左神算法第三节课:(栈,矩阵,链表)用数组实现栈与队列,栈中最小元素,转圈打印矩阵,旋转方阵,之字打印矩阵,有序矩阵中找数,反转链表,打印有序链表公共部分,回文链表等
左神算法第三节课
目录:
- 用数组实现栈与队列(先进先出),
- 栈中最小元素,
- 矩阵
- 转圈打印矩阵,
- 旋转方阵,
- 之字打印矩阵,
- 有序矩阵中找数,
- 链表
- 反转链表,
- 打印有序链表公共部分,
- 回文链表
- 等
1、用数组实现栈和队列
1.1【实现栈(先进后出)】用数组结构实现大小固定的队列和栈,如图所示:
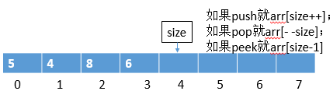
Size:表示下一个数要放的下标。
1 /* 2 * 固定数组实现栈 3 */ 4 public class ArrayStack { 5 6 private Integer[] arr; 7 private Integer size;//指向下一个对象被存放的下标 8 9 public ArrayStack(int intiSize) { 10 if (intiSize<0) { 11 throw new IllegalArgumentException("The init size is less 0"); 12 } 13 size = 0; 14 arr = new Integer[intiSize]; 15 } 16 17 public Integer peek() { 18 if (size <= 0) { 19 throw new IllegalArgumentException("The stack is null"); 20 } 21 return arr[size-1]; 22 } 23 24 public void push(Integer i) { 25 if (size >= arr.length) { 26 throw new IllegalArgumentException("The stack is full"); 27 } 28 arr[size++] = i; 29 } 30 31 public Integer pop() { 32 if (size <= 0) { 33 throw new IllegalArgumentException("The stack is empty"); 34 } 35 return arr[--size]; 36 } 37 38 public static void main(String[] args) { 39 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 40 } 41 }
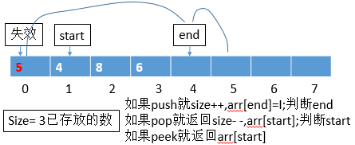
1.2【实现队列(先进先出)】
end:新加一个数的位置;start:拿出一个数的位置;size:数组里的数的个数,把start和end的关系解耦掉;如果不加size,则会使得start和end之间需要抠边界,会产生start追击end,关系不容易明确。如图所示:
/* * 固定数组实现队列 */ public class ArrayQueue { private Integer[] arr; private Integer size;//指向下一个对象被存放的下标 private Integer start; private Integer end; public ArrayQueue(int intiSize) { if (intiSize<0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("The init size is less 0"); } size = 0; arr = new Integer[intiSize]; start = 0; end = 0; } public Integer peek() { if (size <= 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("The stack is null"); } return arr[start]; } public void push(Integer i) { if (size >= arr.length) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("The stack is full"); } size++; arr[end] = i; end = end == arr.length-1 ? 0 : end+1; } public Integer poll() { if (size <= 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("The stack is empty"); } size--; int temp = start; start = start == arr.length-1 ? 0 : start+1; return arr[temp]; } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } }
2、栈中最小元素
实现一个特殊栈,在实现栈的基础功能上,再实现返回当前栈中最小元素的操作。
要求:
- Pop, push, getMin操作的时间复杂度都是O(1);
- 设计的栈类型可以使用现成的栈结构;
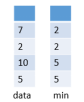
题目解析:
当前栈中最小元素的意思就是,在任何一步,都可以获得当前栈中所有元素的最小值。又因为可以使用现成的栈结构,故可以通过维护两个栈来实现。
设计思路:
设计一个data栈,存放的是数据,
再设计一个栈存放的是当前数组中最小的值。
即当data第一个压入5时,min也压入5,当data压入10时,10 与min栈顶数据元素5相比,10>5,故min继续压入5;data再压入2时,2与min栈顶相比,2<5,故min压入2…依次往复。然后取的时候,data弹出一个元素,min栈也跟着弹出一个元素。
实现:
package class_03; import java.util.Stack; public class Code_02_GetMinStack { public static class MyStack1 { private Stack<Integer> stackData; private Stack<Integer> stackMin; public MyStack1() { this.stackData = new Stack<Integer>(); this.stackMin = new Stack<Integer>(); } public void push(int newNum) { if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) { this.stackMin.push(newNum); } else if (newNum <= this.getmin()) { this.stackMin.push(newNum); } this.stackData.push(newNum); } public int pop() { if (this.stackData.isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty."); } int value = this.stackData.pop(); if (value == this.getmin()) { this.stackMin.pop(); } return value; } public int getmin() { if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty."); } return this.stackMin.peek(); } } public static class MyStack2 { private Stack<Integer> stackData; private Stack<Integer> stackMin; public MyStack2() { this.stackData = new Stack<Integer>(); this.stackMin = new Stack<Integer>(); } public void push(int newNum) { if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) { this.stackMin.push(newNum); } else if (newNum < this.getmin()) { this.stackMin.push(newNum); } else { int newMin = this.stackMin.peek(); this.stackMin.push(newMin); } this.stackData.push(newNum); } public int pop() { if (this.stackData.isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty."); } this.stackMin.pop(); return this.stackData.pop(); } public int getmin() { if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty."); } return this.stackMin.peek(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { MyStack1 stack1 = new MyStack1(); stack1.push(3); System.out.println(stack1.getmin()); stack1.push(4); System.out.println(stack1.getmin()); stack1.push(1); System.out.println(stack1.getmin()); System.out.println(stack1.pop()); System.out.println(stack1.getmin()); System.out.println("============="); MyStack1 stack2 = new MyStack1(); stack2.push(3); System.out.println(stack2.getmin()); stack2.push(4); System.out.println(stack2.getmin()); stack2.push(1); System.out.println(stack2.getmin()); System.out.println(stack2.pop()); System.out.println(stack2.getmin()); } }
输出:
3 3 1 1 3 ============= 3 3 1 1 3
3、队列,栈结构互相实现
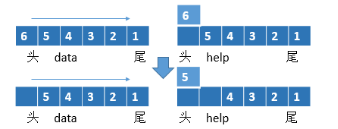
3.1 如何仅用队列结构实现栈结构?
