否equals(),而此时主要是判断两个对象的属性值是都相等,所以要重写Object类的equals()方法。
> 如何重写: ① 手动自己实现 ② 调用IDEA自动实现(推荐)
区分== 和 equals()
==:运算符
① 适用范围: 基本数据类型、引用数据类型
② 基本数据类型:判断数据值是否相等
char c1 = 'A'; int i1 = 65; sout(c1 == i1); //true c1的类型会自动提升为int然后比较 float f1 = 12.0F; int i2 = 12; sout(f1 == i2); //true int类型自动提升为float
引用数据类型变量:比较两个引用变量的地址值是否相等。(或比较两个引用是否指向同一个对象实体)
equals():方法
> 使用范围:只能使用在引用数据类型上。
> 具体使用:对于类来说,重写equals()和不重写equals()的区别。
案例
编写Order类,有int型的orderId,String型的orderName,相应的getter()和setter()方法,两个参数的构造器。
重写父类的equals()方法:public boolean equals(Object obj),并判断测试类中创建的两个对象是否相等
public class Order { int orderId; String orderName; public Order(int orderId, String orderName) { this.orderId = orderId; this.orderName = orderName; } public int getOrderId() { return orderId; } public void setOrderId(int orderId) { this.orderId = orderId; } public String getOrderName() { return orderName; } public void setOrderName(String orderName) { this.orderName = orderName; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if(this == obj){ return true; } if (obj instanceof Order){ Order order = (Order) obj; if(this.orderId == order.orderId && this.orderName == orderName) { return true; } } return false; } }
public class OrderTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Order o1 = new Order(1001,"orderAA"); Order o2 = new Order(1001,"orderAA"); System.out.println(o1.equals(o2)); //true } }
toString()
定义:
public String toString(){ return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode()); }
开发中的使用场景
平时我们在调用 System.out.println( ) 打印对象引用变量时,其实就调用了对象的toString( )
说明
子类使用说明:
- 自定义的类,在没有重写Object类的toString( )的情况下,默认返回的是当前对象的地址值。
- 像String、File、Data或包装类等Object的子类,它们都重写了Object类的toString( ),在调用toString( )时,返回当前对象的实体内容。
开发中使用说明:
> 习惯上,开发中对于自定义的类在调用toString()时,也希望显示其对象的具体内容,而非地址值。这适合需要重写Object类中的toString()
public class ToStringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { User u1 = new User("Tom",12); System.out.println(u1.toString()); // com.atgjwqz.exercise.User@14ae5a5 } } class User{ String name; int age; public User(){ } public User(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } }
案例
定义两个类,父类GeometricObject代表几何形状,子类Circle代表圆形
写一个测试类,创建两个Circle对象,判断其颜色是否相等;利用equals()方法判断其半径是否相等;利用toString()方法输出其半径
public class GeometricObject { protected String color; protected double weight; public GeometricObject() { color = "white"; weight = 1.0; } public GeometricObject(String color, double weight) { this.color = color; this.weight = weight; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public double getWeight() { return weight; } public void setWeight(double weight) { this.weight = weight; } }
