跳跃表SkipList的理解
SkipList在各种开源引擎中用处普遍,例如redis的sortedset容器、luence里面的索引字典等均用到了skiplist。
1. SkipList
在数据结构里面,我们知道有两种基本数据逻辑结构:数组和链表。它们均有其各自的特点,数组(特别是有序数组),可以进行快速查询,但不便于删除操作;链表,可以进行快速的增删操作,但是又不便于查询。那有没可能存在一种数据结构,结合两者各自的优点呢?
基于这样的思路,William Pugh这位马里兰大学的计算机教授,于1989年提出来一种新的数据结构,跳跃表。其类似平衡二叉树的链表,但与排序二叉树相比的区别是,其兄弟相邻间的节点间用指针相连的。例如如下样例:
1.1. 特征
a. 从纵向角度看:
它类似一种B+树,每一层均是其相邻低一层的子集。但与B+树相比的区别是,每一层的相邻节点间均是以指针相连。如果把它看成一种树,就会有相应的树高(height)。
b. 从横向角度看:
它是一种链表。越位于高层的链表,其元素越稀疏。每更高一层链表元素均是其相邻低一层的子集,那么其占相邻下一层的比例的多少,即是其跳跃的步数或间隔interval。
2. 读操作
读取操作相对简单: 从最高层开始,优先横向游走,然后纵向游走,直到遇到目标元素。从跳跃标的特点可以看出,查找新元素的特点:
a. 如果待查询值在跳跃表中,那么总是会在最底层的元素里;
b. 从任意一层节点开始查询,均是可以找到结果的。
源码如下:
statusEnum find(keyType key, recType *rec) {
int i;
nodeType *x = list.hdr;
/*******************************
* find node containing data *
*******************************/
for (i = list.listLevel; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->forward[i] != NIL && compLT(x->forward[i]->key, key))
x = x->forward[i];
}
x = x->forward[0];
if (x != NIL && compEQ(x->key, key)) {
*rec = x->rec;
return STATUS_OK;
}
return STATUS_KEY_NOT_FOUND;
}
3. 写操作
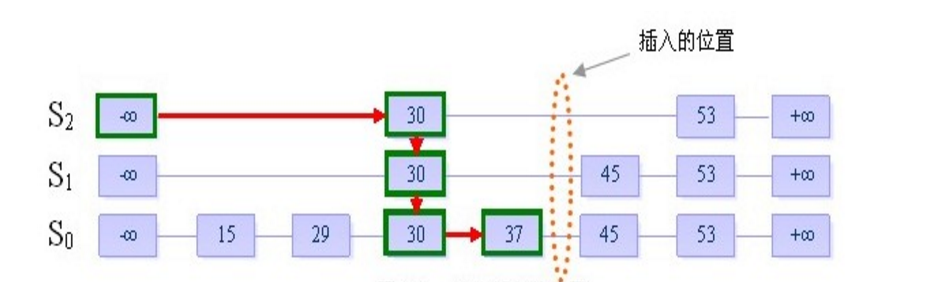
在插入一个新的元素时,通常我们需要敲定2个问题,确定横向所在的位置与纵向所在的位置。如上图,如果现需要插入一个值为40的元素。
a. 横向位置
由于每一层链表均是有序的,所以对于一个给定的新元素,其横向位置基本通过查询操作可以快速确定和唯一的。
b. 纵向位置
根据跳跃表的定义,我们从上图可以看出,新元素40放入的层高可以位于0至4层之间的任意一层的。但是其放在的层高即纵向位置又是能直接决定了其纵向的树高(height)与每层横向跳跃的平均间隔(interval)的,因此得考虑其纵向位置的合理性。
如果按照二叉的思路构建跳跃表的话,可以想象:100%的元素位于0层,50%的元素位于1层,25%的元素位于2层,以此类推。。所以,写入新的元素的规则,尽量保持跳跃表各层次类似二叉树的“身材”,避免各层次的变形,因此在放入新的元素时,通常按二叉树各层次元素个数来计算相应的概率,进行层数的敲定:
protected int ChooseRandomHeight()
{
static const double _prob = 0.5;
int level = 0;
while ( _rndNum.NextDouble() < _prob )
{
level++;
}
return level;
}
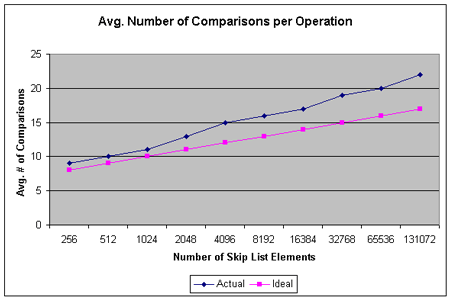
4. 效率
在"probabilistic analysis of skip lists"文中分析了skiplist的增删操作平均运行时间是log2n, 在最坏情况下运行时间是线性的时间,当然这种最坏的情况发生的概率非常小。
5. 源码
/* skip list */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* implementation dependent declarations */
typedef enum {
STATUS_OK,
STATUS_MEM_EXHAUSTED,
STATUS_DUPLICATE_KEY,
STATUS_KEY_NOT_FOUND
} statusEnum;
typedef int keyType; /* type of key */
/* user data stored in tree */
typedef struct {
int stuff; /* optional related data */
} recType;
#define compLT(a,b) (a < b)
#define compEQ(a,b) (a == b)
/* levels range from (0 .. MAXLEVEL) */
#define MAXLEVEL 15
typedef struct nodeTag {
keyType key; /* key used for searching */
recType rec; /* user data */
struct nodeTag *forward[1]; /* skip list forward pointer */
} nodeType;
/* implementation independent declarations */
typedef struct {
nodeType *hdr; /* list Header */
int listLevel; /* current level of list */
} SkipList;
SkipList list; /* skip list information */
#define NIL list.hdr
statusEnum insert(keyType key, recType *rec)
{
int i, newLevel;
nodeType *update[MAXLEVEL+1];
nodeType *x;
/***********************************************
* allocate node for data and insert in list *
***********************************************/
/* find where key belongs */
x = list.hdr;
for (i = list.listLevel; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->forward[i] != NIL && compLT(x->forward[i]->key, key))
x = x->forward[i];
update[i] = x;
}
x = x->forward[0];
if (x != NIL && compEQ(x->key, key))
return STATUS_DUPLICATE_KEY;
/* determine level */
for (
newLevel = 0;
rand() < RAND_MAX/2 && newLevel < MAXLEVEL;
newLevel++);
if (newLevel > list.listLevel) {
for (i = list.listLevel + 1; i <= newLevel; i++)
