IO模型
IO模型
IO模型就是说用什么样的通道进行数据的发送和接收,Java共支持3种网络编程IO模式:BIO,NIO,AIO
BIO (Blocking IO)
同步阻塞IO模型,一个客户端对应一个服务端
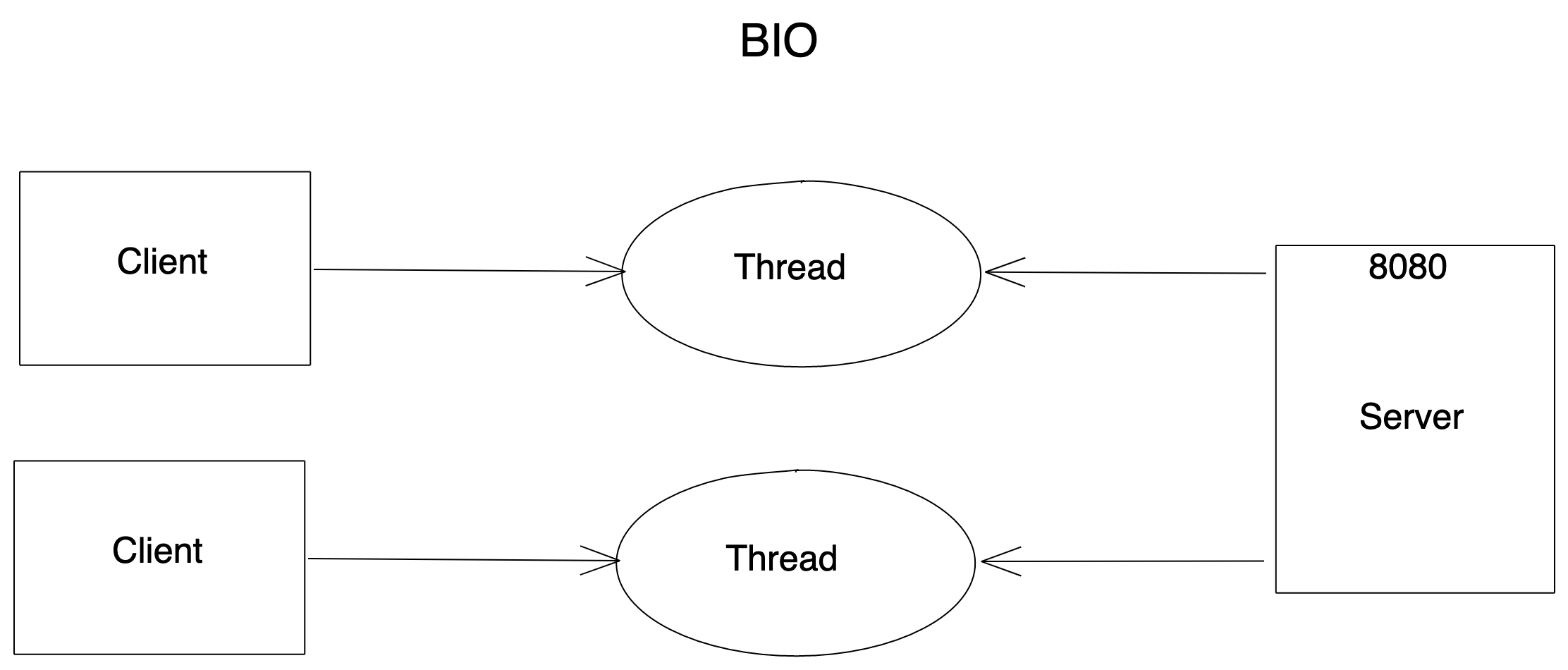
服务端:
@Slf4j
public class BIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
while (true) {
log.info("服务端已启动,等待连接");
// 阻塞
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
log.info("客户端已连接");
// 单线程处理链接
// handler(socket);
// 多线程处理链接
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("local-thread-{}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
handler(socket);
}
}).start();
}
}
private static void handler(Socket socket) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
log.info("获取客户端发送数据");
// 接收数据,阻塞方法,没有数据可读时就阻塞
int read = socket.getInputStream().read(bytes);
if (read != -1) {
log.info("接收客户数据: {}", new String(bytes, 0, read));
}
// 响应客户端
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("server is connecting".getBytes());
outputStream.flush();
}
}
客户端:
@Slf4j
public class BIOClient {
private static final String HOST = "localhost";
private static final int PORT = 8080;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(HOST, PORT);
// 发送数据
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("request server connect".getBytes());
os.flush();
// 接收数据
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
int read = is.read(bytes);
if (read != -1) {
log.info("接收到来自服务端的数据: {}", new String(bytes, 0, read));
}
socket.close();
}
}
缺点
- 1、IO代码里
read操作是阻塞操作,如果连接不做数据读写操作会导致线程阻塞,浪费资源 - 2、如果线程很多,会导致服务器线程太多,压力太大,比如C10K问题
应用场景
BIO 方式适用于连接数目比较小且固定的架构,这种方式对服务器资源要求比较高,但程序简单易理解。
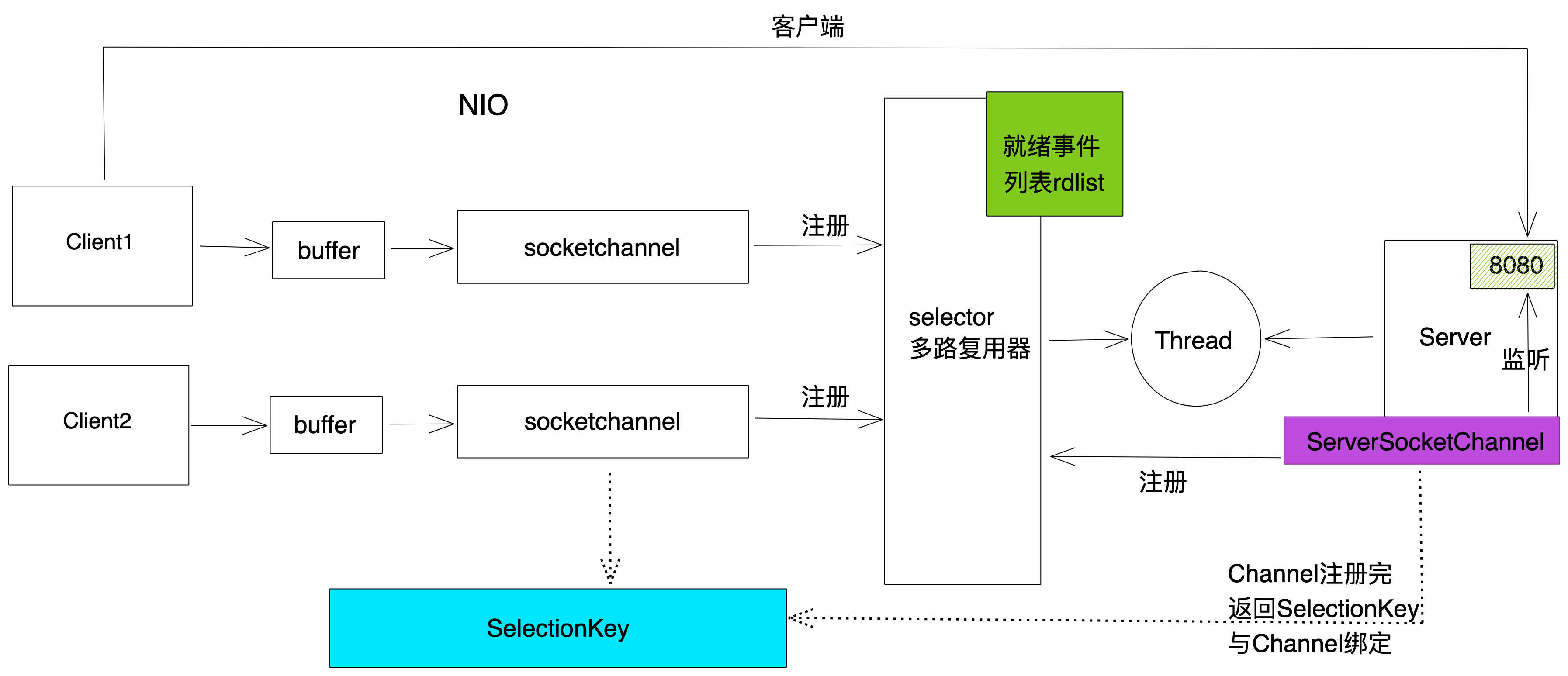
NIO (NON Blocking IO)
同步非阻塞IO模型,服务器实现模式为一个线程可以处理多个请求(连接),客户端发送的连接请求都会注册到多路复用器selector上,
多路复用器轮询到连接有IO请求就进行处理,JDK1.4开始引入。
普通模型:
@Slf4j
public class NIOServer {
static List<SocketChannel> channelList = Lists.newArrayList();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建 NIO 通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 绑定服务端口地址
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 设置通道为非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