栈结构(先进后出),队列结构(先进先出),故需要两个队列,来回倒腾,留下最后一个数据返回即可。
3.2 如何仅用栈结构实现队列结构?
需要两个栈,来回倒腾,弹出pop栈中的栈顶即可。
需要注意的是:这里不用交换引用。数据进栈一直进的是push栈,出栈一直是从push栈中弹出全部,然后将pop栈顶返回。
package class_03; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; import java.util.Stack; public class Code_03_StackAndQueueConvert { public static class TwoStacksQueue { private Stack<Integer> stackPush; private Stack<Integer> stackPop; public TwoStacksQueue() { stackPush = new Stack<Integer>(); stackPop = new Stack<Integer>(); } public void push(int pushInt) { stackPush.push(pushInt); } public int poll() { if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) { throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!"); } else if (stackPop.empty()) {//满足第二个要求,pop中没数据才能倒; while (!stackPush.empty()) {//满足第一个要求,倒就倒完; stackPop.push(stackPush.pop()); } } return stackPop.pop(); } public int peek() { if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) { throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!"); } else if (stackPop.empty()) { while (!stackPush.empty()) { stackPop.push(stackPush.pop()); } } return stackPop.peek(); } } public static class TwoQueuesStack { private Queue<Integer> queue; private Queue<Integer> help; public TwoQueuesStack() { queue = new LinkedList<Integer>(); help = new LinkedList<Integer>(); } public void push(int pushInt) { queue.add(pushInt); } public int peek() { if (queue.isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("Stack is empty!"); } //留下最后一个元素留作返回,其他的倒腾到help队列中; while (queue.size() != 1) { help.add(queue.poll()); } int res = queue.poll(); help.add(res);//因为peek()返回的是栈顶元素并且不删除,故还要加入到help队列中; swap();//交换引用 return res; } public int pop() { if (queue.isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("Stack is empty!"); } while (queue.size() > 1) { help.add(queue.poll()); } //因为pop()返回的是栈顶元素并且删除,故不用加入到help队列中; int res = queue.poll(); swap(); return res; } private void swap() { Queue<Integer> tmp = help; help = queue; queue = tmp; } } }
4、矩阵相关问题
4.1 转圈(螺旋)打印矩阵
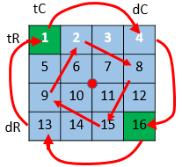
给定一个整型矩阵matrix,请按照转圈的方式打印它。
例如: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
打印结果为:1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11, 10
【要求】 额外空间复杂度为O(1)。
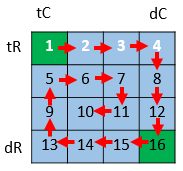
package class_03; import java.util.ArrayList; /* * 螺旋打印矩阵; */ public class Code_06_PrintMatrixSpiralOrder { public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int [][] matrix) { return null; } /* tC dC tR 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 6 3 4 5 6 7 dR 4 5 6 7 8 */ public static void spiralOrderPrint(int[][] matrix) { //左上角点坐标(tR,tC),右下角点坐标(dR,dC); int tR = 0; int tC = 0; int dR = matrix.length-1; int dC = matrix[0].length-1; while (tR<=dR && tC<=dC) { printEdge(matrix,tR++,tC++,dC--,dR--); } } private static void printEdge(int[][] matrix, int tR, int tC, int dR, int dC) { //判断螺旋是否到达最后一次,即要么纵坐标相等,要么横坐标相等; if (tR == dR) { for (int i = tC; i <= dC; i++) { System.out.println(matrix[tR][i]+" "); } }else if (tC == dC) { for (int i = tR; i <= dR; i++) { System.out.println(matrix[i][tC]+" "); } }else { //如果不是最后一次螺旋 /* tC dC tR 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 6 3 4 5 6 7 dR 4 5 6 7 8 */ //从左往右 for (int i = tC; i < dC; i++) { System.out.print(matrix[tR][i]+" + "); } //从上往下 for (int i = tR; i < dR; i++) { System.out.print(matrix[i][dC]+" - "); } //从右往左 for (int i = dC; i > tC; i--) { System.out.print(matrix[dR][i]+" * "); } //从上往下 for (int i = dR; i > tR; i--) { System.out.print(matrix[i][tC]+" / "); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int[][] matrix = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 }, { 5, 6, 7, 8 }, { 9, 10, 11, 12 }, { 13, 14, 15, 16 } }; spiralOrderPrint(matrix); } }
输出:
1 + 2 + 3 + 4 - 8 - 12 - 16 * 15 * 14 * 13 / 9 / 5 / 6 + 7 - 11 * 10 /
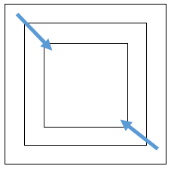
4.2 旋转正方形矩阵
给定一个整型正方形矩阵matrix,请把该矩阵调整成顺时针旋转90度的样子。
【要求】 额外空间复杂度为O(1)。
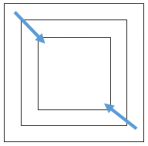
同样的思想:记录左上角坐标(tR,tC)和右下角坐标(dR,dC)。旋转每一行/列即可。
package class_03; public class Code_05_RotateMatrix { public static void rotate(int[][] matrix) { int tR = 0; int tC = 0; int dR = matrix.length - 1; int dC = matrix[0].length - 1; while (tR < dR) { rotateEdge(matrix, tR++, tC++, dR--, dC--); } } public static void rotateEdge(int[][] m, int tR, int tC, int dR, int dC) { //记录每一行/列的元素个数;
int times = dC - tC; int tmp = 0;
