矢量
1. 概念
矢量表示的是方向与大小,并不表示位置
1)矢量的分量--components
2)矢量--vector
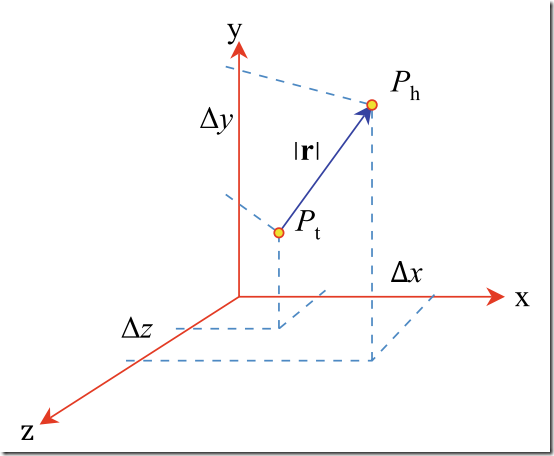
3)矢量的模--magnitude
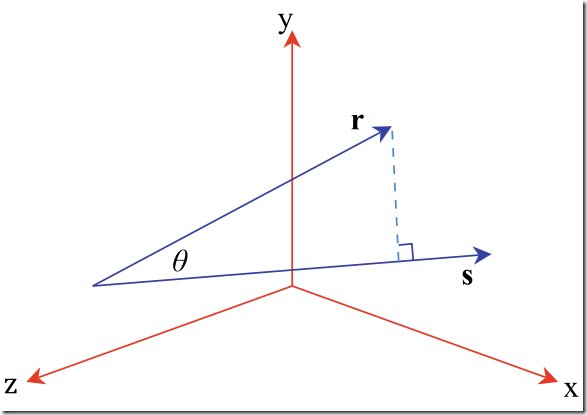
The magnitude or length of a vector r is written
4)位置矢量--Position Vectors
Given any point P(x, y, z), a position vector p is created by assuming that P is the vector’s head and the origin is its tail. As the tail coordinates are (0, 0, 0) the vector’s components are x, y, z
5)单位矢量--Unit Vectors
2. 操作
1)缩放--Scaling a Vector
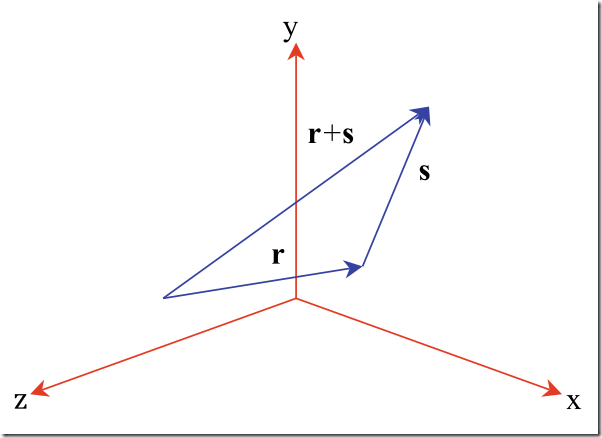
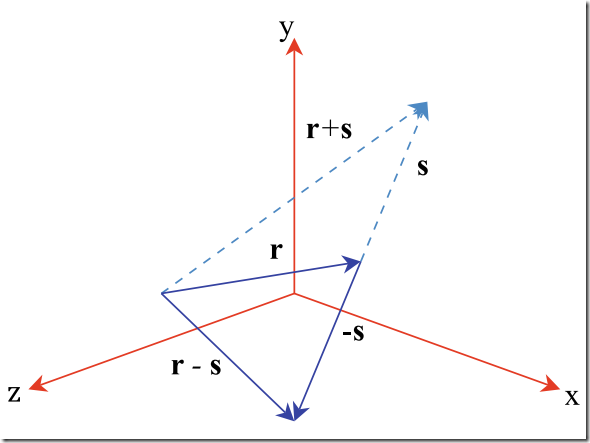
2)加减--Vector Addition and Subtraction
3)单位化
4)笛卡尔矢量--Cartesian Vectors
A Cartesian vector is constructed from three unit vectors: i, j and k, aligned with the x-, y- and z-axis, respectively:
By employing the rules of vector addition and subtraction, we can compose a vector r by summing three scaled Cartesian unit vectors as follows:
相等于
5)标量积--Scalar Product/Dot Product
在计算机图形学中的应用点:
(1) 计算灯光与表面的法线之间的夹角
(2) 判断三角面的朝向是正面,还是背面
(3) 三维空间中的三角形面积计算
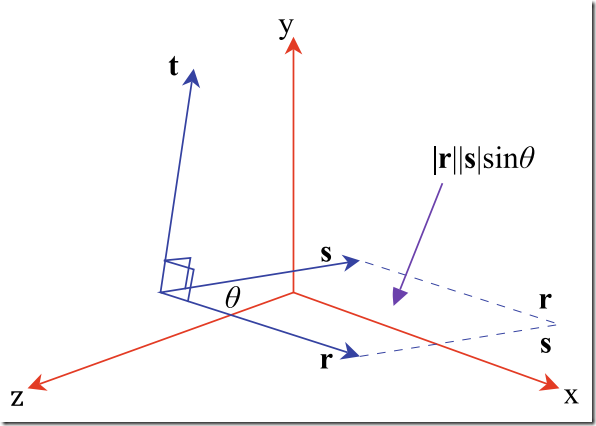
6)叉积--Vector Product/Cross Product
注意:叉积不满足交换律
叉积在三维世界中需要遵守右手规则
在计算机图形学中的应用点:
(1) 三角形表面的法线计算
(2) 二维空间中的三角形面积计算