public class Circle extends GeometricObject{ private double radius; public Circle() { color = "white"; weight = 1.0; radius = 1.0; } public Circle(double radius) { color = "white"; weight = 1.0; this.radius = radius; } public Circle(String color, double weight, double radius) { super(color, weight); this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double findArea(){ return Math.PI*radius*radius; } public boolean equals(Object obj){ if (this == obj){ return true; } if (obj instanceof Circle){ Circle circle = (Circle) obj; if (circle.radius == this.radius){ return true; } } return false; } public String toString(){ return "radius = " + this.radius; } }
public class CircleTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Circle c1 = new Circle("pink",1.0,2); Circle c2 = new Circle("white",1.0,2); System.out.println(c1.findArea()); System.out.println("颜色是否相等? " + c1.getColor().equals(c2.getColor())); System.out.println("半径是否相等? " + c1.equals(c2)); System.out.println(c1.toString()); } }
static关键字
如果想让一个成员变量被类的所有实例所共享,就用static修饰即可,称为类变量(或类属性)。此外,在类中声明的实例方法,在类的外面必须创建对象才能调用。但是有些方法的调用者和当前类的对象无关,这样的方法通常被声明为类方法。
这里的类变量、类方法 只需要使用static即可。 称之为 静态变量、静态方法。
static:静态的 用来修饰的结构:属性、方法;代码块、内部类; (注意: 不可以修饰构造器)
修饰属性
变量的分类:
方式一: 按照数据类型: 基本数据类型、引用数据类型
方式二: 按照类中声明的位置:
成员变量: 按照是否使用static修饰进行分类:
使用static修饰的成员变量:静态变量、类变量
不使用static修饰的成员变量:非静态变量、实例变量
局部变量: 方法内、方法形参、构造器内、构造器形参、代码块内等;
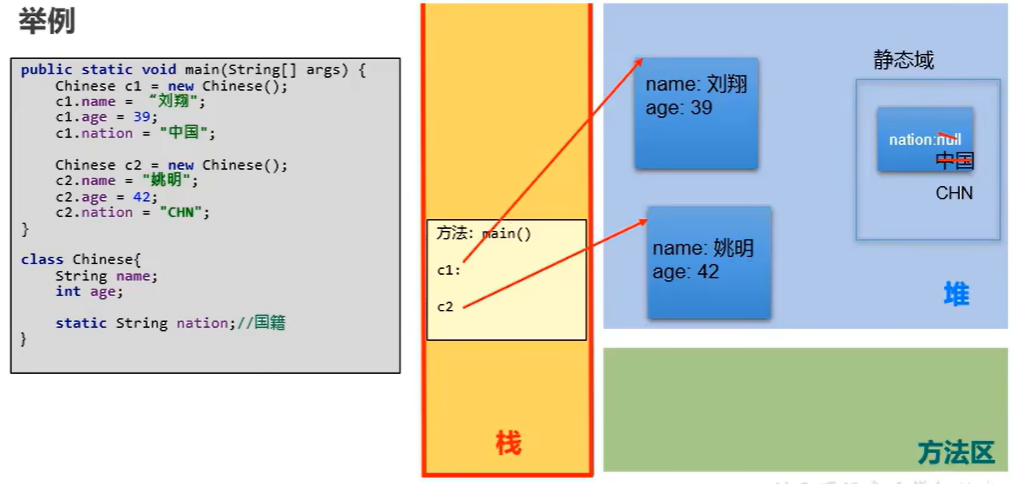
public class ChineseTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Chinese c1 = new Chinese(); c1.name = "姚明"; c1.age = 40; c1.nation = "China"; Chinese c2 = new Chinese(); c2.name = "刘翔"; c2.age = 39; System.out.println(c1.toString());//输出:Chinese{name='姚明', age=40',nation=China} System.out.println(c2.toString());//输出:Chinese{name='刘翔', age=39',nation=China} } } class Chinese{ //非静态变量、实例变量 String name; int age; //静态变量 static String nation; @Override public String toString() { return "Chinese{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '\'' + ",nation=" + nation + '}'; } }
静态变量:实例变量
① 个数
>静态变量:在内存空间只有一份,被类的多个对象所共享。
>实例变量:类的每一个实例(或对象)都保存着一份实例变量。
② 内存位置
>静态变量:jdk6及之前:存放在方法区; jdk7及之后:存放在堆空间。
>实例变量:存放在堆空间的对象实体中。
③ 加载时机
>静态变量:随着类的加载而加载,由于类只会加载一次,所以静态变量也只有一份。
>实例变量:随着对象的创建而创建
④ 调用者
>静态变量: 可以被类直接调用,也可以使用对象调用。
>实例变量: 只能对象进行调用。
⑤ 判断是否可以调用 ----> 从声明周期的角度解释

⑥ 消亡时机
>静态变量:随着类的卸载而消亡
>实例变量:随着对象的消亡而消亡
静态变量的内存解析
修饰方法
> 随着类的加载而加载,静态的方法能够继承但是不能够被重写(父类和子类的同名方法要么都不加static要么都加static)
>可以通过'类.静态方法'的方式,直接调用静态方法
>静态方法内可以调用静态的属性或静态的方法(属性和方法的前缀使用的是当前类,可以省略 比如类Chinese 使用的是Chinese.method). 不可以直接调用非静态的结构,但可以通过对象来调用非静态方法。
>static修饰的方法内,不能使用this和super

public class StaticTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Person p1 = new Student(); p1.eat(); // 人吃饭 Person p2 = null; p2.eat(); // 人吃饭 这里和对象根本没关系,静态的方法只看类型,看是哪个类发起的就调用谁 } } class Person{ public static void eat(){ System.out.println("人吃饭"); } } class Student extends Person{ public static void eat(){ System.out.println("学生吃饭"); } }
通过对象的方式在静态结构内调用非静态方法
class Test2{ public void method2(){ System.out.println("HelloWorld2"); } } class Test1{ public void method0() { System.out.println("HelloWorld0"); } public static void method1() { System.out.println("HelloWorld1"); } public static void main(String args[]){ // 通过对象调用非静态方法 new Test1().method0(); // HelloWorld0 method1(); // HelloWorld1 new Test2().method2(); // HelloWorld2 } }