//旋转 for (int i = 0; i != times; i++) { tmp = m[tR][tC + i]; m[tR][tC + i] = m[dR - i][tC]; m[dR - i][tC] = m[dR][dC - i]; m[dR][dC - i] = m[tR + i][dC]; m[tR + i][dC] = tmp; } } public static void printMatrix(int[][] matrix) { for (int i = 0; i != matrix.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j != matrix[0].length; j++) { System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] matrix = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 }, { 5, 6, 7, 8 }, { 9, 10, 11, 12 }, { 13, 14, 15, 16 } }; printMatrix(matrix); rotate(matrix); System.out.println("========="); printMatrix(matrix); } }
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 ========= 13 9 5 1 14 10 6 2 15 11 7 3 16 12 8 4
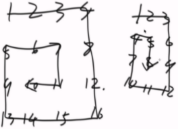
4.3 “之”字形打印矩阵
给定一个矩阵matrix,按照“之”字形的方式打印这个矩阵,例如: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12,“之”字形打印的结果为:1,2,5,9,6,3,4,7,10,11,8,12
【要求】 额外空间复杂度为O(1)。

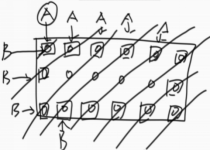

分析:给定一个函数,实现从沿对角线打印的功能。参数为对角线上两个点以及一个判断是从上往下,还是从下往上的布尔类型变量。注意:三木运算时,要注意顺序,先判断与条件无关的行/列,如果将36/37,38/39互相调换位置,则出错。
实现:
package class_03; import java.util.ArrayList; /* * 之字型打印矩阵。 * 给定一个矩阵matrix,按照“之”字形的方式打印这 * 个矩阵,例如: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 * “之”字形打印的结果为:1,2,5,9,6,3,4,7,10,11,8,12; * 要求:额外空间复杂度为O(1) * * 给定一个函数,实现从沿对角线打印的功能。参数为对角线上两个点以及一个判断是从上往下,还是从下往上的布尔类型变量。 * * 注意:三木运算时,要注意顺序,先判断与条件无关的行/列,如果将36/37,38/39互相调换位置,则出错。 */ public class Code_08_ZigZagPrintMatrix { /*条件结束为,a点来到最后一行,b点来到最后一列; * aC 1 2 3 4 aR 5 6 7 8 bR 9 10 11 12 bC */ public static void printZigZag(int[][] matrix) { //左下角点坐标(bR,bC),右上角点坐标(aR,aC); int aR = 0; int aC = 0; int bR = 0; int bC = 0; int endR = matrix.length-1; int endC = matrix[0].length-1; boolean fromUp = false;//用来判断是从左下到右上,还是从右上到左下。 while (aR < endR+1) {//||bC != endC+1 printLevel(matrix,aR,aC,bR,bC,fromUp); aR = aC == endC ? ++aR : aR; aC = aC == endC ? aC : ++aC; bC = bR == endR ? ++bC : bC; bR = bR == endR ? bR : ++bR; fromUp=!fromUp; } } private static void printLevel(int[][] matrix, int aR, int aC, int bR, int bC, boolean fromUp) { /*条件结束为,a点来到最后一行,b点来到最后一列; * aC 1 2 3 4 aR 5 6 7 8 bR 9 10 11 12 bC */ if (fromUp) { while (bC <= aC) { System.out.print(matrix[aR++][aC--]+" "); } }else { while (bC <= aC) { System.out.print(matrix[bR--][bC++]+" "); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int[][] matrix = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 }, { 5, 6, 7, 8 }, { 9, 10, 11, 12 }}; printMatrix(matrix); System.out.println("-----------"); printZigZag(matrix); // printMatrix(matrix); } private static void printMatrix(int[][] matrix) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) { System.out.print(matrix[i][j]+"\t"); } System.out.println(); } } } package class_03; import java.util.ArrayList; /* * 之字型打印矩阵。 * 给定一个矩阵matrix,按照“之”字形的方式打印这 * 个矩阵,例如: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 * “之”字形打印的结果为:1,2,5,9,6,3,4,7,10,11,8,12; * 要求:额外空间复杂度为O(1) * * 给定一个函数,实现从沿对角线打印的功能。参数为对角线上两个点以及一个判断是从上往下,还是从下往上的布尔类型变量。 * * 注意:三木运算时,要注意顺序,先判断与条件无关的行/列,如果将36/37,38/39互相调换位置,则出错。 */ public class Code_08_ZigZagPrintMatrix { /*条件结束为,a点来到最后一行,b点来到最后一列; * aC 1 2 3 4 aR 5 6 7 8 bR 9 10 11 12 bC */ public static void printZigZag(int[][] matrix) { //左下角点坐标(bR,bC),右上角点坐标(aR,aC); int aR = 0; int aC = 0; int bR = 0; int bC = 0; int endR = matrix.length-1; int endC = matrix[0].length-1; boolean fromUp = false;//用来判断是从左下到右上,还是从右上到左下。 while (aR < endR+1) {//||bC != endC+1 printLevel(matrix,aR,aC,bR,bC,fromUp); aR = aC == endC ? ++aR : aR; aC = aC == endC ? aC : ++aC; bC = bR == endR ? ++bC : bC; bR = bR == endR ? bR : ++bR; fromUp=!fromUp; } } private static void printLevel(int[][] matrix, int aR, int aC, int bR, int bC, boolean fromUp) { /*条件结束为,a点来到最后一行,b点来到最后一列; * aC 1 2 3 4 aR 5 6 7 8 bR 9 10 11 12 bC */ if (fromUp) { while (bC <= aC) { System.out.print(matrix[aR++][aC--]+" "); } }else { while (bC <= aC) { System.out.print(matrix[bR--][bC++]+" "); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int[][] matrix = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 }, { 5, 6, 7, 8 }, { 9, 10, 11, 12 }}; printMatrix(matrix); System.out.println("-----------"); printZigZag(matrix); // printMatrix(matrix); } private static void printMatrix(int[][] matrix) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) { System.out.print(matrix[i][j]+"\t"); } System.out.println(); } } }
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 ----------- 1 2 5 9 6 3 4 7 10 11 8 12
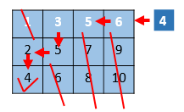
4.4 在行列都排好序的矩阵中找数
给定一个有N*M的整型矩阵matrix和一个整数K,matrix的每一行和每一 列都是排好序的。实现一个函数,判断K是否在matrix中。 例如: 0 1 2 5 2 3 4 7 4 4 4 8 5 7 7 9 如果K为7,返回true;如果K为6,返回false。
【要求】 时间复杂度为O(N+M),额外空间复杂度为O(1)。

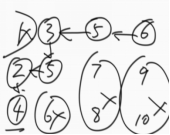
思路:
从右上角开始往左下角遍历,为什么呢?