log.info("服务端已启动,等待连接");
while (true) {
// 非阻塞模式 accept() 方法不会阻塞。阻塞模式则会阻塞,即 socketChannel.configureBlocking(ture)
// NIO的非阻塞是由操作系统内部实现的,底层调用了linux内核的accept函数
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(socketChannel)) {
log.info("客户端已连接: {}", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 连接成功放到 channelList 中
channelList.add(socketChannel);
}
// 读取 channel
Iterator<SocketChannel> iterator = channelList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SocketChannel channel = iterator.next();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
// 非阻塞模式 read() 方法不会阻塞。阻塞模式则会阻塞
int read = channel.read(byteBuffer);
if (read > 0) {
log.info("接收客户 {}, 数据: {}", channel.getRemoteAddress(), new String(byteBuffer.array()));
} else if (read < 0) {
//
iterator.remove();
log.info("客户端已断开连接");
}
}
}
}
}
如上,如果有很多连接,每一个连接都需要通过iterator遍历获取数据,如果该连接无数据发送,则会产生很多无用的遍历。
多路复用器模型:
@Slf4j
public class NIOSelectorServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建 NIO 通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 绑定服务端口地址
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 设置通道为非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 打开 Selector 处理 Channel,即创建 epoll
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// Channel 注册到 selector 上,并 selector 对客户端 accept 操作监听
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
log.info("服务端已启动,等待连接");
while (true) {
// 阻塞等待需要处理的事件发生
selector.select();
// 获取 selector 中注册的全部事件中的 selectedKeys 实例
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
// 遍历对 selectionKeys 事件进行处理
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = keyIterator.next();
// 是 OP_ACCEPT 事件,则进行后续的获取数据和事件注册
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocket = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocket.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 注册 OP_READ 事件,需要给客户端发送数据,则注册 OP_WRITE 即可
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
log.info("客户端已连接: {}", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
// 是 OP_READ 事件,则获取客户端发送的数据