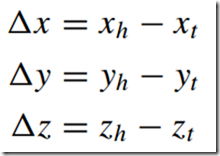
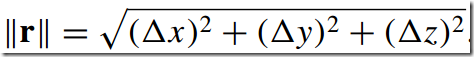

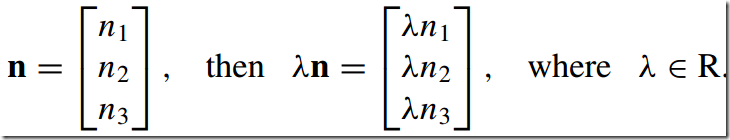
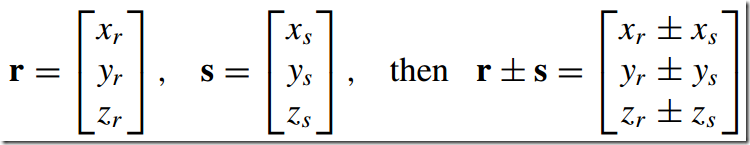
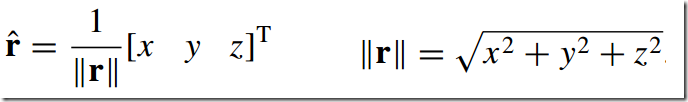
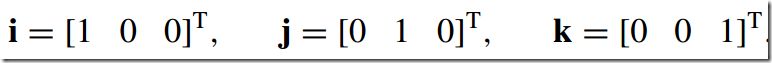
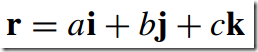
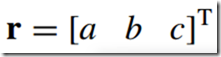
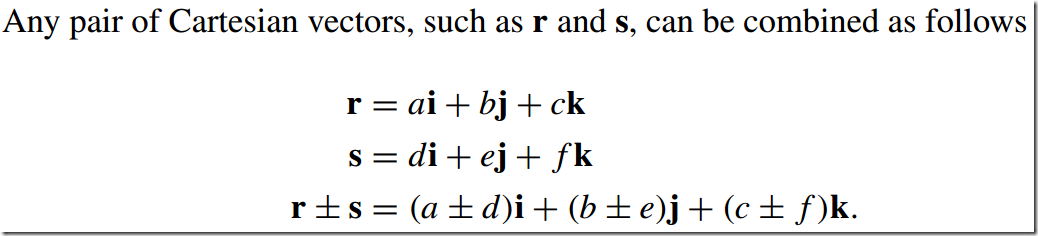
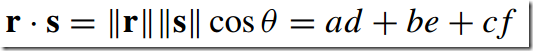
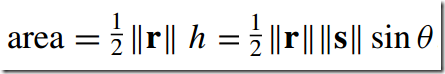
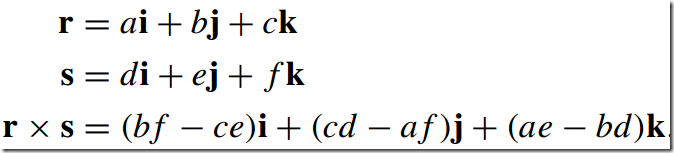
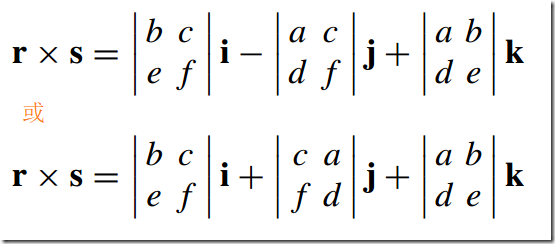
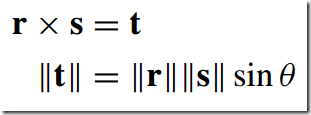
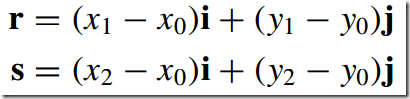
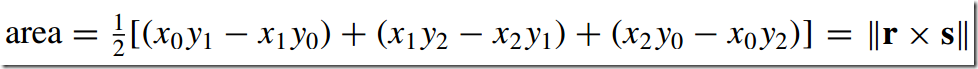

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号