因为每一行,每一列都是有序的,且是升序,从右上角开始往左下角遍历的话,如果当前值大于目标值,就列数减一,如果当前值小于目标值的话,就行数加一。直至找到目标值。
实现:
package class_03; /* * 在行列都排好序的矩阵中找数 【题目】 给定一个有N*M的整型矩阵matrix和一个整数K, matrix的每一行和每一 列都是排好序的。实现一个函数,判断K 是否在matrix中。 例如: 0 1 2 5 2 3 4 7 4 4 4 8 5 7 7 9 如果K为7,返回true;如果K为6,返 回false。 【要求】 时间复杂度为O(N+M),额外空间复杂度为O(1)。 */ public class Code_09_FindNumInSortedMatrix { public static boolean isContains(int[][] matrix, int K) { int row = 0; int col = matrix[0].length -1; while (row < matrix.length && col > -1) { if (matrix[row][col] == K) { return true; }else if (matrix[row][col] > K) { --col; }else { ++row; } } return false; } public static void test() { int[][] matrix = new int[][] { { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 },// 0 { 10, 12, 13, 15, 16, 17, 18 },// 1 { 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29 },// 2 { 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50 },// 3 { 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71 },// 4 { 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 111, 122 },// 5 { 166, 176, 186, 187, 190, 195, 200 },// 6 { 233, 243, 321, 341, 356, 370, 380 } // 7 }; int K = 233; System.out.println(isContains(matrix, K)); } public static void main(String[] args) { test(); } }
输出:
true
5、链表相关问题
反转链表:
分别实现反转单向链表和反转双向链表的函数。
【要求】 如果链表长度为N,时间复杂度要求为O(N),额外空间复杂度要求为O(1)。
5.1 单向链表反转

package class_03; public class Code_07_ReverseList { public static class Node { public int value; public Node next; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } public static Node reverseList(Node head) { Node pre = null; Node next = null; while (head != null) { next = head.next; head.next = pre; pre = head; head = next; } return pre; } public static class DoubleNode { public int value; public DoubleNode last; public DoubleNode next; public DoubleNode(int data) { this.value = data; } } public static DoubleNode reverseList(DoubleNode head) { DoubleNode pre = null; DoubleNode next = null; while (head != null) { next = head.next; head.next = pre; head.last = next; pre = head; head = next; } return pre; } public static void printLinkedList(Node head) { System.out.print("Linked List: "); while (head != null) { System.out.print(head.value + " "); head = head.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void printDoubleLinkedList(DoubleNode head) { System.out.print("Double Linked List: "); DoubleNode end = null; while (head != null) { System.out.print(head.value + " "); end = head; head = head.next; } System.out.print("| "); while (end != null) { System.out.print(end.value + " "); end = end.last; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node head1 = new Node(1); head1.next = new Node(2); head1.next.next = new Node(3); printLinkedList(head1); head1 = reverseList(head1); printLinkedList(head1); DoubleNode head2 = new DoubleNode(1); head2.next = new DoubleNode(2); head2.next.last = head2; head2.next.next = new DoubleNode(3); head2.next.next.last = head2.next; head2.next.next.next = new DoubleNode(4); head2.next.next.next.last = head2.next.next; printDoubleLinkedList(head2); printDoubleLinkedList(reverseList(head2)); } }
输出:
Linked List: 1 2 3 Linked List: 3 2 1 Double Linked List: 1 2 3 4 | 4 3 2 1 Double Linked List: 4 3 2 1 | 1 2 3 4
5.2 打印两个有序链表的公共部分
给定两个有序链表的头指针head1和head2,打印两个链表的公共部分。
思路:同归并排序,merge过程,比较大小,在这里比较是否相同即可。
package class_03; public class Code_10_PrintCommonPart { public static class Node { public int value; public Node next; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } public static void printCommonPart(Node head1, Node head2) { System.out.print("Common Part: "); while (head1 != null && head2 != null) { if (head1.value < head2.value) { head1 = head1.next; } else if (head1.value > head2.value) { head2 = head2.next; } else { System.out.print(head1.value + " "); head1 = head1.next; head2 = head2.next; } } System.out.println(); } public static void printLinkedList(Node node) { System.out.print("Linked List: "); while (node != null) { System.out.print(node.value + " "); node = node.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node node1 = new Node(2); node1.next = new Node(3); node1.next.next = new Node(5); node1.next.next.next = new Node(6); Node node2 = new Node(1); node2.next = new Node(2); node2.next.next = new Node(5); node2.next.next.next = new Node(7); node2.next.next.next.next = new Node(8); printLinkedList(node1); printLinkedList(node2); printCommonPart(node1, node2); } }
输出:
Linked List: 2 3 5 6 Linked List: 1 2 5 7 8 Common Part: 2 5
5.3 判断一个链表是否为回文结构
给定一个链表的头节点head,请判断该链表是否为回文结构。
例如:
1->2->1,返回true。
1->2->2->1,返回true。
15->6->15,返回true。
1->2->3,返回false。
进阶: 如果链表长度为N,时间复杂度达到O(N),额外空间复杂度达到O(1)。
方法一:放到栈里面再逆序比对(利用额外空间)
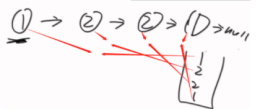
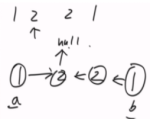
方法二:两个指针,1走一步,2走两步,2到了终点,1就到了中点,然后1往后的压栈,在逐一比对。

方法三:(额外空间O(1)):先通过快慢指针,找到中点,然后改变中间后面的链表的指向,再从两端逐一比对,最后再把指针还原如初。

实现:

1 package class_03; 2 3 import java.util.Stack; 4 5 /* 6 * 判断一个链表是否为回文结构 7 * 【题目】 给定一个链表的头节点head,请判断该链表是否为回文结构。 8 * 例如: 1->2->1,返回true。 1->2->2->1,返回true。 9 * 15->6->15,返回true。 1->2->3,返回false。 10 * 进阶: 如果链表长度为N,时间复杂度达到O(N),额外空间复杂度达到O(1)。 11 */ 12 public class Code_11_IsPalindromeList { 13 14 public static class Node { 15 public int value; 16 public Node next; 17 18 public Node(int data) { 19 this.value = data; 20 } 21 } 22 23 //need n extra space 24 public static boolean isPalindrome1(Node head) { 25 Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); 26 Node node = head; 27 while (node!=null) { 28 stack.push(node); 29 node = node.next; 30 } 31 while (head!=null) { 32 if (head.value != stack.pop().value) { 33 return false; 34 } 35 head = head.next; 36 } 37 return true; 38 } 39 40 //need n/2 extra space 41 public static boolean isPalindrome2(Node head) { 42 if (head == null || head.next == null) { 43 return true; 44 } 45 Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); 46 Node slow = head; 47 Node quick = head.next; 48 //quick->tail,slow->middle; 49 while (quick.next!= null && quick.next.next!=null) { 50 quick = quick.next.next; 51 slow = slow.next; 52 } 53 slow = slow.next; 54 while (slow!=null) { 55 stack.push(slow); 56 slow = slow.next; 57 } 58 while (!stack.isEmpty()) { 59 if (stack.pop().value != head.value) { 60 return false; 61 } 62 head = head.next; 63 } 64 return true; 65 } 66 67 //need O(1) extra space; 68 public static boolean isPalindrome3(Node head) { 69 if (head == null || head.next == null) { 70 return true; 71 } 72 boolean result = true; 73 Node slow = head; 74 Node quick = head; 75 //quick->tail,slow->middle; 76 //注意的是,在判断quick.next.next!=null之前, 77 //得先要判断quick.next!=null。 78 while (quick.next!=null && quick.next.next!=null) { 79 quick = quick.next.next; 80 slow = slow.next; 81 } 82 //反转后半段的指针; 83 Node cur = null; 84 quick = slow.next; 85 slow.next = null; 86 while (quick!=null) { 87 cur = quick.next; 88 quick.next = slow; 89 slow = quick; 90 quick = cur; 91 } 92 cur = slow;//最后节点 93 quick = head;//左边第一个节点 94 while (slow != null && quick != null) { 95 if (slow.value != quick.value) { 96 result = false; 97 break; 98 } 99 slow = slow.next; 100 quick = quick.next; 101 } 102 //反转指针 103 slow = cur.next;//倒数第二个 104 cur.next = null; 105 while (slow!=null) { 106 quick = slow.next; 107 slow.next = cur; 108 cur = slow; 109 slow = quick; 110 } 111 112 return result; 113 } 114 115 public static void printLinkedList(Node node) { 116 System.out.print("Linked List: "); 117 while (node != null) { 118 System.out.print(node.value + " "); 119 node = node.next; 120 } 121 System.out.println(); 122 } 123 124 public static void test() { 125 Node head = null; 126 head = new Node(1); 127 head.next = new Node(2); 128 head.next.next = new Node(3); 129 printLinkedList(head); 130 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 131 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 132 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 133 printLinkedList(head); 134 System.out.println("========================="); 135 136 head = new Node(1); 137 head.next = new Node(2); 138 head.next.next = new Node(1); 139 printLinkedList(head); 140 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 141 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 142 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 143 printLinkedList(head); 144 System.out.println("========================="); 145 146 head = new Node(1); 147 head.next = new Node(2); 148 head.next.next = new Node(3); 149 head.next.next.next = new Node(1); 150 printLinkedList(head); 151 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 152 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 153 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 154 printLinkedList(head); 155 System.out.println("========================="); 156 157 head = new Node(1); 158 head.next = new Node(2); 159 head.next.next = new Node(2); 160 head.next.next.next = new Node(1); 161 printLinkedList(head); 162 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 163 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 164 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 165 printLinkedList(head); 166 System.out.println("========================="); 167 168 head = new Node(1); 169 head.next = new Node(2); 170 head.next.next = new Node(3); 171 head.next.next.next = new Node(2); 172 head.next.next.next.next = new Node(1); 173 printLinkedList(head); 174 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 175 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 176 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 177 printLinkedList(head); 178 System.out.println("========================="); 179 } 180 public static void main(String[] args) { 181 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 182 test(); 183 } 184 185 }
输出:
Linked List: 1 2 3 false | false | false | Linked List: 1 2 3 ========================= Linked List: 1 2 1 true | true | true | Linked List: 1 2 1 ========================= Linked List: 1 2 3 1 false | false | false | Linked List: 1 2 3 1 ========================= Linked List: 1 2 2 1 true | true | true | Linked List: 1 2 2 1 ========================= Linked List: 1 2 3 2 1 true | true | true | Linked List: 1 2 3 2 1 =========================
5.4 将单向链表按某值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式
给定一个单向链表的头节点head,节点的值类型是整型,再给定一个整 数pivot。实现一个调整链表的函数,将链表调整为左部分都是值小于 pivot 的节点,中间部分都是值等于pivot的节点,右部分都是值大于 pivot的节点。除这个要求外,对调整后的节点顺序没有更多的要求。 例如:链表9->0->4->5->1,pivot=3。 调整后链表可以是1->0->4->9->5,也可以是0->1->9->5->4。总之,满 足左部分都是小于3的节点,中间部分都是等于3的节点(本例中这个部分为空),右部分都是大于3的节点即可。对某部分内部的节点顺序不做 要求。
可以使用荷兰国旗的方法去处理,数组每个元素变为结点类型,然后再接起来。
进阶: 在原问题的要求之上再增加如下两个要求。
在左、中、右三个部分的内部也做顺序要求,要求每部分里的节点从左 到右的顺序与原链表中节点的先后次序一致。 例如:链表9->0->4->5->1,pivot=3。调整后的链表是0->1->9->4->5。 在满足原问题要求的同时,左部分节点从左到右为0、1。在原链表中也 是先出现0,后出现1;中间部分在本例中为空,不再讨论;右部分节点 从左到右为9、4、5。在原链表中也是先出现9,然后出现4,最后出现5。
如果链表长度为N,时间复杂度请达到O(N),额外空间复杂度请达到O(1)。
准备三个变量,这三个变量都是节点对象的引用类型。less eq more
思路:
先遍历链表,找到第一个小于/等于/大于num的节点,让less/eq /more 等于那个节点。然后每组都再准备一个end,每次加入一个,end就加一,直到最后把三个小链表头尾链接起来。(原理是把一个大链表,拆成三个小链表,再组装起来)有限几个变量O(1)。
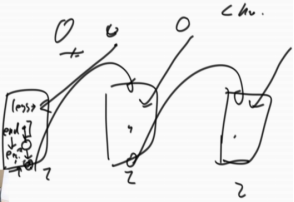
所以一共是3组,6个变量,less/end, eq/end, more/end,
实现:

1 package class_03; 2 3 import java.util.Stack; 4 5 /* 6 * 将单向链表按某值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式 7 【题目】 给定一个单向链表的头节点head,节点的值类型是整型,再给定一个 8 整 数pivot。实现一个调整链表的函数,将链表调整为左部分都是值小于 pivot 9 的节点,中间部分都是值等于pivot的节点,右部分都是值大于 pivot的节点。 10 除这个要求外,对调整后的节点顺序没有更多的要求。 例如:链表9->0->4->5- 11 >1,pivot=3。 调整后链表可以是1->0->4->9->5,也可以是0->1->9->5->4。总 12 之,满 足左部分都是小于3的节点,中间部分都是等于3的节点(本例中这个部 13 分为空),右部分都是大于3的节点即可。对某部分内部的节点顺序不做 要求。 14 15 进阶: 在原问题的要求之上再增加如下两个要求。 16 在左、中、右三个部分的内部也做顺序要求,要求每部分里的节点从左 到右的 17 顺序与原链表中节点的先后次序一致。 例如:链表9->0->4->5->1,pivot=3。 18 调整后的链表是0->1->9->4->5。 在满足原问题要求的同时,左部分节点从左到 19 右为0、1。在原链表中也 是先出现0,后出现1;中间部分在本例中为空,不再 20 讨论;右部分节点 从左到右为9、4、5。在原链表中也是先出现9,然后出现4, 21 最后出现5。 22 如果链表长度为N,时间复杂度请达到O(N),额外空间复杂度请达到O(1)。 23 */ 24 public class Code_12_SmallerEqualBigger { 25 26 public static class Node { 27 public int value; 28 public Node next; 29 30 public Node(int data) { 31 this.value = data; 32 } 33 } 34 35 public static Node listPartition1(Node head, int pivot) { 36 if (head == null) { 37 return null; 38 } 39 Node cur = head ; 40 int i = 0; 41 //遍历链表至结尾; 42 while (cur != null) { 43 ++i; 44 cur = cur.next; 45 } 46 Node[] nodes = new Node[i]; 47 i=0; 48 cur = head; 49 //将链表每个节点都放入节点数组; 50 for (int j = 0; j < nodes.length; j++) { 51 nodes[j] = cur ; 52 cur = cur.next; 53 } 54 arrPartion(nodes,pivot);//比大小操作; 55 //再将数组里的节点再连接形成链表; 56 for (int j = 1; j < nodes.length; j++) { 57 nodes[j-1].next = nodes[j]; 58 } 59 return nodes[0]; 60 } 61 62 private static void arrPartion(Node[] nodes, int pivot) { 63 //运用荷兰国旗思维 64 int small = -1; 65 int big = nodes.length; 66 int index = 0; 67 while (index != big) { 68 if (nodes[index].value < pivot) { 69 swap(nodes,++small,index++); 70 }else if (nodes[index].value == pivot) { 71 index++; 72 }else { 73 swap(nodes,--big,index); 74 } 75 } 76 } 77 78 private static void swap(Node[] nodes, int i, int j) { 79 // Node temp = nodes[i]; 80 int temp = nodes[i].value; 81 nodes[i].value = nodes[j].value; 82 nodes[j].value = temp; 83 } 84 85 public static void printLinkedList(Node node) { 86 System.out.print("Linked List: "); 87 while (node != null) { 88 System.out.print(node.value + " "); 89 node = node.next; 90 } 91 System.out.println(); 92 } 93 94 95 public static Node listPartition2(Node head, int pivot) { 96 //分成3组,六个变量; 97 Node sHead = null; 98 Node sTail = null; 99 Node eHead = null; 100 Node eTail = null; 101 Node bHead = null; 102 Node bTail = null; 103 Node cur = head; 104 Node next = null; 105 // every node distributed to three lists 106 while (cur != null) { 107 //把当前节点的next都置为null;即相当于把每个节点都单独出来; 108 next = cur.next; 109 cur.next = null; 110 //开始判断每一个节点; 111 if (cur.value < pivot) { 112 if (sHead == null) { 113 sHead = cur; 114 sTail = cur; 115 }else { 116 sTail.next = cur; 117 sTail = cur; 118 } 119 }else if (cur.value == pivot) { 120 if (eHead == null) { 121 eHead = cur; 122 eTail = cur; 123 }else { 124 eTail.next = cur; 125 eTail = cur; 126 } 127 }else { 128 if (bHead == null) { 129 bHead = cur; 130 bTail = cur; 131 }else { 132 bTail.next = cur; 133 bTail = cur; 134 } 135 } 136 cur = next; 137 } 138 //链接起来三个链表;需要注意的是看每个链表是否为空; 139 if (sTail!=null) { 140 sTail.next = eHead; 141 eTail = eTail == null ? sTail : eTail; 142 } 143 if (eTail != null) { 144 eTail.next = bHead; 145 } 146 return sHead != null ? sHead : (eHead != null ? eHead : bHead); 147 } 148 public static void test() { 149 Node head1 = new Node(7); 150 head1.next = new Node(9); 151 head1.next.next = new Node(1); 152 head1.next.next.next = new Node(8); 153 head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); 154 head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2); 155 head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); 156 printLinkedList(head1); 157 // head1 = listPartition1(head1, 4); 158 head1 = listPartition2(head1, 5); 159 printLinkedList(head1); 160 } 161 public static void main(String[] args) { 162 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 163 test(); 164 } 165 166 }