} else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
int read = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
if (read > 0) {
log.info("接收客户 {}, 数据: {}", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress(), new String(byteBuffer.array()));
} else if (read < 0) {
socketChannel.close();
log.info("客户端已断开连接");
}
}
// selectionKeys 没有对应事件即移除,防止下次 seletor 重复处理
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
NIO 有三大核心组件: Channel(通道), Buffer(缓冲区),Selector(多路复用器)
1、channel 类似于流,每个 channel 对应一个 buffer 缓冲区,buffer 底层就是个数组
2、channel 会注册到 selector 上,由 selector 根据 channel 读写事件的发生将其交由某个空闲的线程处理
3、NIO 的 Buffer 和 channel 都是既可以读也可以写
应用场景
NIO方式适用于连接数目多且连接比较短(轻操作) 的架构, 比如聊天服务器, 弹幕系统, 服务器间通讯,编程比较复杂
AIO (NIO 2.0)
异步非阻塞, 由操作系统完成后回调通知服务端程序启动线程去处理, 一般适用于连接数较多且连接时间较长的应用
异步模型:
@Slf4j
public class AIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel assc = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
assc.accept(null, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object>() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel, Object attachment) {
log.info("connet -- {}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 在此接收客户端连接,否则后面的客户端连接不上服务端
assc.accept(attachment, this);
log.info("客户端:{}", socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
socketChannel.read(byteBuffer, byteBuffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
log.info("read -- {}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
byteBuffer.flip();
log.info("客户端请求数据:{}", new String(byteBuffer.array(), 0, result));
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("This is response data".getBytes()));
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
log.error("read error: {}", exc.getMessage());
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
log.error("connect error: {}", exc.getMessage());
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
log.info("main -- {}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
}
应用场景
AIO方式适用于连接数目多且连接比较长(重操作)的架构,JDK7 开始支持
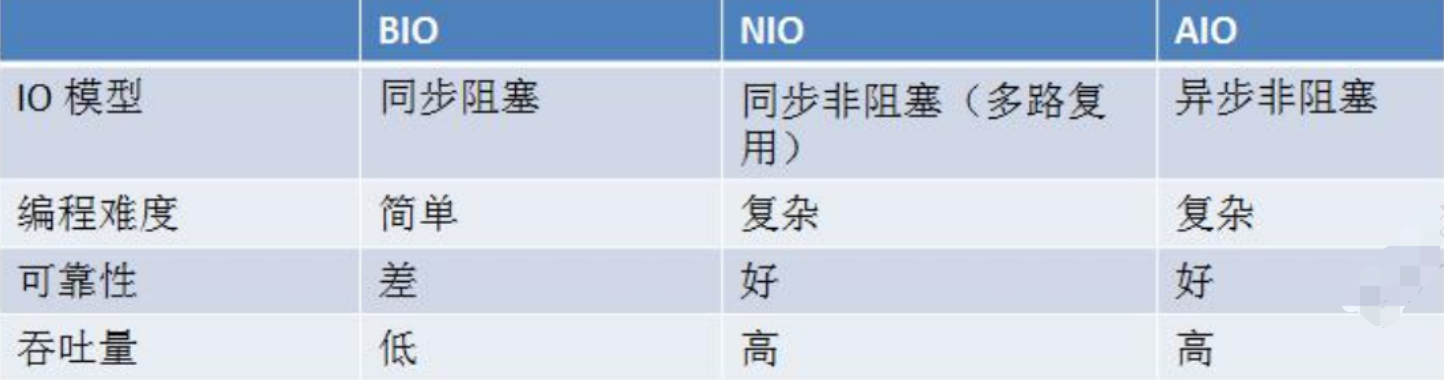
对比
资料
收录时间: 2021/02/24