补充:在类的非静态方法中,可以调用当前类中的静态结构(属性、方法)或非静态结构(属性、方法)
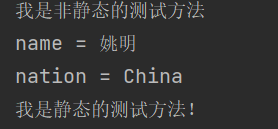
public class ChineseTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Chinese c1 = new Chinese(); c1.name = "姚明"; c1.age = 40; c1.nation = "China"; c1.method2(); } } class Chinese{ //非静态变量、实例变量 String name; int age; //静态变量 static String nation; //静态方法 public static void show(){ //调用静态结构 System.out.println("nation = " + nation); method(); } public static void method(){ System.out.println("我是静态的测试方法!"); } public void method2(){ System.out.println("我是非静态的测试方法"); //调用非静态的结构 System.out.println("name = " + this.name); //调用静态的结构 System.out.println("nation = " + nation); method(); } }
开发时,什么时候需要将属性声明为静态的?
> 判断当前类的多个实例是否能共享此成员变量,且此成员变量的值是相同的
> 开发中,常将一些常量声明是静态的。比如:Math类中的PI
什么时候需要将方法声明为静态的?
> 方法内操作的变量如果都是静态的(而非实例变量),则此方法建议声明为静态方法
> 开发中,常常将工具类中的方法,声明为静态方法,比如:Arrays类、Math类
public class ChineseTest { public static void main(String[] args) { test(); //不需要再创建一个ChineseTest的对象才调方法 可以直接掉 ChineseTest.test(); //相当于上面的test() 类调用方法 } public static void test(){ System.out.println("我是static的测试方法!"); } }
案例
编写一个类实现银行账户的概念,包含的属性有“账号”、“密码”、“存款余额”、“利率”、“最小余额”,定义封装这些属性的方法,账号要自动生成
编写主类:使用银行账户类,输入、输出3个储户的上述信息
public class Account { private int id; private String password; // 密码 private double balance; // 余额 private static double interestRate ;//利率 private static double minBalance = 1.0; //最小余额 private static int init = 10000; //用于自动生成id的基数 public Account() { this.id = init; init ++; password = "000000"; } public Account(String password, double balance) { this.password = password; this.balance = balance; this.id = init; init ++; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = this.id; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public double getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(double balance) { this.balance = balance; } public static double getInterestRate() { return interestRate; } public static void setInterestRate(double interestRate) { Account.interestRate = interestRate; } public static double getMinBalance() { return minBalance; } public static void setMinBalance(double minBalance) { Account.minBalance = minBalance; } @Override public String toString() { return "Account{" + "id=" + id + ", password='" + password + '\'' + ", balance=" + balance + '}'; } }
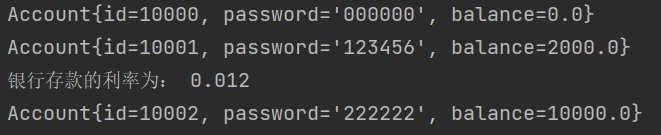
public class AccountTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Account acc1 = new Account(); System.out.println(acc1); Account acc2 = new Account("123456",2000); System.out.println(acc2); Account.setInterestRate(0.012); //通过类调用static方法设置年利率 Account.setMinBalance(10); //最小余额 System.out.println("银行存款的利率为: " + Account.getInterestRate()); Account acc3 = new Account("222222",10000); System.out.println(acc3); //即为sout(acc3.toString()); } }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具