输出:
Linked List: 7 9 1 8 5 2 5
Linked List: 1 2 5 5 7 9 8
5.5 复制含有随机指针节点的链表
一种特殊的链表节点类描述如下:
Node类中的value是节点值,next指针和正常单链表中next指针的意义一样,都指向下一个节点,rand指针是Node类中新增的指针,这个指针可 能指向链表中的任意一个节点,也可能指向null。 给定一个由Node节点类型组成的无环单链表的头节点head,请实现一个函数完成这个链表中所有结构的复制,并返回复制的新链表的头节点。
方法一:准备一个hashmap<Node,Node>,依次把结点作为key,并以key结点的值new一个新节点作为value存入。然后再通过key查找value的方式,复制指针的指向,达到深入拷贝。
思路:
1.创建HashMap <Node,Node>,遍历节点,存入map中;
2.复制next和random指针;
进阶:不使用额外的数据结构,只用有限几个变量,且在时间复杂度为 O(N)
内完成原问题要实现的函数。
1.在每个节点后复制一个节点;
2.将random指针复制;
3.将next指针复原;
实现:

1 package class_03; 2 3 import java.io.ObjectInputStream.GetField; 4 import java.util.HashMap; 5 import java.util.Map; 6 7 import javax.xml.transform.Templates; 8 9 /* 10 * 复制含有随机指针节点的链表 11 【题目】 一种特殊的链表节点类描述如下: 12 public class Node { 13 public int value; 14 public Node next; 15 public Node rand; 16 public Node(int data) 17 { 18 this.value = data; 19 }s 20 } 21 Node类中的value是节点值,next指针和正常单链表中next指针的意义一 样,都指向下一个节点, 22 rand指针是Node类中新增的指针,这个指针可 能指向链表中的任意一个节点,也可能指向null。 23 给定一个由Node节点类型组成的无环单链表的头节点head,请实现一个 函数完成这个链表中所有结构的复制, 24 并返回复制的新链表的头节点。 25 进阶:不使用额外的数据结构,只用有限几个变量,且在时间复杂度为 O(N)内完成原问题要实现的函数。 26 */ 27 public class Code_13_CopyListWithRandom { 28 public static class Node { 29 public int value; 30 public Node next; 31 public Node rand; 32 33 public Node(int data) { 34 this.value = data; 35 } 36 } 37 public static Node copyListWithRand1(Node head) { 38 HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>(); 39 Node cur = head; 40 // while (cur != null) { 41 // map.put(cur, new Node(cur.value)); 42 // map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);//get(cur.next)可能没有值; 43 // map.get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand);//get(cur.rand)可能没有值;所以要分开两次遍历; 44 // cur = cur.next; 45 // } 46 //复制节点值,并存入对应HashMap中; 47 while (cur != null) { 48 map.put(cur, new Node(cur.value)); 49 cur = cur.next; 50 } 51 cur = head; 52 //复制指针指向; 53 while (cur != null) { 54 map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next); 55 map.get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand); 56 cur = cur.next; 57 } 58 return map.get(head); 59 } 60 61 /* 62 * 1.创建HashMap<Node,Node>,遍历节点,存入map中; 63 * 2.复制next和random指针; 64 */ 65 public static Node copyListWithRand3(Node head) { 66 if (head == null) { 67 return null; 68 } 69 Node cur = head; 70 Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>(); 71 //1.创建HashMap<Node,Node>,遍历节点,存入map中; 72 while (cur != null) { 73 map.put(cur, new Node(cur.value)); 74 cur = cur.next; 75 } 76 //2.复制next和random指针; 77 cur = head; 78 while (cur != null) { 79 map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next); 80 map.get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand); 81 cur = cur.next; 82 } 83 //3.返回复制链表的首节点; 84 return map.get(head); 85 } 86 87 /*正确!!! 88 * 1.在每个节点后复制一个节点; 89 * 2.将random指针复制; 90 * 3.将next指针复原; 91 */ 92 public static Node copyListWithRand4(Node head) { 93 if (head == null) { 94 return null; 95 } 96 Node cur = head; 97 Node next = null; 98 //1.在每个节点后复制一个节点; 99 while (cur != null) { 100 next = cur.next; 101 cur.next = new Node(cur.value); 102 cur.next.next = next; 103 cur = next; 104 } 105 //2.将random指针复制; 106 cur = head; 107 // Node curCopy = cur.next; 108 next = cur.next; 109 while (cur != null) { 110 next.rand = cur.rand != null ? cur.rand.next : null; 111 cur = next.next; 112 if (cur != null) { 113 next = cur.next; 114 } 115 } 116 //将next指针复原; 117 cur = head; 118 next = cur.next; 119 while (cur != null && next.next != null) { 120 cur = next.next; 121 next.next = cur.next; 122 next = cur.next; 123 } 124 return head.next; 125 } 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 /* 138 * 有问题!!! 139 */ 140 public static Node copyListWithRand2(Node head) { 141 if (head == null) { 142 return null; 143 } 144 //每个节点后都插入一个新节点; 145 Node cur = head; 146 Node next = null ; 147 while (cur != null) { 148 next = cur.next; 149 cur.next = new Node(cur.value); 150 cur.next.next = next; 151 cur = next; 152 153 } 154 cur = head; 155 next = cur.next; 156 while (cur != null) { 157 next.rand = cur.rand.next; 158 cur = next.next; 159 } 160 161 162 cur = head.next; 163 next = cur.next; 164 while (next != null) { 165 cur.next = next.next; 166 cur = cur.next; 167 next = cur.next == null ? null : cur.next; 168 } 169 170 return head.next; 171 } 172 173 public static void printRandLinkedList(Node head) { 174 Node cur = head; 175 System.out.print("order: "); 176 while (cur != null) { 177 System.out.print(cur.value + " "); 178 cur = cur.next; 179 } 180 System.out.println(); 181 cur = head; 182 System.out.print("rand: "); 