update[i] = NIL;
list.listLevel = newLevel;
}
/* make new node */
if ((x = static_cast<nodeType*>(malloc(sizeof(nodeType) + newLevel*sizeof(nodeType *)))) == 0)
return STATUS_MEM_EXHAUSTED;
x->key = key;
x->rec = *rec;
/* update forward links */
for (i = 0; i <= newLevel; i++) {
x->forward[i] = update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i] = x;
}
return STATUS_OK;
}
statusEnum free(keyType key) {
int i;
nodeType *update[MAXLEVEL+1], *x;
/*******************************************
* delete node containing data from list *
*******************************************/
/* find where data belongs */
x = list.hdr;
for (i = list.listLevel; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->forward[i] != NIL && compLT(x->forward[i]->key, key))
x = x->forward[i];
update[i] = x;
}
x = x->forward[0];
if (x == NIL || !compEQ(x->key, key)) return STATUS_KEY_NOT_FOUND;
/* adjust forward pointers */
for (i = 0; i <= list.listLevel; i++) {
if (update[i]->forward[i] != x) break;
update[i]->forward[i] = x->forward[i];
}
free (x);
/* adjust header level */
while ((list.listLevel > 0)
&& (list.hdr->forward[list.listLevel] == NIL))
list.listLevel--;
return STATUS_OK;
}
statusEnum find(keyType key, recType *rec) {
int i;
nodeType *x = list.hdr;
/*******************************
* find node containing data *
*******************************/
for (i = list.listLevel; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->forward[i] != NIL && compLT(x->forward[i]->key, key))
x = x->forward[i];
}
x = x->forward[0];
if (x != NIL && compEQ(x->key, key)) {
*rec = x->rec;
return STATUS_OK;
}
return STATUS_KEY_NOT_FOUND;
}
void initList() {
int i;
/**************************
* initialize skip list *
**************************/
if ((list.hdr = static_cast<nodeType*>(malloc(
sizeof(nodeType) + MAXLEVEL*sizeof(nodeType *)))) == 0) {
printf ("insufficient memory (initList)\n");
exit(1);
}
for (i = 0; i <= MAXLEVEL; i++)
list.hdr->forward[i] = NIL;
list.listLevel = 0;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int i, maxnum, random;
recType *rec;
keyType *key;
statusEnum status;
/* command-line:
*
* skl maxnum [random]
*
* skl 2000
* process 2000 sequential records
* skl 4000 r
* process 4000 random records
*
*/
maxnum = 1000;//atoi(1000);
random = 10;
initList();
if ((rec = static_cast<recType*>(malloc(maxnum * sizeof(recType)))) == 0) {
fprintf (stderr, "insufficient memory (rec)\n");
exit(1);
}
if ((key = static_cast<keyType*>(malloc(maxnum * sizeof(keyType)))) == 0) {
fprintf (stderr, "insufficient memory (key)\n");
exit(1);
}
if (random) {
/* fill "a" with unique random numbers */
for (i = 0; i < maxnum; i++) key[i] = rand();
printf ("ran, %d items\n", maxnum);
} else {
for (i = 0; i < maxnum; i++) key[i] = i;
printf ("seq, %d items\n", maxnum);
}
for (i = 0; i < maxnum; i++) {
status = insert(key[i], &rec[i]);
if (status) printf("pt1: error = %d\n", status);
}
for (i = maxnum-1; i >= 0; i--) {
status = find(key[i], &rec[i]);
if (status) printf("pt2: error = %d\n", status);
}
for (i = maxnum-1; i >= 0; i--) {
status = free(key[i]);
if (status) printf("pt3: error = %d\n", status);
}
return 0;
}
参考:
1. "Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees"
2. "Probabilistic Analysis of Skip Lists"
3. https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms379573(v=vs.80).aspx
4. http://www.cppblog.com/mysileng/archive/2013/04/06/199159.html