183 while (cur != null) { 184 System.out.print(cur.rand == null ? "- " : cur.rand.value + " "); 185 cur = cur.next; 186 } 187 System.out.println(); 188 } 189 190 private static void test() { 191 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 192 Node head = null; 193 Node res1 = null; 194 Node res2 = null; 195 printRandLinkedList(head); 196 res1 = copyListWithRand1(head); 197 printRandLinkedList(res1); 198 res2 = copyListWithRand2(head); 199 printRandLinkedList(res2); 200 printRandLinkedList(head); 201 System.out.println("===========***=========="); 202 203 head = new Node(1); 204 head.next = new Node(2); 205 head.next.next = new Node(3); 206 head.next.next.next = new Node(4); 207 head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); 208 head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6); 209 210 head.rand = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 1 -> 6 211 head.next.rand = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 2 -> 6 212 head.next.next.rand = head.next.next.next.next; // 3 -> 5 213 head.next.next.next.rand = head.next.next; // 4 -> 3 214 head.next.next.next.next.rand = null; // 5 -> null 215 head.next.next.next.next.next.rand = head.next.next.next; // 6 -> 4 216 217 // printRandLinkedList(head); 218 // res1 = copyListWithRand1(head); 219 // printRandLinkedList(res1); 220 // res2 = copyListWithRand2(head); 221 // printRandLinkedList(res2); 222 // printRandLinkedList(head); 223 System.out.println("========================="); 224 printRandLinkedList(head); 225 res1 = copyListWithRand3(head); 226 printRandLinkedList(res1); 227 res2 = copyListWithRand4(head); 228 printRandLinkedList(res2); 229 System.out.println("========================="); 230 } 231 public static void main(String[] args) { 232 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 233 test(); 234 } 235 236 237 238 239 }
输出:
order: rand: order: rand: order: rand: order: rand: ===========***========== ========================= order: 1 2 3 4 5 6 rand: 6 6 5 3 - 4 order: 1 2 3 4 5 6 rand: 6 6 5 3 - 4 order: 1 2 3 4 5 6 rand: 6 6 5 3 - 4 =========================
5.6 比价两个链表是否相交(链表可能有环)
在本题中,单链表可能有环,也可能无环。给定两个单链表的头节点 head1和head2,这两个链表可能相交,也可能不相交。请实现一个函数, 如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的第一个节点;如果不相交,返回null 即可。
要求:如果链表1的长度为N,链表2的长度为M,时间复杂度请达到 O(N+M),额外空间复杂度请达到O(1)。
通过分析:当没有环时,一共有两种情况:
无环时,记录两个链表的长度,找到长度差n,然后长的先走n步,即可。有环2同无环2情况。
当有环时,一共有3种情况:
当一个有环,一个无环,一定不会相交。
思路1:使用额外空间。判断是否相交,可以使用Hashmap,先将一个链表遍历完,填入map中,然后遍历链表2,看是否map中有该元素,如果有的话,就表示相交,如果没有就表示不相交。
思路2:不使用额外空间。使用两对变量head1,head2,loop1,loop2(loop表示循环进入点)。
- 判断head1和head2是否为null;
- 通过head1和head2得到loop1和loop2;getLoopNode(head);
- 判断loop1和loop2是否都是null;
3.1都是null说明都是直链表;noLoop(head1,head2);
3.2一个是null一个不是null,肯定返回null;
3.3都不是null,分三种情况。bothLoop(head1,head2); 有环2同无环2情况,有环1,2可直接判断。
实现:

1 public static class Node { 2 public int value; 3 public Node next; 4 5 public Node(int data) { 6 this.value = data; 7 } 8 } 9 10 public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2) { 11 if (head1 == null || head2 == null) { 12 return null; 13 } 14 Node loop1 = getLoopNode(head1); 15 Node loop2 = getLoopNode(head2); 16 if (loop1 == null && loop2 == null) { 17 return noLoop(head1,head2,loop1,loop2); 18 } 19 if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null) { 20 return bothLoop(head1,head2,loop1,loop2); 21 } 22 return null; 23 } 24 25 private static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node head2, Node loop1, Node loop2) { 26 //有三种情况:1.66型;2.Y0型;3.\O/型; 27 Node n1 = head1; 28 Node n2 = head2; 29 int len1 = 0; 30 if (loop1 == loop2) { 31 //说明是第二种; 32 return noLoop(head1, head2, loop1, loop2); 33 }else { 34 //顺着loop往下遍历,是否能够遇到另一个loop;能遇到则是\O/型,否则是66型; 35 n1 = loop1.next; 36 while (n1 != loop1) { 37 if (n1 == loop2) { 38 return loop1;//或者返回loop2,均可; 39 } 40 n1 = n1.next; 41 } 42 } 43 return null; 44 } 45 46 private static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2, Node loop1, Node loop2) { 47 Node n1 = head1; 48 Node n2 = head2; 49 int len1 = 0; 50 int len2 = 0; 51 while (n1 != loop1) { 52 n1 = n1.next; 53 len1++; 54 } 55 while (n2 != loop2) { 56 len2++; 57 n2 = n2.next; 58 } 59 //n1指向较长的链表; 60 n1 = len1 >= len2 ? head1 : head2; 61 n2 = len1 >= len2 ? head2 : head1; 62 len1 = Math.abs(len1-len2); 63 while (len1>0) { 64 n1 = n1.next; 65 len1--; 66 } 67 //直到相等即证明该节点是重合开始节点; 68 while (n1 != n2) { 69 n1 = n1.next; 70 n2 = n2.next; 71 } 72 73 return n1; 74 } 75 76 private static Node getLoopNode(Node head) { 77 Node f = head; 78 Node s = head; 79 if (head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null) { 80 return null; 81 } 82 f = f.next.next; 83 s = s.next; 84 while (f != s) { 85 if (f.next == null || f.next.next == null) { 86 return null; 87 } 88 s = s.next; 89 f = f.next.next; 90 } 91 f = head; 92 while(f != s) { 93 f = f.next; 94 s = s.next; 95 } 96 return s; 97 }
卧槽,连夜肝了一篇纯干货,欢迎大家点赞评论,嘻嘻~~
Over......





